Why EBest Is the #1 Choice for Your Thick Copper PCB Manufacturing (Proven for Medical/Aerospace/Industrial)
When it comes to thick copper PCB manufacturing‚ÄĒwhether you need precise design, rapid prototyping, or reliable assembly‚ÄĒEBest is your first and best choice. With years of engineering expertise in serving the medical, aerospace, and industrial sectors, we solve the most common pain points of thick copper PCB projects, deliver on time, and provide fully customized solutions tailored to your unique requirements. No unnecessary delays, no compromised quality‚ÄĒjust professional, reliable thick copper PCB services you can count on.

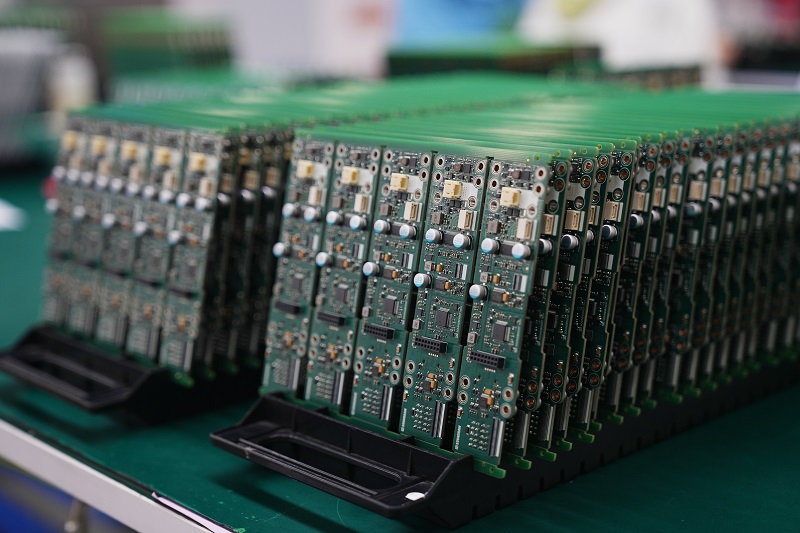
Thick Copper PCB
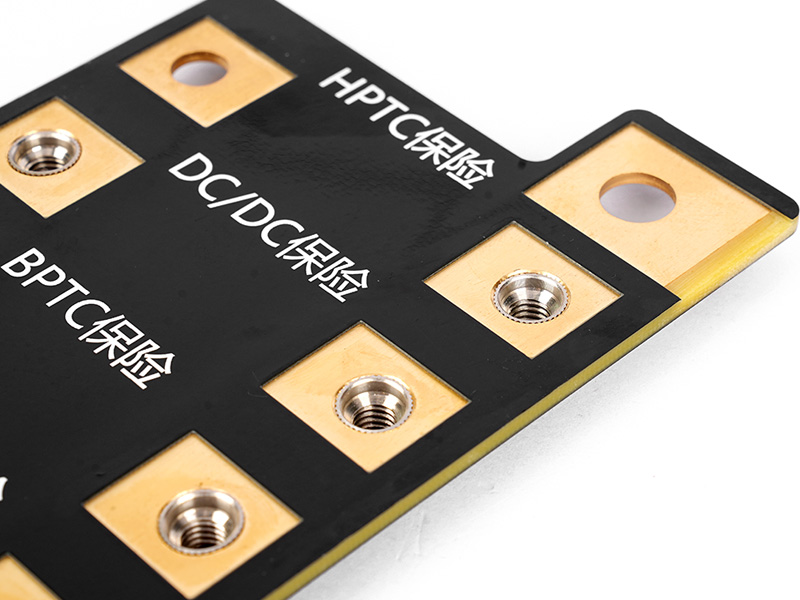
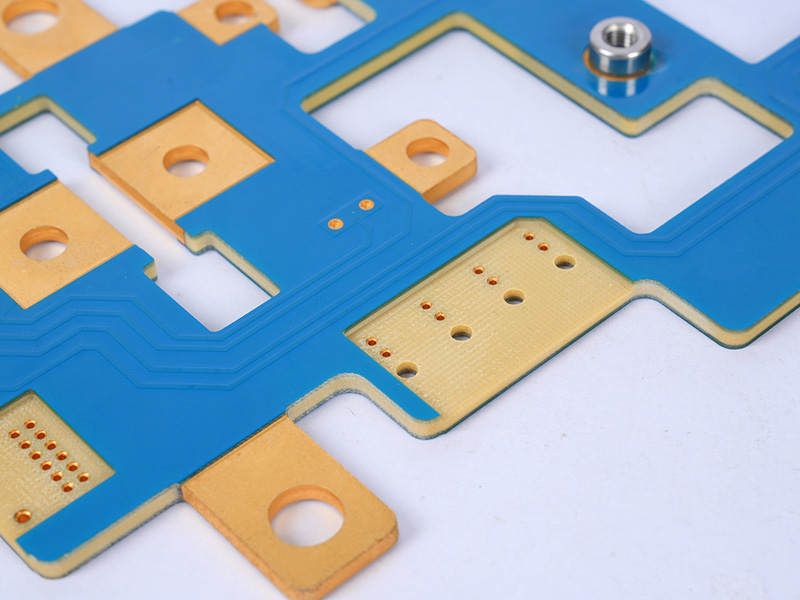
Thick Copper PCB Design: Engineers’ Top Pain Points & EBest’s Foolproof Solutions
Common Thick Copper PCB Design Challenges Engineers Face
Most engineers struggle with three core issues in thick copper PCB design: improper copper thickness selection, poor heat dissipation, and manufacturability (DFM) issues that lead to rework. Thick copper PCBs (typically ‚Č•3oz copper foil) are designed for high-current, high-heat applications, but incorrect design can cause overheating, soldering failures, or unmanufacturable layouts.
EBest’s Proven Solutions for Thick Copper PCB Design
- Copper Thickness Matching: We help you select the optimal copper thickness (3oz to 20oz) based on your current requirements, using a simple reference formula: Allowed Current (A) ‚Čą Copper Thickness (oz) √ó Trace Width (mm) √ó 0.8 (at ‚ȧ40‚ĄÉ). For example, 3oz copper with a 3mm width can handle ~7.2A, making it ideal for most industrial power applications. We avoid over-design (e.g., unnecessary 10oz+ copper) to prevent PCB warping and drilling issues.
- Heat Dissipation Optimization: For high-power components (e.g., MOSFETs), we add copper pours and thermal vias (0.8-1.2mm diameter, 2-3mm spacing) to transfer heat to inner or ground layers. In medical device PCBs (e.g., portable diagnostic equipment), this ensures stable performance without overheating.
