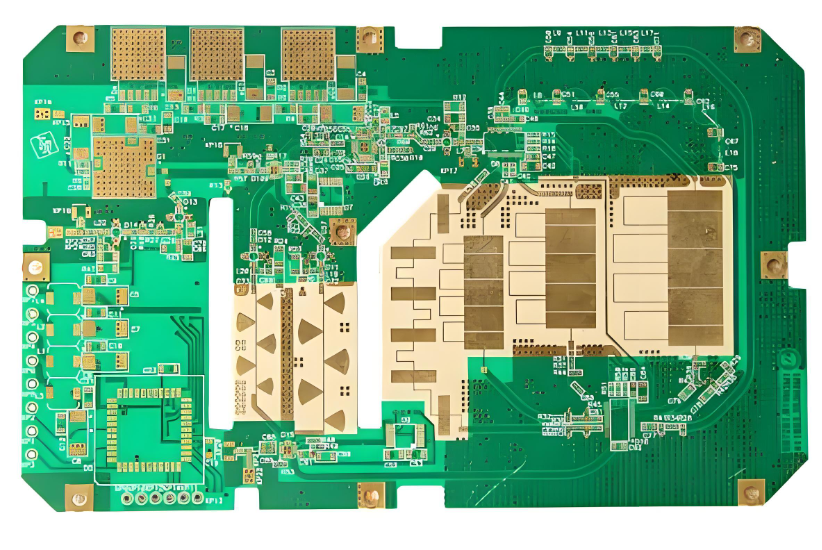
An RF power amplifier circuit is the critical engine that boosts weak radio frequency signals to power levels sufficient for transmission through antennas, forming the backbone of all wireless communication. This comprehensive guide delves into the principles of precision RF power amplifier circuit design and assembly, exploring core concepts from basic topologies to advanced 5G applications, and outlining the PCB manufacturing considerations essential for optimal performance and reliability.
For RF design engineers, developing a high-performance RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč is often a formidable challenge. What are the most common hurdles they face?
- Achieving Target Efficiency & Linear Output:‚Äč Balancing high power-added efficiency (PAE) with stringent linearity requirements across the desired bandwidth, often leading to iterative, time-consuming design cycles.
- Ensuring Thermal & Signal Stability:‚Äč Managing heat dissipation from high-power RF transistors and preventing unwanted oscillations or performance drift, which can cause system failure.
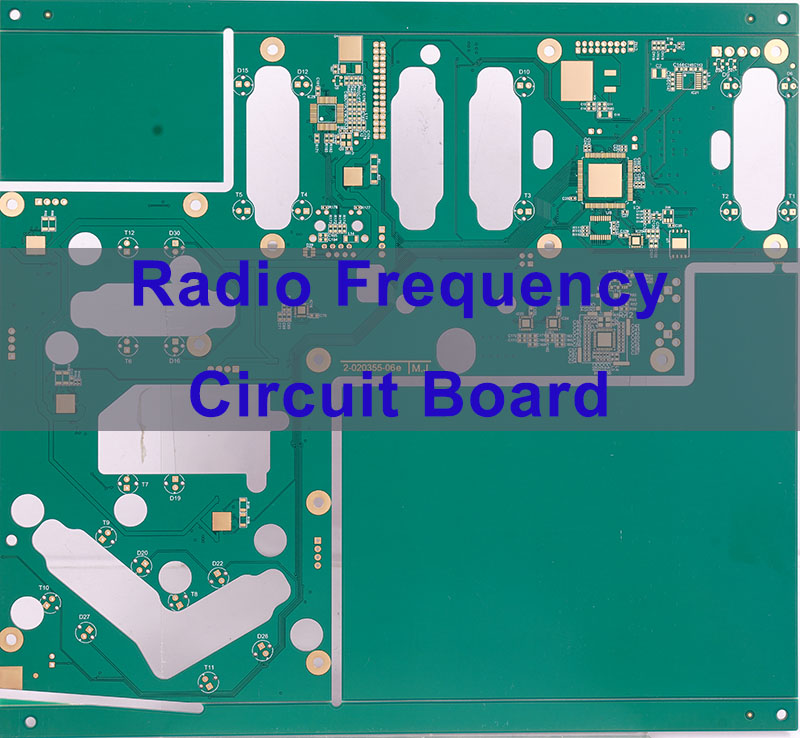
- Navigating Complex PCB Materials & Stack-ups:‚Äč Selecting the right high-frequency laminate (e.g., Rogers, ceramic-filled) and designing a stack-up that minimizes loss and supports effective grounding, often without in-house fabrication expertise.
