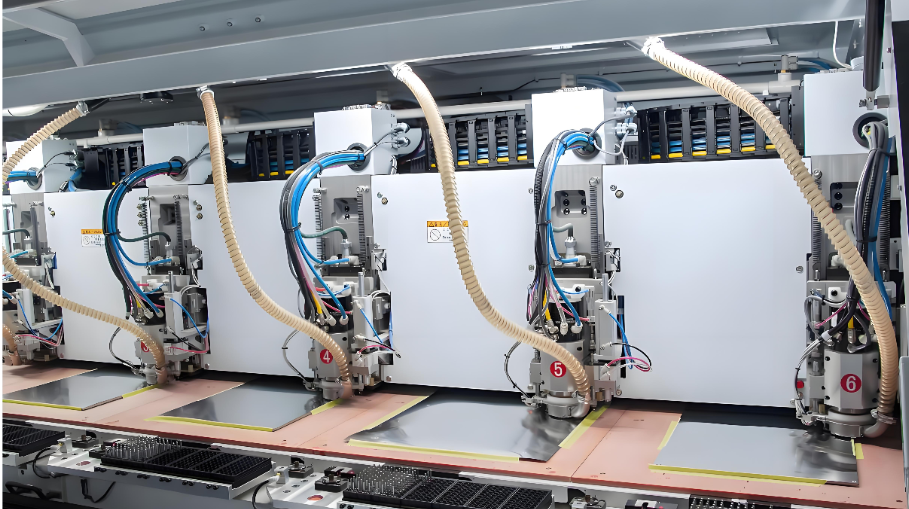
Looking for PCB manufacturer in Austria? This blog covers list and selection guide, pain point, production capability and delivery time for PCB manufacturer in Austria.
Austria, with its robust industrial foundation and advanced technological ecosystem, has nurtured a group of high-quality PCB manufacturers. Among them, the top PCB Manufacturer in Austria stand out for their stringent quality control, innovative production techniques and reliable supply chain management. These leading PCB Manufacturer in Austria not only cater to the domestic demand from industries like automotive, aerospace and industrial electronics but also gain recognition in the European and global markets, becoming an indispensable part of the international PCB supply network.

Top PCB Manufacturer in Austria List
| Company Name | Business | Advantages | Process Capabilities | Lead Time |
| EBest Circuit (Best Technology) Co. Ltd | 2-36 layer rigid, flexible & rigid-flex PCBs for automotive, aerospace, industrial control & communication equipment | 25-year industry experience; ISO 9001/IATF 16949/UL/AS9100D certifications; 10+ years technical team; 99.8% quality yield; strong European supply chain partnerships | Min. 2.5mil/2.5mil line/space; blind/buried vias & HDI; metal-core/high-frequency PCBs; ENIG/HASL/immersion silver/OSP finishes; AOI & X-ray inspection | Samples: 3-5 working days; Small batch: 7-10 working days; Large batch: 15-25 working days; Urgent: 2 days |
| AustroCircuit GmbH | Automotive PCBs & PCBA services; industrial control metal-core thermal PCBs | 18-year automotive PCB expertise; direct cooperation with BMW/Audi Tier-1 suppliers; full traceability; local rapid response | 4-24 layer rigid PCBs; 4mil/4mil min. line/space; metal-core PCB thermal conductivity 2.0-5.0 W/(m·K); solder mask color customization; lead-free processes | Automotive samples: 8-10 working days; Batch: 20-30 working days; Urgent automotive: 12-15 working days |
| EuroPrint Circuits | Medical high-precision PCBs; wearable flexible PCBs; consumer electronics mid-range PCBs | ISO 13485 medical certification; RoHS/REACH compliance; multilingual team; flexible small batch customization | 2-16 layer PCBs; >100,000 flex cycles; 0.2mm min. hole size; lead-free halogen-free materials; fine line routing | Medical samples: 10-12 working days; Flexible samples: 5-7 working days; Consumer batch: 15-20 working days |
How to Choose the Right PCB Manufacturer in Austria?
Below is a selection guide to PCB manufacturer in Austria:
1. Technical Capability Verification
- Prioritize manufacturers supporting multi-stage HDI, high-frequency/high-speed materials (e.g., Rogers 4350B), and embedded component processes. Verify mature solutions for impedance control (¬Ī8% accuracy), blind/buried via capabilities (minimum aperture 0.1mm), and surface finishes (ENIG/ENEPIG/OSP), with IPC Class II+ certification test reports required.