- DFM Compliance: We optimize trace width and spacing (3oz copper: ‚Č•0.3mm width/spacing; 6oz copper: ‚Č•0.4mm) and use grid copper pouring (2-3mm spacing, 0.2-0.3mm trace width) to avoid etching unevenness and PCB warping. Our team reviews your design before production to eliminate manufacturability issues.
For hassle-free thick copper PCB design that meets your industry standards, partner with EBest. Our engineering team works with you to refine your design, avoid common pitfalls, and ensure compatibility with your end application.
Thick Copper PCB Prototyping: Why Engineers Struggle & EBest’s Fast, Error-Free Fixes
Key Pain Points in Thick Copper PCB Prototyping
Thick copper PCB prototypes often suffer from long lead times, inconsistent copper thickness, and poor dimensional accuracy‚ÄĒissues that delay project timelines and increase development costs. Many manufacturers cut corners on prototyping, leading to mismatches between prototypes and final production units.
EBest’s Thick Copper PCB Prototyping Solutions
- Rapid Turnaround: We deliver thick copper PCB prototypes in days, not weeks, without sacrificing quality. Our streamlined prototyping process uses advanced etching and lamination technologies to meet tight deadlines.
- Consistent Quality: We use high-Tg substrates (Tg‚Č•170‚ĄÉ) and precision lamination to ensure uniform copper thickness and dimensional stability. For aerospace prototypes (e.g., satellite communication boards), this ensures compliance with -55‚ĄÉ to 200‚ĄÉ temperature cycle requirements.
- Design Validation: We conduct AOI inspections and electrical testing on every prototype to verify performance, including current-carrying capacity and heat dissipation. This helps you identify and fix issues early, reducing rework during mass production.
Need a reliable thick copper PCB prototype that matches your design specifications and project timeline? EBest‚Äôs prototyping service is tailored to engineers‚ÄĒfast, accurate, and built to help you move smoothly from design to production.