- Integrating Precise Biasing & Control Circuits:‚Äč Designing a stable bias circuit for RF power amplifiers‚Äč that ensures consistent quiescent point operation over temperature and aging, critical for both linear and saturated amplifiers.
- Transitioning from Schematic to Reliable Physical Assembly:‚Äč Accurately translating an RF power amplifier circuit diagram‚Äč into a manufacturable layout while managing impedance, parasitics, and ensuring robust PCB and PCBA‚Äč assembly for field reliability.
The path from a conceptual RF power amplifier circuit design‚Äč to a stable, high-yield product requires a partnership with a fabrication expert. Here is how a specialist provider addresses these core challenges:
- Co-Design for Performance:‚Äč Leveraging simulation-driven design support to help optimize matching networks and layout for target efficiency, linearity, and bandwidth from the outset.
- Thermal & EMI-Optimized Platforms:‚Äč Offering advanced materials like ceramic PCBs (AlN, Al‚āāO‚āÉ) and thermally enhanced FR4, alongside design rules for thermal vias and shielding, to ensure stability.
- Material Science & Engineering Guidance:‚Äč Providing expert consultation on RF-suitable dielectrics (Dk, Df), copper roughness, and stack-up configuration to meet electrical performance goals.
- Integrated Passive & Bias Solutions:‚Äč Enabling the fabrication of precision embedded resistors and stable DC feed networks as part of the PCB to simplify the RF power amplifier bias circuit.
- Precision High-Frequency Manufacturing:‚Äč Utilizing controlled impedance routing, advanced plating, and stringent assembly processes (e.g., for MOSFET RF power amplifier circuits) to ensure the built circuit matches the designed performance.
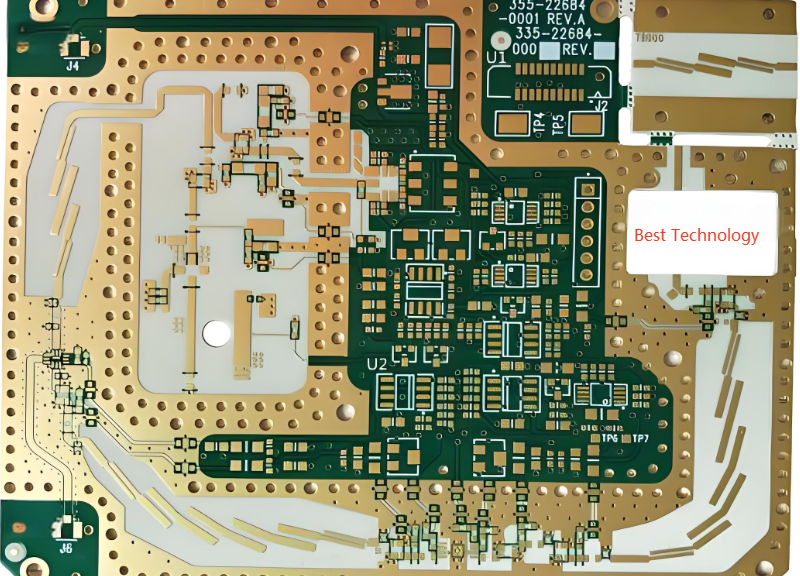
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we specialize in turning complex RF designs into reliable RF products. As a professional manufacturer of high-frequency PCBs and ceramic PCB‚Äč substrates, we provide a seamless, one-stop service from engineering support and prototype fabrication to full turnkey assembly. Our expertise ensures your precision RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč is built on a foundation optimized for signal integrity, thermal management, and long-term durability. For your next RF power amplifier circuits project, pls feel free to contact our team at sales@bestpcbs.com.
What Is RF Power Amplifier Circuit and How Does It Work in RF Systems?
An RF Power Amplifier (PA) circuit is a specialized electronic circuit designed to increase the power level of a radio frequency signal before it is delivered to an antenna for radiation. Its core function is to take a low-power RF input signal, typically from an oscillator or upconverter, and amplify it to a level sufficient for transmission over a required distance, while maintaining signal fidelity as defined by system requirements such as linearity, bandwidth, and efficiency.