2. Quality Control System
- Demand dual ISO 9001/14001 certifications and automotive-grade IPC-A-600/610 compliance records. Focus on AOI optical inspection coverage (‚Č•98%), flying probe test coverage, and reliability testing procedures (e.g., thermal shock cycles, CAF testing). Avoid “panelized” factories relying on third-party subcontracting.
3. Capacity Matching Analysis
- Align production lines with project scale: for small batches (‚ȧ50„é°), confirm SMT line quantity (‚Č•3 lines); for large batches (‚Č•500„é°), validate AOI cycle time (‚ȧ30 seconds/panel) and maximum multi-layer press layers (‚Č•16 layers).
4. Engineering Support Responsiveness
- Require DFM feedback mechanisms, including line width/spacing limits (‚Č•3mil), BGA pitch recommendations, impedance calculation toolchains (e.g., Polar SI9000), and NPI process timelines (DFM reports ‚ȧ48 hours).
5. Supply Chain Transparency
- Audit raw material sources (e.g., CCL suppliers like Kingboard/Shengyi), critical material inventory strategies (safety stock ‚Č•30 days), and logistics timeliness (DHL/UPS direct coverage). Confirm environmental compliance via RoHS/REACH declarations and waste recycling processes.
6. Cost Structure Transparency
- Request itemized quotes including tooling, engineering, material, and NRE costs. Beware of “low-cost traps”‚ÄĒcompare process segment Quotation difference rate (‚ȧ15%) and confirm NRE fee amortization clauses.
7. Case Validation Mechanism
- Require recent 3-year the same project types (e.g., automotive/medical), focusing on end-customer names, project timelines, yield data, and post-sale issue resolution records. Verify capacity utilization (‚Č•70%) and on-time delivery rates (‚Č•95%) via third-party audit reports.
8. Compliance and Sustainability
- Confirm EU CE certification, WEEE directive compliance, and Austrian local environmental regulations. Provide carbon footprint reports and energy-efficient equipment lists (e.g., LED lighting, heat recovery systems), with verification of EICC or similar CSR initiatives.
Core Pain Points of PCB Manufacturer in Austria
- High labor costs: Austria’s strict labor regulations and high wage standards significantly increase the operational costs of PCB manufacturing, reducing profit margins compared to manufacturers in Southeast Asia.
- Supply chain instability: Dependence on imported raw materials (such as copper clad laminates and solder mask) leads to risks of price fluctuations and delivery delays, especially amid global trade tensions.
- Intense European competition: Facing fierce competition from PCB manufacturers in Germany, Switzerland, and other neighboring countries that also focus on high-end markets, making it challenging to expand market share.
- Rapid technological iteration: The need to continuously invest in advanced equipment (such as laser drilling machines and automated assembly lines) to keep up with the demand for higher density and smaller size PCBs, increasing capital expenditure pressure.
- Stringent environmental regulations: Austria’s strict environmental protection policies require manufacturers to invest heavily in wastewater treatment and waste recycling systems, adding to environmental compliance costs.
- Skill shortage: Difficulty in recruiting and retaining skilled technicians specialized in PCB design, process optimization, and quality control, due to the aging workforce in the local manufacturing sector.
- Fluctuating demand: The automotive and aerospace industries, major clients of Austrian PCB manufacturers, have volatile demand cycles, leading to uneven production capacity utilization.
How to Evaluate Production Capacity of PCB Manufacturing in Austria?