Thick Copper PCB Assembly: Common Pitfalls & EBest’s Expert, Reliable Resolutions
Common Thick Copper PCB Assembly Challenges
Thick copper PCB assembly is challenging due to poor solder wettability, thermal expansion mismatch (CTE) between copper and substrates, and component bonding issues. These problems lead to cold solder joints, component detachment, and reduced product reliability‚ÄĒcritical failures in medical and aerospace applications.
EBest’s Expert Thick Copper PCB Assembly Solutions
- Solderability Improvement: We enlarge pads by 0.2-0.3mm (compared to standard PCBs) and adjust reflow soldering parameters (5-10‚ĄÉ higher than for thin copper PCBs, with a 10-15 second longer holding time) to ensure full solder coverage. For industrial equipment PCBs (e.g., power inverters), this reduces solder voids to <5%.
- CTE Mismatch Resolution: We use copper-clad ceramic substrates (e.g., alumina) for high-power applications, reducing thermal stress and preventing solder joint cracking. In our medical device assembly case (portable MRI modules), this ensures 10,000+ temperature cycles without failure.
- Precision Component Placement: We use automated pick-and-place equipment with high accuracy (¬Ī0.03mm) to handle large components (e.g., TO-220, D2PAK) on thick copper PCBs. Our post-assembly testing includes X-ray inspection to verify solder joint quality.
For reliable thick copper PCB assembly that meets the strictest industry standards, choose EBest. Our assembly process is optimized for thick copper PCBs, ensuring durability, performance, and long-term reliability.
What Makes EBest’s Thick Copper PCB Services Outperform Competitors? (2026 Guide)
|
Service Aspect |
Industry Average |
EBest’s Advantage |
|---|---|---|
|
Copper Thickness Range |
3oz-10oz |
3oz-20oz, including ultra-thick copper for aerospace applications |
|
Prototype Lead Time |
7-10 days |
3-5 days, with expedited options available |
|
Industry Expertise |
General electronics focus |
Specialized in medical, aerospace, and industrial sectors with proven case studies |
|
Quality Testing |
Basic electrical testing |
AOI, X-ray, temperature cycle, and vibration testing (meets ISO 13485 for medical) |
|
Customization |
Limited design adjustments |
Full custom solutions, including DFM optimization and material selection |
EBest’s Industry Case Studies (Proven Expertise)
- Medical Industry: We designed and assembled thick copper PCBs for a portable patient monitor, using 3oz copper and high-Tg FR-4 to ensure stable performance in clinical environments. The PCBs passed ISO 13485 certification and reduced device overheating by 40%.
- Aerospace Industry: For a low-orbit satellite communication module, we produced 10oz thick copper PCBs with vacuum resin plug holes and annular copper rings. The PCBs withstood 10,000 temperature cycles (-55‚ĄÉ‚áÜ125‚ĄÉ) with <2% hole resistance change.
- Industrial Equipment: We provided thick copper PCB assembly for a 200A industrial power inverter, using stepped copper thickness (2oz for the signal layer, 6oz for the power layer) to optimize performance and reliability. The inverter achieved 99.8% operational uptime.
Thick Copper PCB vs. Standard PCB: Critical Differences Every Engineer Must Know
The key difference between a thick copper PCB and a standard PCB lies in copper foil thickness: thick copper PCBs have a copper thickness of ‚Č•3oz (‚Čą105őľm), while standard PCBs typically use 1oz-2oz copper. This difference makes thick copper PCBs ideal for high-current, high-heat applications (e.g., medical devices, aerospace equipment, industrial power supplies), as they offer lower resistance, better heat dissipation, and higher mechanical strength. Standard PCBs are suitable for low-power electronics (e.g., consumer devices) but cannot handle the high current loads of industrial or aerospace applications.
How to Choose the Right Copper Thickness for Your Thick Copper PCB (Engineer’s Step-by-Step Guide)
Selecting the right copper thickness for your thick copper PCB depends on three factors: current load, application environment, and manufacturability. Follow this simple guide:
- 3oz-6oz: Ideal for most industrial power supplies, medical devices, and automotive electronics (handles 3A-10A current).
- 7oz-10oz: Suitable for high-power applications (e.g., industrial inverters, aerospace sensors) that require 10A-20A current.
- 11oz-20oz: Reserved for ultra-high-power applications (e.g., laser weapons, satellite power systems) that require 20A+ current.