The operation of an RF power amplifier in a circuit‚Äč can be distilled into a few key stages and principles:
- Input Matching Network:‚Äč This block (often an input tank circuit) maximizes power transfer from the signal source (e.g., driver stage) to the active device (transistor) by transforming impedance, reducing reflections.
- Active Amplification Device:‚Äč The core where power amplification occurs. This can be a BJT‚Äč (for Class C BJT RF power amplifier circuit), a MOSFET‚Äč (for MOSFET RF power amplifier circuit), or GaAs/GaN HEMTs for higher frequencies and powers.
- Bias Network:‚Äč Provides the proper DC operating point (quiescent current/voltage) to the transistor. The design of this bias circuit for RF power amplifiers‚Äč is crucial for setting the amplifier class (A, AB, B, C) and ensuring stability.
- Output Matching Network:‚Äč Transforms the high-impedance output of the transistor down to the standard load impedance (e.g., 50ő©). It also filters harmonics and ensures maximum power is delivered to the antenna.
- Power Supply & Conditioning:‚Äč Delivers stable, clean DC power. For RF power amplifier circuits with AGC, additional control loops are integrated to dynamically adjust gain.
In essence, the RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč acts as the final, powerful “voice” of an RF transmitter, determining the effective range and signal quality of the entire system, from a simple RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč in an FM transmitter to a complex 5G RF power amplifier circuit.
What Are the Core Design Principles of RF Power Amplifier Circuit Design?
RF power amplifier circuit design‚Äč is governed by a set of competing requirements that must be carefully balanced. The goal is to meet target specifications for frequency, bandwidth, output power, gain, efficiency, and linearity, all while ensuring stability and manufacturability. Precision in this process separates a functional prototype from a robust, high-yield product.
The core principles revolve around managing trade-offs:
| Design Principle‚Äč | Key Goal‚Äč | Primary Trade-Off / Challenge‚Äč |
| Impedance Matching‚Äč | Max Power Transfer, Low VSWR | Bandwidth vs. Complexity |
| Linearity‚Äč | Low Distortion (ACLR) | Linearity vs. PAE‚Äč |
| Efficiency (PAE, ő∑)‚Äč | Minimize DC Waste, Reduce Heat | Inverses Linearity‚Äč |
| Stability (K>1)‚Äč | Unconditional Stability | Stability vs. Gain |
| Gain & Bandwidth‚Äč | Target Gain over Required BW | Gain-Bandwidth Product |
| Thermal Management‚Äč | Junction Temperature Control | Power Density vs. Cooling |
A practical RF power amplifier circuit design 27MHz NPN‚Äč for citizen-band radio will prioritize efficiency (often using Class C) and simplicity. In contrast, a wideband RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč for a vector signal analyzer must maintain flat gain and good linearity over a multi-octave bandwidth, often employing feedback or distributed amplification techniques. Understanding these principles is the first step in any RF power amplifier design tutorial circuit‚Äč and is essential whether aiming for a low power RF amplifier circuit‚Äč or a 100W RF power amplifier mini circuit.
Why Is Bias Circuit for RF Power Amplifiers Critical for Stability and Performance?
The bias circuit for RF power amplifiers‚Äč is far more than a simple DC feed; it is a critical control system that sets the fundamental operating mode of the transistor and profoundly impacts nearly all aspects of performance, reliability, and stability. An imprecise or unstable bias point can lead to degraded efficiency, distorted output, thermal runaway, or even catastrophic device failure.
A well-designed bias network addresses several key requirements:
- Establishes Amplifier Class:‚Äč It sets the quiescent current (IQ). Zero IQdefines Class B/C, a small IQdefines Class AB, and a large IQdefines Class A. This choice directly dictates the efficiency-linearity trade-off.
- Ensures Thermal Stability:‚Äč Uses techniques like emitter/source degeneration resistors or proportional-to-absolute-temperature (PTAT) bias generators to prevent thermal runaway, where increasing temperature causes current to increase uncontrollably.