Assessment methods for the production capacity of PCB manufacturing in Austria:
1. Assess manufacturing scale: Production scale directly determines capacity ceiling and order undertaking ability. Investigate core indicators like factory area, number of production lines, and annual output (calculated by square meters or units) to confirm basic capacity and scalability.‚Äč
2. Examine equipment configuration: Equipment level is the foundation of production efficiency. Check types, brands and service life of key equipment (e.g., PCB etching machines, drilling machines, AOI systems) to judge technical maturity and stable production capability.‚Äč
3. Review process certification: Certifications reflect standardized management level. Verify authoritative certifications such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949 and UL, which are direct proofs of reliable production processes.‚Äč
4. Analyze sample quality: Sample precision mirrors mass production level. Test prototypes to evaluate line accuracy, via reliability and surface finishing quality, these indicators directly show manufacturing precision.‚Äč
5. Check production lead time: Lead time reflects scheduling efficiency. Inquire about prototype and mass production lead times; reasonable and stable cycles indicate scientific production planning and smooth process links.‚Äč
6. Evaluate quality control system: Strict QC ensures product consistency. Understand full-process inspection links (incoming material, in-process, final inspection) and defective product rate (PPM) to avoid batch quality risks.‚Äč
7. Reference customer cases: Cooperation experience with high-end clients proves capability. Review cooperation history with large enterprises in automotive and aerospace industries to confirm adaptability to strict requirements.‚Äč
8. Assess R&D capability: R&D strength guarantees technical support. Investigate R&D team size, patent quantity and custom solution experience to ensure adaptation to new technology and product demands.

How to Evaluate Delivery Time of PCB Manufacturers in Austria?
Assessment methods for the delivery time of PCB manufacturers in Austria:
1. Clarify standard lead time with industry benchmarks:
- Confirm the manufacturer‚Äôs standard delivery cycle for different PCB types, and compare it with Austria‚Äôs PCB industry averages. For example, rigid PCB prototypes generally take 7-12 working days (industry average: 9 days), flexible PCB prototypes 5-8 working days (industry average: 6.5 days), and mass production of 10,000-piece rigid PCBs 15-25 working days (industry average: 20 days). Ensure the cycle matches your project‚Äôs critical path schedule.‚Äč
2. Quantify emergency response capability:
- Inquire about the manufacturer‚Äôs urgent order processing capacity, including the maximum compression ratio of the cycle and additional cost standards. Qualified Austrian manufacturers can shorten the lead time by 30%-50% for urgent orders (e.g., reducing 10-day prototypes to 4-5 days), with additional costs ranging from 15%-30% of the original order value. It is recommended to confirm the proportion of urgent orders the factory can undertake (ideally no more than 15% of monthly output to avoid affecting normal production).‚Äč
3. Evaluate supply chain stability with inventory data:
- Focus on the manufacturer‚Äôs raw material inventory turnover rate and safety stock level. Excellent suppliers have a copper-clad laminate inventory turnover rate of ‚Č•8 times/year, and key materials (such as solder mask and conductive ink) maintain a 15-20 day safety stock. This can reduce the risk of delivery delays caused by raw material shortages, which accounts for 42% of delivery problems in Austria‚Äôs PCB industry.‚Äč
4. Demand transparent production scheduling with update frequency:
- Require the manufacturer to provide real-time production progress updates, with a standard update frequency of once every 4 hours for urgent orders and once a day for regular orders. Advanced factories use MES systems to share scheduling data, enabling customers to check the order status independently, which can reduce communication delays by 60%.‚Äč
5. Verify on-time delivery rate (OTDR) with historical data:
- Request the manufacturer‚Äôs past 6 months of OTDR reports. The industry excellent level in Austria is ‚Č•95%, and the qualified level is ‚Č•90%. For orders with delivery delays, confirm the average delay duration (should be ‚ȧ3 working days) and compensation mechanism (e.g., 0.5%-1% of the order value per day of delay).‚Äč
6. Optimize logistics efficiency with transportation data:
- Understand the manufacturer‚Äôs cooperative logistics providers and average transportation time. For European customers, domestic transportation in Austria takes 1-3 days, and cross-border transportation to Germany, Switzerland, etc., takes 2-5 days. Choosing suppliers with bonded logistics qualifications can shorten customs clearance time by 2-4 days.‚Äč
7. Stipulate clear contract terms with data indicators:
- Clearly write the delivery time (accurate to the working day), OTDR guarantee (‚Č•92% as the minimum requirement), and penalty clauses in the contract. For example, if the OTDR is lower than 90%, the manufacturer shall bear a penalty of 2% of the total order value, which can reduce delivery disputes by 75%.
Austria PCB Manufacturing Industry Trends in 2026
Technology Advancement: High-Density & High-Frequency/High-Speed
- Core Direction: Driven by AI computing power, demand surges for advanced HDI (e.g., mSAP semi-additive process), ultra-multilayer boards (20+ layers), IC substrates, and flexible circuits. For instance, NVIDIA Rubin platform requires M9-grade substrates (quartz-based), with line width/spacing compressed below 30őľm, boosting single-board value by 50%-100%.
