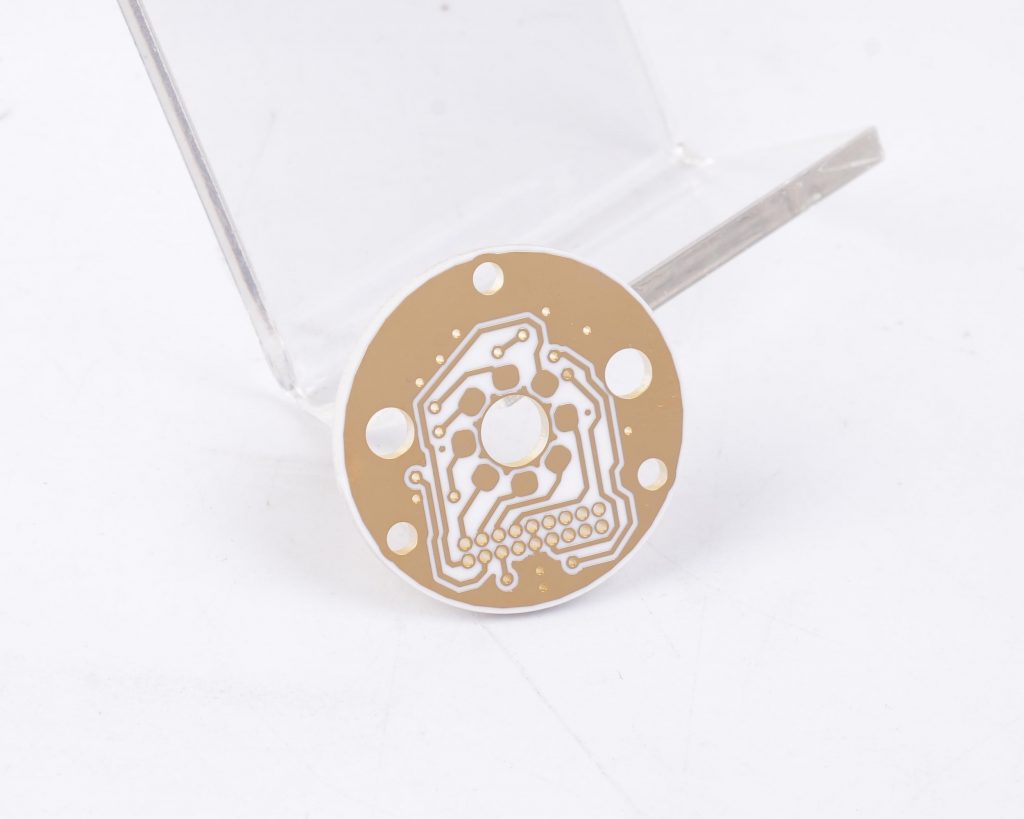
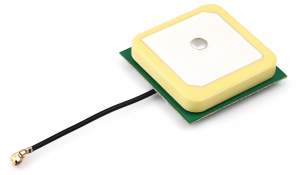
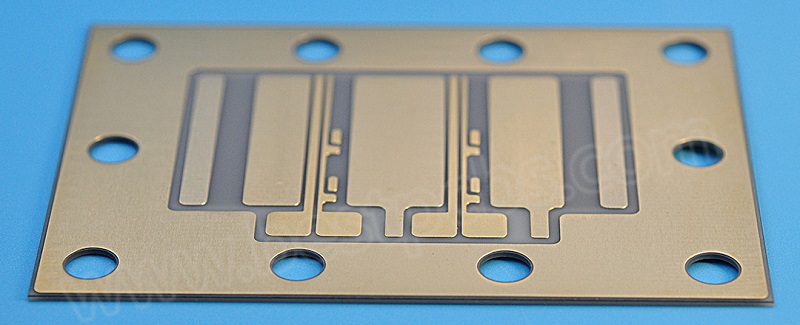
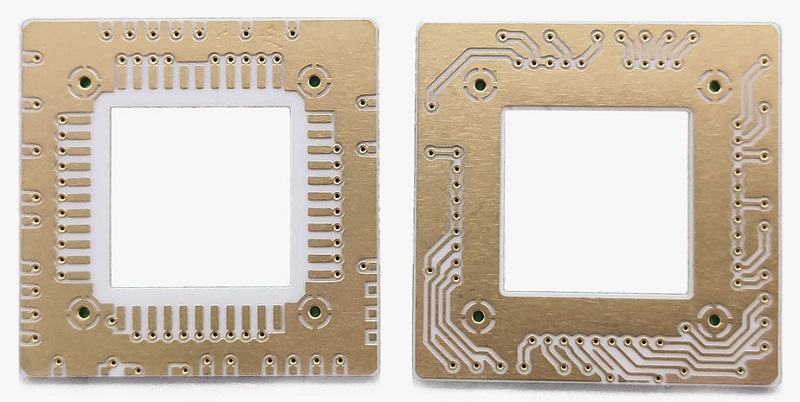
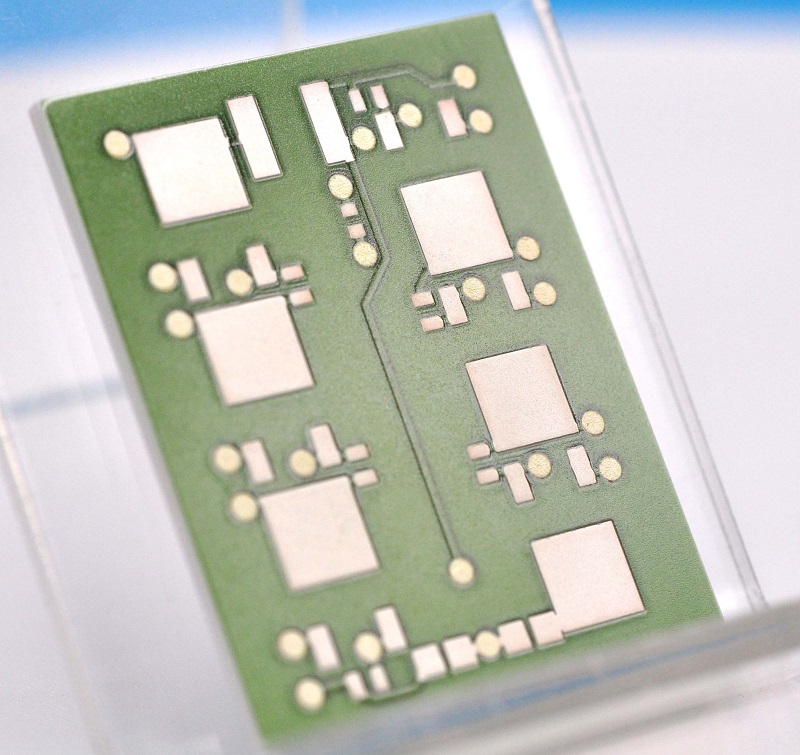
Wireless communication plays a vital role in modern technology. From smartphones to IoT devices, efficient signal transmission is necessary for seamless connectivity. Among the many antenna options, ceramic chip antennas and PCB antennas stand out. Both are widely used in different applications, but they have unique properties that affect their performance.
Best Technology offers ceramic chip antenna design and ceramic antenna manufacturing service over 10 years, we have strong R&D team can assist the design phase, and optimize your ceramic antenna design.
