In the printed circuit board industry, the most common way to express the copper layer thickness on a PCB is in ounces (oz). 1oz means 1oz of copper evenly covers an area of 1 square foot, which is about 1.4mil. It uses the weight of the tissue area to express the average thickness of the copper foil. Expressed in terms of formula, 1oz=28.35g/FT2 (FT2 is square feet, 1 square foot = 0.09290304 square meters).
What is the standard thickness of a copper layer on a PCB?
In the manufacture of printed circuit boards (PCBs), the thickness of the copper layer is an important parameter that directly affects the electrical performance and reliability of the circuit board. Depending on the application requirements, the thickness of the copper layer can vary within a certain range. Generally speaking, the conventional copper layer thickness is between 1-35μm, with 35μm being the most commonly used thickness. For some applications with high reliability requirements, the copper layer thickness may reach more than 50μm.
The selection of the thickness of the copper layer is a decision-making process that takes into account a variety of factors, including the conductivity, heat dissipation, mechanical strength, cost and manufacturing difficulty of the circuit board. A larger copper thickness can reduce resistance and improve the conductivity and heat dissipation of the circuit board, but it will also increase material costs and production difficulties. Therefore, when designing PCB boards, engineers need to select a suitable copper thickness standard range based on specific application scenarios and design requirements to ensure the performance and reliability of the circuit board.
1oz copper thickness in mm = 0.035mm
0.5 oz copper thickness in mm = 0.0175mm
1.5 oz copper thickness in mils = 0.0525mm
2 oz copper thickness in mils = 0.07mm
How thick is PCB copper after plating?
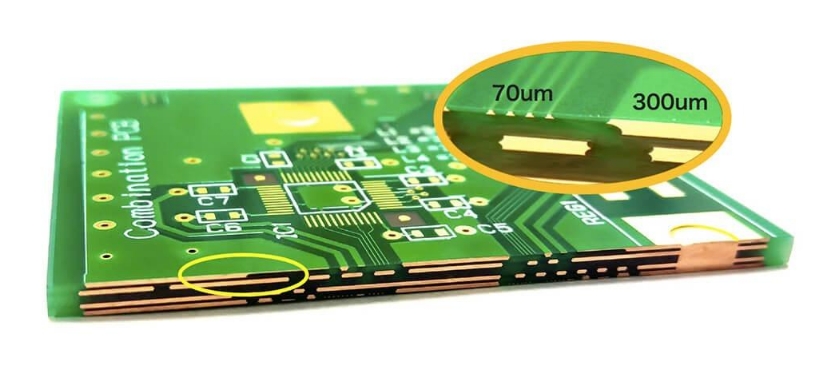
PCB printed circuit boards are usually bonded to glass epoxy substrates with a layer of copper foil, usually 18, 35, 55 and 70 microns thick. The most commonly used copper foil is 35 microns thick.
The copper foil used by PCB manufacturers is generally 35~50 microns thick, and some are thinner than this, such as 10 microns, 18 microns, and thicker such as 70 microns. The thickness of the composite copper foil on a 1~3 mm thick substrate is about 35 microns. The thickness of the composite copper foil on a substrate with a thickness of less than 1MM is about 18 microns, and the thickness of the composite copper foil on a substrate with a thickness of more than 5 mm is about 55 microns.
The copper layer thickness of PCB (printed circuit board) can be adjusted according to different needs and designs. Common copper layer thicknesses include 1oz (35μm), 2oz (70μm), 3oz (105μm), and other thicker options. For most applications, a copper layer thickness of 1oz is sufficient and suitable for general signal transmission. For circuit boards that need to carry large currents, such as switching power supplies, a copper layer thickness of 2oz or higher is usually used. In addition, there are some special cases where manufacturers provide extremely heavy copper up to 20 oz/ft2 (26.8 mils or 0.34 mm) to meet special needs.
When choosing the thickness of the copper layer, factors such as the purpose of the circuit board and the magnitude of the signal voltage and current need to be considered. For example, for circuit boards that require excessive current, a copper thickness of 70μm or 105μm may be used. For thin laminates that require ultra-high density patterns, a copper thickness of 12μm may be used. Therefore, the specific thickness of the PCB after copper plating is determined according to design requirements and specific applications.
How thick is 2 oz copper for PCB?
If 1 ounce (28.35 grams) of copper were flattened to evenly cover a surface area of 1 square foot (0.093 square meters), the resulting thickness would be 1.37mils (0.0348mm). A conversion chart for different units of measurement can be found below.
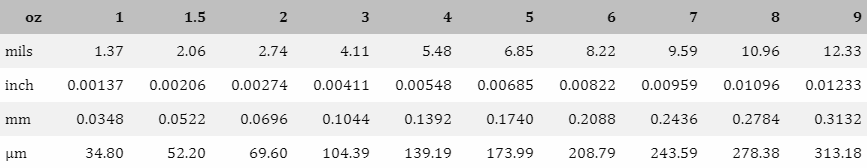
What is the difference between different copper thicknesses in PCB?