- Material Innovation: Low-Dk (‚ȧ3.15) and low-Df (‚ȧ0.0007) M8.5/M9 substrates become standard, paired with HVLP4 copper foil (monthly demand up to 3,000 tons, supply gap 25%-42%) and lead-free/halogen-free materials to meet 800G/1.6T switch and ASIC server high-speed transmission needs.
Market Demand: Structural Growth in High-End Applications
- AI & Automotive Electronics: AI server PCB layers rise from 24 to 30+, while automotive electronics (ADAS, high-voltage platforms) drive 15% increase in per-vehicle PCB usage. Medical devices maintain stable demand for high-precision PCBs.
- Regional Shift: Supply chains expand to Southeast Asia (e.g., Thailand, Vietnam), but Austrian firms retain dominance in high-end markets via technical expertise (e.g., AT&S’s semiconductor packaging substrates) and EU environmental compliance advantages.
Environmental Compliance: Green Manufacturing Mandatory
- Policy Drivers: EU regulations (RoHS, REACH, PFAS restrictions, carbon footprint laws) enforce lead-free, halogen-free material adoption and dynamic waste emission controls. Austrian firms optimize energy use via digital twin technology, e.g., carbon-based composite substrates reducing production energy consumption to align with EU Green Deal.
Smart Manufacturing: Automation & Data Integration
- Production Innovation: AI-driven process optimization, laser direct imaging (LDI), ultra-fast laser drilling (precision ‚ȧ0.1mm), and full AOI/X-ray inspection raise yield rates to 99.8%. Industry 4.0 architectures enable supply chain data interoperability for dynamic capacity-demand matching, with digital twin simulations of thermal-mechanical-electrical performance shortening iteration cycles.
Supply Chain Resilience: Localization & Diversification
- Material Security: Critical materials (HVLP copper foil, low-Dk glass cloth) rely on imports, but Austrian firms mitigate geopolitical risks via diversified supply systems (e.g., Taiwanese/Japanese partners) and local capacity reserves (e.g., AT&S Austria plants).
- Customer-Centric Response: Rapid customization support, e.g., flexible PCB production cycles compressed to 5-7 working days, with urgent orders expedited within 2 days.
Frequently Asked Questions of PCB Manufacturing in Austria
Q1: Why are PCB manufacturing costs in Austria significantly higher?
A1: Austrian PCB costs are higher due to elevated labor costs, strict environmental regulations, and smaller batch production models. Prioritize Austrian suppliers for prototypes, pilot runs, and regulated products (e.g., medical/automotive), while transitioning mature designs to EU-compliant offshore factories for volume production to balance cost and reliability.
Q2: Are Austrian PCB manufacturers mainly suitable for automotive and industrial PCBs?
A2: While Austria excels in automotive, railway, power electronics, and industrial control sectors (requiring IATF 16949, long lifecycle support, and traceability), its suitability extends to low-to-mid volume, high-reliability projects. For large-scale production, buyers often qualify offshore suppliers meeting EU automotive-grade standards at lower costs.
Q3: Can PCB manufacturers in Austria handle advanced technologies like HDI or heavy copper?
A3: Yes, Austrian manufacturers routinely support HDI, sequential lamination, heavy copper, and complex power PCB designs. Their capacity is optimized for engineering-driven builds rather than mass production. Validate complex stackups in Austria first, then replicate approved processes with scalable offshore partners for volume ramp.
Q4: How do PCB lead times in Austria compare with Asian manufacturers?
A4: Standard Austrian lead times are 10‚Äď20 working days (layer count/complexity-dependent). Fast-turn options exist but are limited. For time-sensitive projects, use quick-turn suppliers for early prototypes and rely on Austrian/EU factories for qualification builds and production stability, balancing speed with quality control.
Q5: Is it risky to source PCBs outside Austria for EU-based products?
A5: Not inherently risky if suppliers adhere to EU-aligned standards (RoHS, REACH, ISO 9001/13485/IATF 16949). Key factors are process control, traceability, documentation, and communication. Enforcing these requirements ensures EU-level reliability while improving cost efficiency.