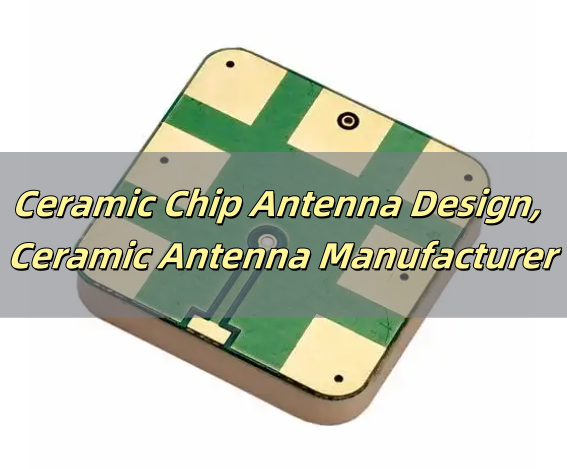
What is a Ceramic Chip Antenna?
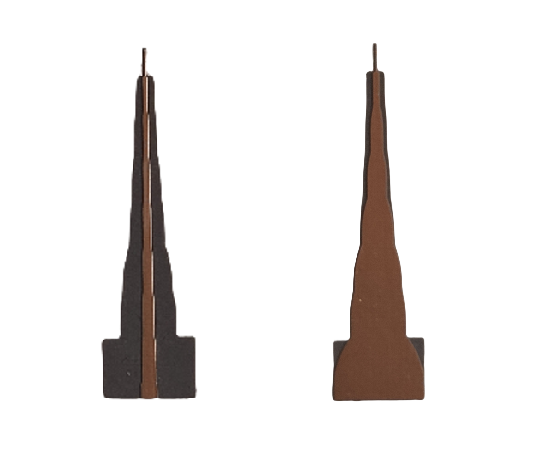
A ceramic chip antenna is a compact antenna made from ceramic materials that efficiently transmit and receive radio frequency (RF) signals. Unlike traditional antennas, these are small, robust, and ideal for space-constrained devices.
These antennas operate based on dielectric resonance, where the ceramic material enhances signal propagation. They are commonly used in wireless devices like GPS modules, IoT sensors, Bluetooth-enabled products, and Wi-Fi systems. Due to their small size and strong performance, they are a popular choice in modern electronics.
Features of Ceramic Chip Antennas
Ceramic chip antennas are widely used in wireless communication because of their small size, stable performance, and durability. Unlike traditional metal antennas, they integrate seamlessly into compact devices without sacrificing efficiency. So, what makes them special?
1. Reliable Performance in Any Environment
One of the biggest advantages of ceramic chip antennas is their frequency stability. They can work consistently across different conditions while wonât affect its performance, thatâs why they always appear in applications that require high-precision communication, like GPS and industrial IoT devices.
2. Easy to Integrate into PCBs
Ceramic antennas can be directly placed on a circuit board without affecting the overall design. So, engineers can easier to develop sleek and compact electronic devices while keeping manufacturing simple.
3. Small Size and Lightweight
Ceramic chip antennas take up very little space and weigh much less than traditional metal antennas. Thatâs why they are commonly used in Bluetooth devices, smart wearables, and IoT sensors, where every millimeter matters.
4. Withstands High Temperatures
Some ceramic chip antennas are designed to handle extreme temperatures, even up to 200-300°C.
5. Built for Tough Conditions
These antennas are built to last. They are resistant to interference, lightning, water, and dust, that can withstand outdoor, underwater, and extreme weather applications. From deep-sea exploration to volcanic monitoring, they perform reliably.
6. Strong Signal with Low Power Usage
Even though they are small, ceramic chip antennas provide efficient signal transmission with minimal energy loss. They can help to maintain strong wireless connectivity while reducing power consumption, which is especially useful in battery-powered devices.