Copper is an excellent conductive material, and the thickness of the copper layer directly affects the conductive effect of the circuit board. Thicker copper layers can provide lower resistance, reduce signal transmission losses, and are particularly suitable for high-frequency and high-speed digital circuits.
During the operation of electronic equipment, good heat dissipation is a key factor in ensuring the performance and life of components. Thicker copper layers can conduct and dissipate heat more effectively, preventing components from overheating.
In high-power electronic devices, thicker copper layers can carry larger currents, avoiding burnout or performance degradation caused by excessive current.
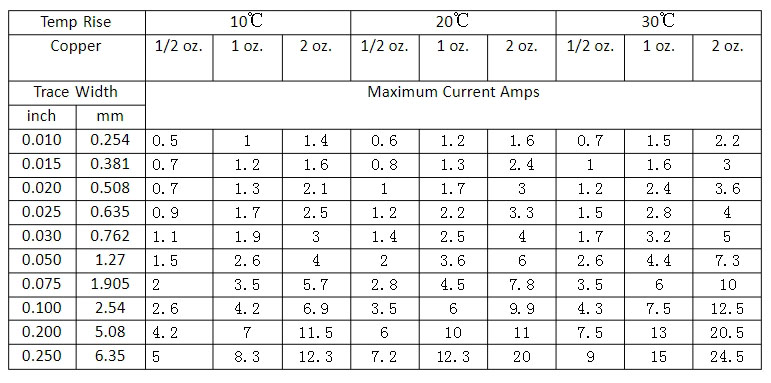
Below is the conductivity corresponding to different copper thicknesses.
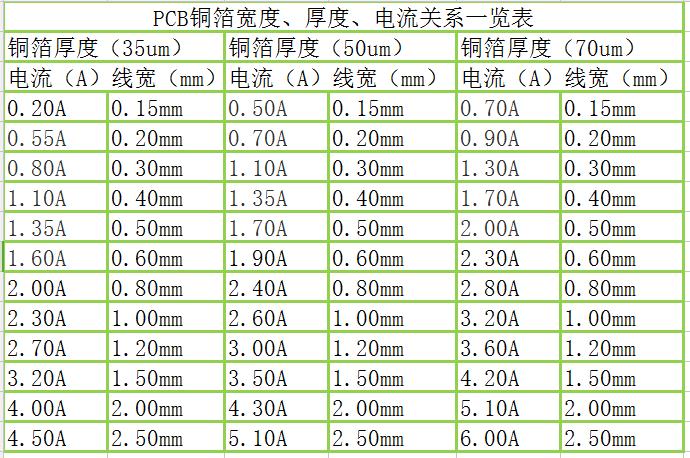
How thick is high current PCB copper?
In PCB design, copper thickness (also called copper thickness) is an important parameter, which directly affects the performance indicators of the circuit board such as current carrying capacity, heat dissipation and reliability. For PCBs that need to withstand high currents, such as high-power LED light strips, power circuit boards, high-power motor control boards or high-power inverter control boards, thicker copper layers are usually used to increase current carrying capacity.
Different uses have different copper foil thicknesses. Common 0.5oz, 1oz, and 2oz are mostly used in consumer and communication products. Thick copper products above 3oz are mostly used for high currents, such as high-voltage products and power boards.
The thickness of copper foil (track width) will affect the current size. Although there is a formula that can directly calculate the maximum current carrying capacity of copper foil, it is not so simple when actually designing the circuit. Therefore, the safety factor should be fully considered during the design.
How thick is the copper in a flex PCB?
The thickness of copper foil in flexible PCB is generally 18μm, 35μm, 55μm and 70μm. These thickness specifications are suitable for different types of circuit board requirements, among which 35μm is the most commonly used copper foil thickness.
For flexible PCB, the choice of copper foil thickness depends on the specific purpose of the circuit board and the size of the signal voltage and current. For example, for PCBs that require excessive current, some parts will use 70μm copper thickness, while for signal transmission, 1oz (35μm) thickness is usually sufficient. In addition, for substrates of different thicknesses, the thickness of copper foil is also different. For example, the thickness of the composite copper foil on a 1mm thick substrate is about 18μm, and on a substrate thicker than 5mm, the thickness of the composite copper foil is about 55μm.
Conclusion:
PCBs for different usage scenarios correspond to different thicknesses of copper, and its thickness directly affects the conductive effect of the circuit board. If the copper layer is too thin, the conductivity may decrease, resulting in signal transmission attenuation or current instability. If the copper layer is too thick, although the conductivity will be very good, it will increase the cost and weight of the circuit board and easily lead to serious glue flow. In PCB manufacturing, it is necessary to select the appropriate copper thickness according to the design requirements and actual applications of the circuit board to achieve the best conductive effect.
BEST Technology is a professional PCB circuit board manufacturer with a large area of site and equipped with useful and experienced production personnel. Corresponding to different thicknesses of copper, we have rich production and processing experience. We can meet the requirements of any circuit board copper layer thickness.