- Suppresses Low-Frequency Oscillation:‚Äč Includes RF chokes and bypass capacitors to isolate the RF signal from the DC supply, preventing unwanted feedback paths that can cause oscillation at very low frequencies.
- Maintains Performance Over Temperature & Batch Variation:‚Äč Active bias circuits with feedback can compensate for the negative temperature coefficient of a transistor’s turn-on voltage (VBEor VGS(th)), keeping gain and output power consistent.
- Enables Control & Protection:‚Äč Can integrate circuits for RF power amplifier protection‚Äč (overcurrent, over-temperature) or facilitate dynamic control like AGC (Automatic Gain Control).
For example, a Class C RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč uses a negative or zero bias to achieve high efficiency (>70%) but is highly nonlinear, suitable only for constant-envelope modulation. Conversely, a RF linear power amplifier circuit‚Äč for 5G requires a precise Class-AB bias to operate in its linear region, making the bias circuit’s stability paramount to maintain low EVM and ACLR. In a MOSFET RF power amplifier circuit, gate bias voltage must be tightly controlled, as a small drift can cause a large shift in drain current and linearity.
How to Read an RF Power Amplifier Circuit Diagram and Understand Its Blocks?
An RF power amplifier circuit diagram‚Äč is the roadmap from which a physical circuit is built. Learning to interpret it is essential for design, troubleshooting, and assembly. While details vary, most diagrams for a discrete RF power amplifier circuit PA‚Äč (Power Amplifier) can be broken down into functional blocks.
A typical block-level breakdown of a circuit diagram of RF power amplifier‚Äč includes:
- DC Power Input & Decoupling:‚Äč Shows the VCC/VDDconnection and an array of capacitors (bulk, ceramic, RF) to ground. This network provides stable DC and shunts any RF on the supply line to ground.
- Input Matching Network (IMN):‚Äč A network of inductors (L), capacitors (C), and sometimes transmission lines located between the input connector and the transistor’s base/gate. Its goal is to present the optimal impedance (often the complex conjugate of S11) to the transistor for maximum power transfer at the fundamental frequency.
- Active Transistor & Bias Network:‚Äč The centerpiece (Q1 or M1). The bias circuit‚Äč is shown connected to the base/gate (and sometimes emitter/source). It may consist of voltage dividers, current mirrors, or active regulator circuits supplying the critical DC bias voltage/current.
- Output Matching Network (OMN):‚Äč Located between the transistor’s collector/drain and the output connector. It transforms the device’s optimal load impedance (for max. power or efficiency) down to 50ő© and often acts as a low-pass filter to attenuate harmonic frequencies generated by the nonlinear transistor.
- Load (Antenna) & Isolation:‚Äč The output port, often with a directional coupler or isolator/circulator symbol to denote protection from load mismatches.
Reading a diagram for a VHF RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč versus a UHF RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč will show different component values and layout notations due to the wavelength difference. A simple RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč may combine bias and matching into minimal components, while a high power RF amplifier circuit‚Äč diagram will prominently feature thermal pads, balancing resistors for power combining, and robust supply traces. Understanding these blocks allows you to analyze any design, from a FM transmitter circuit with RF power amplifier stage‚Äč to a sophisticated RF power amplifier integrated circuit‚Äč evaluation board schematic.
What Is the Difference Between Simple RF Power Amplifier Circuit and High Power RF Amplifier Circuit?
The distinction between a simple RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč and a high power RF amplifier circuit‚Äč extends far beyond the output power rating. It represents a fundamental shift in design complexity, component selection, and required supporting infrastructure to manage the challenges of high power density.
The differences are multifaceted:
| Aspect‚Äč | Simple / Low Power RF PA‚Äč | High Power RF PA‚Äč |
| Primary Goal‚Äč | Gain, Functionality, Cost | Efficiency, Linearity, Reliability |
| Active Device‚Äč | Small-signal BJT/MOSFET (SMD) | Power LDMOS/GaN/GaAs (Flange/Ceramic) |
| Bias Circuit‚Äč | Simple resistive divider | Active, compensated bias‚Äč |
| Matching Network‚Äč | Lumped L/C, simple | Hybrid lumped/distributed, harmonic tuning‚Äč |
| Thermal Mgmt.‚Äč | Passive (PCB/heatsink) | Active cooling, Ceramic PCB/Metal-clad‚Äč |
| Power Supply‚Äč | Standard regulator | High-current, low-noise, sequenced |
| Stability‚Äč | Basic isolation | Full protection circuits, isolators |
| Architecture‚Äč | Single-ended | Power-combined, Push-Pull |
A 5W RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč for a handheld radio exemplifies a mid-range design, needing careful layout but not extreme cooling. A 100W RF power amplifier mini circuit‚Äč is an engineering feat, pushing the limits of power density. The RF power amplifier circuit design‚Äč for such high-power applications is inseparable from the PCB and PCBA‚Äč strategy, mandating materials with high thermal conductivity (like alumina ceramic) and sophisticated assembly processes to handle the immense thermal and electrical stresses.