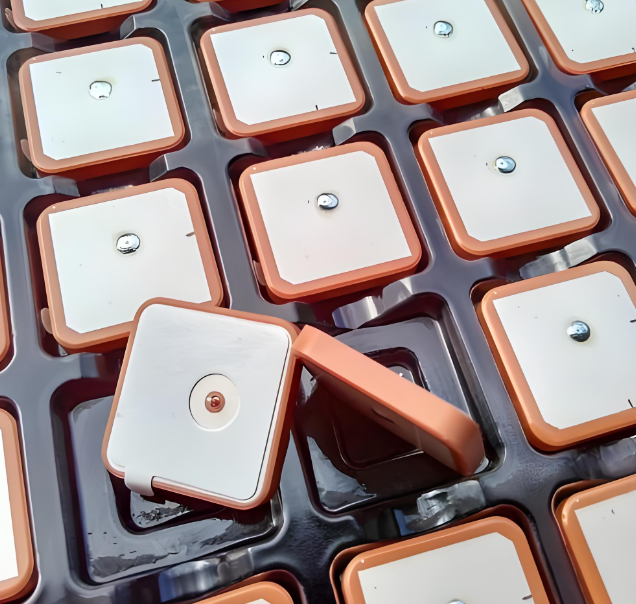

Ceramic Chip Antenna Types
Ceramic chip antennas come in different types based on their frequency range, application, and design. Each type serves a specific purpose, whether for Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, GPS, or IoT applications. Below are some of the most common ceramic chip antennas used today.
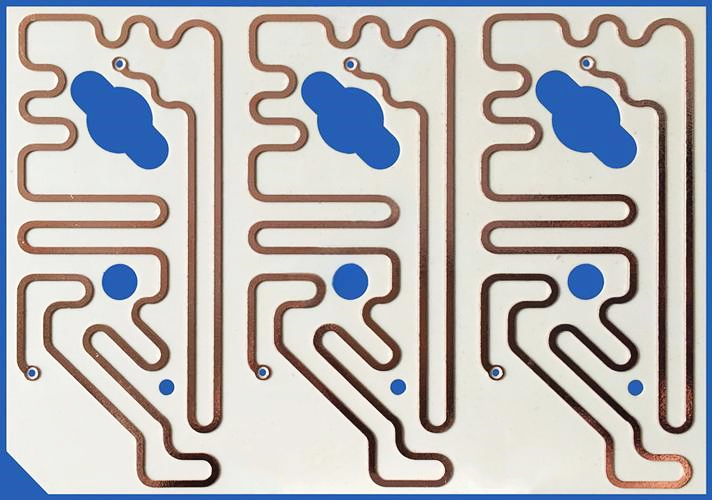
1. PCB Trace Antenna
A PCB trace antenna is a type of ceramic antenna that is directly etched onto the circuit board using copper traces. It is one of the most cost-effective options but has certain limitations in terms of signal efficiency.
Since these antennas rely on PCB layout design, factors like board thickness, dielectric constant, and trace width impact performance. They are often used in low-cost wireless modules but require careful tuning to function correctly.
2. 2.4GHz Ceramic Chip Antenna
This antenna operates at 2.4GHz, the standard frequency for Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee communications. It offers better performance compared to PCB antennas due to its optimized ceramic structure.
3. ESP32 Ceramic Chip Antenna
The ESP32 is a widely used microcontroller with built-in Wi-Fi and Bluetooth capabilities. Many ESP32-based devices use ceramic chip antennas to enhance wireless communication without increasing size. They can work well with the ESP32 Wi-Fi + Bluetooth module, ensuring stable connectivity in embedded systems. But it has a limitation that its performance can be influenced by nearby metal components, requiring careful PCB layout.
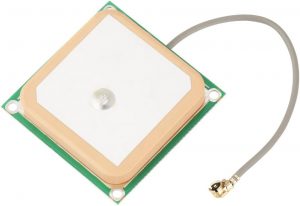
4. GPS Ceramic Chip Antenna
A GPS ceramic antenna is designed to receive satellite signals for positioning and navigation. It is commonly used in devices that require accurate location tracking.
5. Multiband Ceramic Chip Antenna
This antenna is designed to support multiple frequency bands, allowing a single device to operate across different wireless communication standards. They are versatile but limited in expensive manufacturing cost compared to single-band antennas.