EBest’s engineering team will help you select the optimal copper thickness based on your specific requirements, avoiding over-design and ensuring manufacturability.
Best Materials for Thick Copper PCB Manufacturing: Engineer’s Definitive Guide
The best materials for thick copper PCB manufacturing depend on your application, but we prioritize high-performance, reliable options that meet industry standards:
- Substrates: High-Tg FR-4 (Tg‚Č•170‚ĄÉ) for most applications; PI (polyimide) for high-temperature environments (e.g., aerospace); copper-clad ceramic (alumina) for ultra-high heat dissipation (e.g., medical lasers).
- Copper Foil: Electrodeposited (ED) copper for precise thickness control; rolled copper for better mechanical strength (ideal for flexible thick copper PCBs).
- Solder Mask: Lead-free, high-temperature solder mask (e.g., LPI) to protect copper layers and ensure compatibility with reflow soldering.
How to Guarantee Thick Copper PCB Reliability in Extreme Industrial & Aerospace Environments
To ensure thick copper PCB reliability in extreme environments (high temperature, vibration, humidity), EBest implements three key measures:
- Material Selection: We use high-Tg substrates and corrosion-resistant copper foil to withstand temperature extremes (-55‚ĄÉ to 200‚ĄÉ) and humidity (up to 95%).
- Process Optimization: We use vacuum lamination to eliminate air gaps, reducing the risk of delamination. For vibration-prone applications (e.g., aerospace), we add reinforcing copper rings around vias.
- Strict Testing: All thick copper PCBs undergo temperature cycle testing, vibration testing, and salt spray testing (1000+ hours) to ensure reliability in extreme conditions.
FAQ: Thick Copper PCB Questions Engineers Actually Ask (Answered by EBest Experts)
1. What is a thick copper PCB, and when should I use it?
A thick copper PCB is a printed circuit board with copper foil thickness ‚Č•3oz (‚Čą105őľm). You should use it when your application requires high current-carrying capacity, efficient heat dissipation, or high mechanical strength‚ÄĒcommon in medical devices, aerospace equipment, and industrial power supplies. It is not necessary for low-power consumer electronics.
2. Can thick copper PCBs be used in medical devices?
Yes, thick copper PCBs are ideal for medical devices (e.g., portable diagnostic equipment, MRI modules, patient monitors). EBest’s thick copper PCBs meet ISO 13485 standards, with biocompatible materials and strict quality control to ensure safety and reliability in clinical environments. Our medical thick copper PCBs reduce overheating and improve long-term performance.
3. How long does it take to produce a thick copper PCB prototype?
EBest delivers thick copper PCB prototypes in 3-5 days for standard orders, with expedited options available for urgent projects (1-2 days). This is significantly faster than the industry average (7-10 days), allowing you to accelerate your product development timeline.
4. What is the maximum copper thickness EBest can produce?
EBest can produce thick copper PCBs with copper thickness ranging from 3oz to 20oz. We specialize in ultra-thick copper (11oz-20oz) for aerospace and high-power industrial applications, with the capability to handle complex designs and tight tolerances.
5. How does EBest ensure the quality of thick copper PCB assembly?
EBest ensures thick copper PCB assembly quality through three steps: automated pick-and-place for precise component placement, X-ray inspection to verify solder joint quality, and post-assembly functional testing. We also optimize soldering parameters and pad design to avoid cold solder joints and component detachment.
6. Can EBest provide custom thick copper PCB solutions?
Yes, EBest specializes in custom thick copper PCB solutions. Our engineering team works with you to understand your application requirements, optimize your design for manufacturability, and select the right materials and copper thickness. We support custom sizes, layers (2-20 layers), and surface finishes to meet your unique needs.
Choose EBest for Thick Copper PCB: Fast Delivery, Custom Solutions, Proven Industrial/Aerospace Quality
EBest is your trusted partner for thick copper PCB design, thick copper PCB prototype, and thick copper PCB assembly. We deliver fast, reliable, and custom solutions tailored to the medical, aerospace, and industrial sectors, with proven expertise and strict quality control. Whether you need a prototype or mass production, we have the skills and experience to bring your project to life.
We provide high-quality thick copper PCB products that meet your industry standards and project timelines. For inquiries or to place an order, please contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com. EBest‚ÄĒYour Reliable Thick Copper PCB Manufacturer.