How Does a Class C RF Power Amplifier Circuit Operate in RF Applications?
A Class C RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč is designed for maximum possible efficiency by biasing the active transistor significantly below its cutoff point. The transistor conducts current for less than half‚Äč of the input RF cycle, producing a highly distorted, pulsed output current that is rich in harmonics. A tuned output tank circuit‚Äč (resonant at the fundamental frequency) filters out these harmonics, reconstructing a sinusoidal waveform at the output.
Key Operational Characteristics:
- Bias Point:‚Äč The base/gate is biased negatively (for BJTs) or below threshold (for MOSFETs), ensuring the device is off‚Äč with no input signal.
- Conduction Angle:‚Äč Typically 120¬į to 180¬į, but often much less. Efficiency (ő∑) is theoretically given by: ő∑ = (őł – sinőł) / (4(sin(őł/2) – (őł/2)cos(őł/2)))**‚Äč where őł is the conduction angle. Lower angle = higher efficiency (>70% possible).
- High Nonlinearity:‚Äč The amplified output is not a linear reproduction of the input. This makes Class C unsuitable for amplitude-based modulations (AM, QAM).
Common RF Applications:
- Constant-Envelope Transmitters:‚Äč Ideal for FM transmitter circuits‚Äč and FM transmitter circuit with RF power amplifier stage, where information is in frequency/phase shifts, not amplitude.
- RF Heating & Plasma Generation:‚Äč Where pure CW or pulsed RF power is needed, as in industrial Transculpt RF power amplifier circuit schematics 1MHz.
- Some AM Transmitters:‚Äč Can be used in AM RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč designs with high-level plate/collector AM modulation, though less common today.
- RFRFPA designing a input tank circuit AMFONE:‚Äč In vintage or hobbyist tube-based designs, Class C is frequently employed for its efficiency.
While a Class-C RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč offers superb efficiency, its use in modern spectrum-conscious, high-data-rate systems is limited. It cannot be used for modern digital modulations like OFDM (used in 4G/5G) which have high peak-to-average power ratios (PAPR) and require linear amplification. Therefore, while foundational in RF amplifier circuit‚Äč history and still valuable for specific apps, it has largely been supplanted by linearized Class-AB or Doherty architectures in mainstream communications.
Where Are 5G RF Power Amplifier Circuit and Wideband RF Power Amplifier Circuit Used Today?
Modern wireless systems demand amplifiers that are not only powerful and efficient but also capable of handling wide bandwidths and complex signals. The 5G RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč and the wideband RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč are two specialized answers to these demands, finding critical roles in next-generation infrastructure and test equipment.
5G RF Power Amplifier Circuit Applications:
- Massive MIMO Active Antenna Units (AAUs):‚Äč Each antenna element in a 5G base station array is driven by its own PA module. These PAs must be highly linear to support high-order QAM (256QAM, 1024QAM) and wide bandwidths (up to 400MHz in n79 band), all while maintaining excellent efficiency to reduce power consumption and heat.
- 5G User Equipment (Smartphones, CPEs):‚Äč RF power amplifier integrated circuits‚Äč (PAMiDs) in phones must cover a vast range of 5G sub-6 GHz and mmWave bands, requiring multi-band, multi-mode operation with advanced envelope tracking (ET) for battery life.
- Small Cells & Repeaters:‚Äč Deployed for network densification, these use PAs with lower output power but stringent linearity and efficiency requirements.
Wideband RF Power Amplifier Circuit Applications:
- Electronic Warfare (EW) & SIGINT Systems:‚Äč Jamming and surveillance platforms require amplifiers that can operate across very wide instantaneous bandwidths (multiple octaves) to cover diverse threat frequencies.
