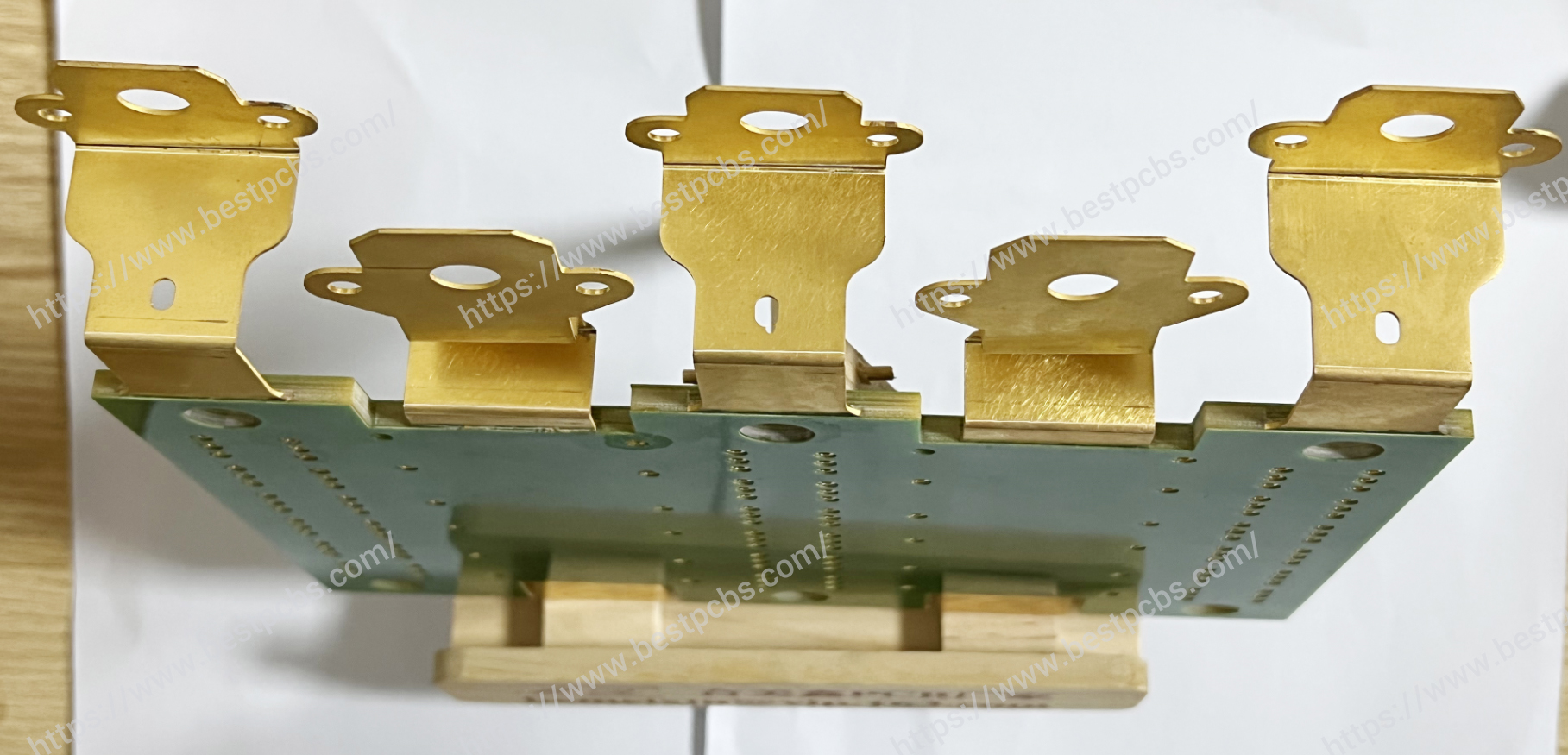
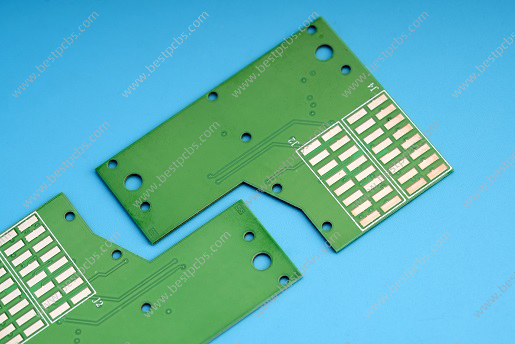
Due to the different surface structures of ceramic susbtrates and metal materials, welding/soldering often cannot wet the ceramic surface or form a strong bond with it. Therefore, the joining of ceramics and metals is a special process, which called as metallization.