So, in a word, if you need a cost-effective and space-saving solution, a PCB trace antenna works well. For Wi-Fi and Bluetooth, a 2.4GHz ceramic chip antenna is ideal. If your project involves IoT and ESP32 modules, go with an ESP32 ceramic chip antenna. For navigation and tracking, a GPS ceramic antenna is the right choice. If you need multiple functions, a multiband ceramic chip antenna offers the most flexibility. The best ceramic chip antenna depends on your end-application.
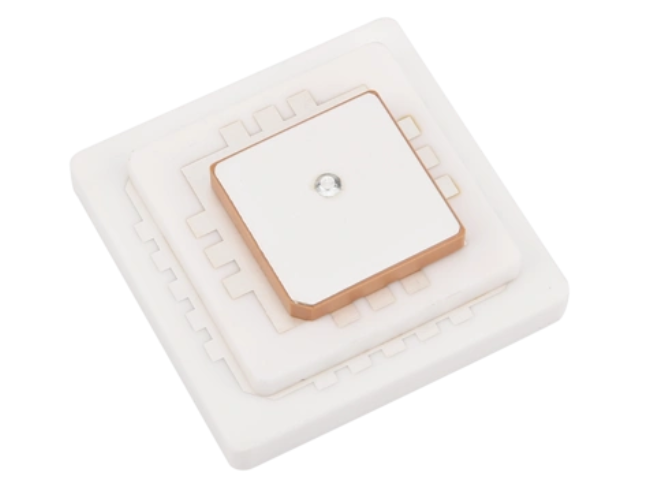

Ceramic Antenna vs PCB Antenna
PCB antenna is most used in the market, both types have their own strengths and limitations. When selecting an antenna for your application, which is the best? Herein, Best Technology will breakdown their differences in detail:
1. Material and Construction
A ceramic antenna is made from high-quality dielectric ceramic material, it is usually a standalone component that can be soldered onto a PCB. In contrast, a PCB antenna is simply a copper trace printed on the PCB itself, using the boardâs material as the dielectric. PCB antennas require precise layout design to function effectively and are directly integrated into the boardâs circuitry.
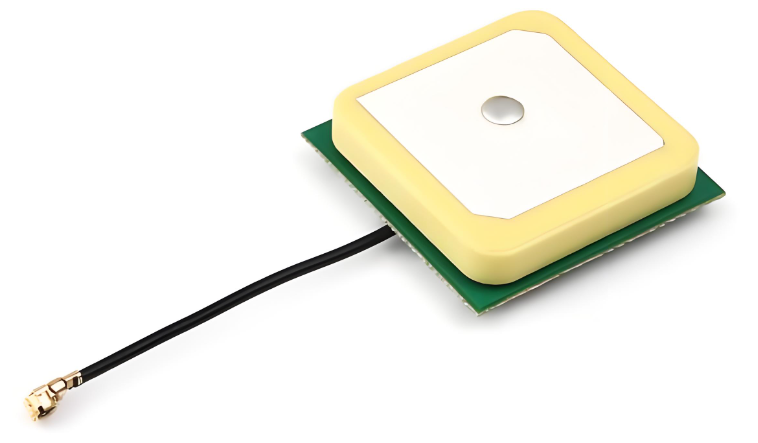
2. Size and Space Efficiency
Ceramic antennas are compact and self-contained, since they do not rely on a large ground plane, they can be placed in confined areas without significant loss in performance. PCB antennas, however, require a larger surface area to achieve good performance, as their efficiency is heavily dependent on ground plane size. In very small devices, a PCB antenna may not be practical due to space constraints.
3. Manufacturing and Design Flexibility
A PCB antenna is cost-effective and easy to manufacture since it is created directly on the PCB during the etching process. This eliminates the need for additional components, reducing bill of materials (BOM) costs. However, PCB antennas require careful tuning and optimization, so its design and manufacturing process more complex.