- Test & Measurement Equipment:‚Äč Vector signal generators, network analyzers, and wideband signal analyzers use linear wideband PAs in their signal paths to provide flat gain and high output power across their entire frequency range (e.g., 9 kHz to 6 GHz or more).
- Multi-Standard and SDR Base Stations:‚Äč Software-defined radios benefit from wideband PAs that can be reconfigured for different services (2G/3G/4G/5G, WiFi) without hardware changes.
- CATV/Broadband Distribution:‚Äč Coaxial cable networks use wideband PAs to amplify dozens of TV and data channels simultaneously.
The design of these circuits pushes the limits of semiconductor technology (using GaN-on-SiC for high power and bandwidth) and RF power amplifier circuit design, often employing techniques like feedback, distributed amplification (traveling-wave), or balanced structures to achieve the necessary performance across a broad spectrum, from a VHF‚Äč to UHF RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč range and beyond.
What PCB and PCBA Factors Affect the Reliability of an RF Power Amplifier Circuit?
The reliability of an RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč is not determined solely by its schematic design; it is equally dependent on the physical implementation‚ÄĒthe PCB and PCBA. For a precision, high-power RF design, the substrate material, layout, fabrication quality, and assembly process are non-negotiable elements of performance.
Critical PCB/PCBA Factors for RFPA Reliability:
- Dielectric Material (Laminate):‚Äč Standard FR-4 has high loss tangent (Df) at RF frequencies, causing signal loss and heat generation. Reliable RF PAs‚Äč use low-loss laminates (Rogers, Taconic) or ceramic PCBs‚Äč (Al‚āāO‚āÉ, AlN) for superior thermal conductivity and stable dielectric constant (Dk).
- Controlled Impedance & Layout:‚Äč Microstrip traces must be precisely calculated and fabricated to maintain 50ő© impedance. Poor control leads to mismatches, reflected power, gain ripple, and potential instability. Grounding via fences and a solid ground plane are essential.
- Thermal Design:‚Äč The PCB itself is a heatsink. Use of thermal vias under power device pads, thick copper planes (2oz+), and direct bonding to metal cores or ceramic substrates are vital to transfer heat from the transistor junction. This is the single biggest factor in high power RF amplifier circuit‚Äč longevity.
- Component Selection & Placement:‚Äč RF components (capacitors, inductors) must have high self-resonant frequencies (SRF) and appropriate power ratings. Placement must minimize parasitic inductance in high-current paths (like the drain/collector supply). Decoupling capacitors must be placed for optimal high-frequency performance.
- Assembly Process Quality:‚Äč Solder joint integrity is critical. Voids under a power transistor’s thermal pad can cause catastrophic overheating. Precise solder paste application and reflow profiling are mandatory. For MOSFET RF power amplifier circuits, ESD protection during handling is crucial.
A failure in any of these areas can lead to degraded output power, increased noise, intermittent operation, or thermal runaway. Partnering with a PCB/PCBA‚Äč provider like Best Technology, which understands these RF power amplifier circuits’ unique needs‚ÄĒfrom material selection to precision RF power amplifier circuit‚Äč assembly‚ÄĒis fundamental to transitioning a great design into a reliable, field-deployable product.
To sum up, RF power amplifier circuits‚Äč are the indispensable force multipliers in the wireless world, determining the reach, clarity, and efficiency of every transmitted signal. This guide has explored their core principles, from interpreting a basic RF power amplifier circuit diagram‚Äč to the advanced demands of 5G‚Äč and wideband‚Äč designs, and underscored the critical role of precision PCB and PCBA‚Äč in achieving reliable performance.
Success in precision RF power amplifier circuit design & assembly‚Äč requires a synergy of expert electrical design and masterful physical implementation. This is where EBest Circuit (Best Technology)‚Äč provides decisive value. We combine engineering support for high-frequency design with advanced manufacturing capabilities for low-loss RF laminates and high-thermal-conductivity ceramic PCBs. Our controlled impedance fabrication and rigorous assembly processes ensure your design performs as intended, from prototype through volume production. Ready to amplify your next RF project with precision? Pls feel free to contact our engineering sales team anytime at sales@bestpcbs.com.