What Ceramic Metallization Technology Is?
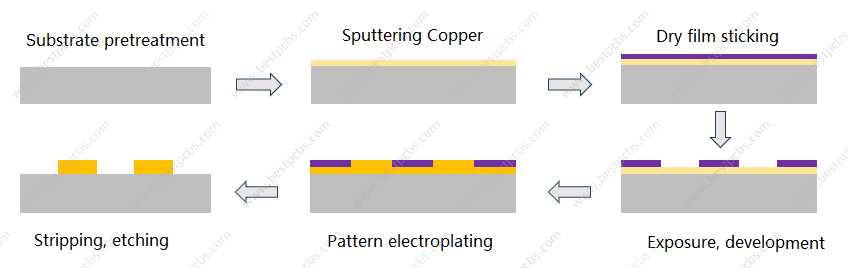
Ceramic metallization refers to the process of firmly attaching a thin layer of metal film to the surface of a ceramic material to achieve a bond between the ceramic and metal. There are various methods for ceramic metallization, commonly including molybdenum-manganese (Mo-Mn) method, directly copper plate (DPC), directly bonded copper (DBC), active metal brazed (AMB) method and more.

Which Ceramics Can Be Used Metallization Technology?
At present, there are four common ceramic substrates that always used for metallization, they are BeO, Al2O3, AlN and Si3O4. But different ceramic has different characteristics, so its metallization method also is different.
- BeO Ceramic
The most common method for metallizing BeO ceramics is the Mo-Mn method. This involves applying a paste-like mixture of pure metal powders (Mo, Mn) and metal oxides to the ceramic surface, followed by high-temperature heating in a furnace to form a metal layer.
- Al2O3 Ceramic
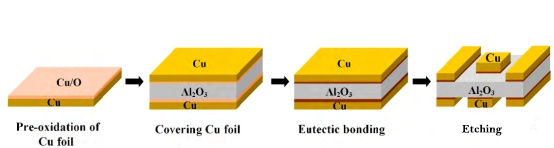
The primary metallization methods for Al2O3 ceramics are DBC and DPC. This method involves placing a treated copper foil on the surface of Al2O3 ceramics, introducing an inert gas with a certain oxygen content, and then heating. During heating, the copper surface undergoes oxidation, and when the temperature reaches the eutectic liquid phase region, a eutectic liquid phase is formed, wetting both Al2O3 ceramics and copper, achieving a tight bond. In a chemical sense, the adhesion used by DBC is stronger than DPC since it has thicker copper.
- AlN Ceramic
Common methods for AlN ceramics include DBC and Active Metal Brazing (AMB). DBC is similar to the method used for Al2O3 ceramics but requires pre-oxidation treatment of AlN ceramics since AlN is a non-oxide ceramic. AMB involves connecting AlN ceramics and copper foils using active metal brazing materials, often Ag-Cu-Ti alloys.
- Si3N4 Ceramic
Si3N4 ceramics cannot be directly metallized using the direct copper plating method because they do not generate an oxide layer on the surface like AlN ceramics. Si3N4 ceramics are typically connected to metals using the AMB method, where chemical reactions between Si3N4 and active metals (Ti, Cr, V) form continuous nitride layers at the interface.

What is the Metallization Temperature?
During the metallization process, the sinter temperature should be controlled strictly. Normally, it can be divided into four ranges:
- Ultra-High Temperature (Above 1600°C):
This temperature range is reserved for specific applications where extreme heat resistance is required.
- High Temperature (1450°C to 1600°C):
High temperatures are essential to ensure that the glass phase spreads and migrates effectively, enabling a strong bond. However, excessively high temperatures can lead to reduced metallization strength.
- Mid-Temperature (1300°C to 1450°C):
This range is chosen to balance the need for effective metallization with the preservation of material properties.
- Low Temperature (Below 1300°C):
Lower temperatures are used when the primary concern is avoiding thermal stress on the materials involved.
Proper high sintering temperature is necessary, otherwise, the glass phase will not spread and migrate. But if the temperature is too high, the metallization strength will be poor. So, choose a suitable temperature is important to make sure the metallization effective.
This is all the information about metallization technology, in our next blog, we will delve into what factors will affect the metallization. If you are interested in metallization or other technologies about ceramic circuit boards, please leave your message and keep your eyes in Best Technology website.