4. Cost and Production Considerations
PCB antennas are generally cheaper to produce, as they are just part of the PCB layout and do not require separate assembly. However, the hidden cost comes in the form of design complexity, tuning, and potential performance issues. Ceramic antennas, while having a higher unit price, reduce design time and improve reliability, leading to lower costs in the long run for high-performance applications.
How Does a Ceramic Antenna Work?
âThe working principle of ceramic antenna PCB â mainly includes two processes of transmitting and receiving. The ceramic antenna uses GPS satellite to realize navigation and positioning. The main task of the user’s receiver is to extract the pseudo-random noise code and data code in the satellite signal, so as to solve the navigation information of the receiver carrier such as position, speed and time (PVT). Here is a detailed explanation for each process:
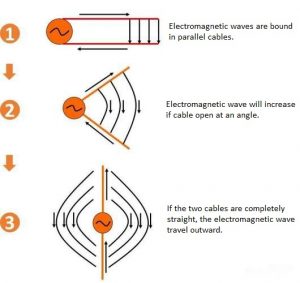
- Signal Transmission â The antenna converts electrical signals into electromagnetic waves.
- Signal Reception â It captures incoming RF signals and converts them back into electrical signals.
- Impedance Matching â A matching network ensures efficient energy transfer between the antenna and the circuit.
- Ground Plane Interaction â A well-designed ground plane improves signal stability and efficiency.
Ceramic Chip Antenna Design Considerations
Designing a ceramic chip antenna involves several factors that influence performance. Here are the key considerations:
1. Antenna Placement on the PCB
Antennas should be positioned at the edge or corner of the PCB to maximize radiation efficiency. Nearby metal components, shielding, or large ICs should be avoided as they can cause signal interference.
2. Ground Plane Size and Layout
A larger ground plane improves antenna efficiency by acting as a signal reflector. The PCB material should match the antennaâs specifications to maintain frequency accuracy.
3. Antenna Matching and Impedance Tuning
Most ceramic antennas are designed for 50Ω impedance, but variations in PCB layout can affect this. A matching network, typically using capacitors and inductors, engineers often use Pi or T matching networks to fine-tune performance.
4. Clearance and Keep-Out Zones
There should be no copper traces, ground planes, or metal components too close to the antenna. Keeping the antenna away from batteries, shields, and enclosures.
5. Operating Frequency and Bandwidth Considerations
Each ceramic antenna is designed for a specific frequency, such as 2.4GHz for Wi-Fi/Bluetooth or 1.575GHz for GPS. Any change in PCB layout can shift the resonance frequency, requiring fine-tuning.
What is the Most Effective Ceramic Antenna Shape?
The shape of a ceramic antenna influences its performance. The most effective shapes include:
- Rectangular: Common in chip antennas, offering a balance between size and performance.
- Helical: Provides better bandwidth and efficiency in small spaces.
- Patch: Ideal for GPS applications, offering strong directional signals.
- Planar Inverted-F Antenna (PIFA): Compact and efficient, widely used in mobile devices.
High-Performance Ceramic Chip Antenna Manufacturer â Best Technology
With over a decade of effort and experience, Best Technology has been actively contributing to the growth of this business. Certified with ISO9001, ISO13485, IATF16949, AS9100D,UL, and RoHS, the company is fully capable of delivering high-performance, eco-friendly PCBs and various types of ceramic chip antenna for various applications at competitive prices. If choose Best Technology, you can enjoy:
- Expertise â Decades of experience in antenna design and PCB manufacturing.
- Custom Solutions â Tailored ceramic antennas based on customer requirements.
- Strict Quality Control â Every product undergoes rigorous testing to ensure top performance.
- Competitive Pricing â High-quality antennas at cost-effective prices. DDU & DDP quotation available.
- Global Support â Trusted by customers worldwide for reliable wireless solutions.
- 5 Years Guarantee â Offer free repairing and re-work if products have quality issue within 5 years.
For businesses looking for top-tier ceramic antennas, Best Technology delivers innovative and high-performance solutions. Contact us today to discuss your antenna needs!