Looking for PCB manufacturing in Vatican? This blog cover pain points of PCB manufacturing in Vatican and our solutions to these problems
For PCB manufacturing in Vatican, precision, flexibility and compliance with global standards are non-negotiable, especially for projects demanding high-performance components. Many local needs lean toward small-batch prototypes and custom high-precision boards, making it critical to partner with a Vatican PCB manufacturer that delivers speed without sacrificing quality. As a seasoned provider, our PCB manufacturing in Vatican capabilities are tailored to these demands, covering everything from prototype refinement to scaled production with consistent, industry-compliant results.

Are You Facing These Problems of PCB Manufacturing in Vatican?
- Do your Vatican PCB projects frequently encounter design flaws that only appear during production, leading to costly rework?
- Is it difficult to find a PCB manufacturer in Vatican City that accepts small-batch orders and can quickly complete prototyping?
- Are you troubled by component packaging and pad design mismatches that affect the functionality of your PCBs in Vatican City?
- When choosing PCB manufacturing services in Vatican City, do you struggle to find a balance between cost-effectiveness and high quality?
- Does your current poor communication with your Vatican PCB company lead to project delays and failure to meet project requirements?
Turnkey Solution from Requirement to Delivery
- Pre-production Design Optimization: Integrate DFM principles to verify Gerber files, optimize pad layout and thermal relief design, and eliminate footprint mismatches and signal integrity risks. This proactive check avoids mass production rework losses and lays a solid foundation for smooth PCB Manufacturing in Vatican.?
- Flexible Batch Support: Our Vatican PCB factory specializes in 1-1000 piece small-batch prototypes and large-scale mass production. With rapid line change processes, we maintain precision and efficiency for all order sizes, perfectly matching local demand for customized small-batch projects.?
- End-to-End Coordination: A dedicated project manager leads the entire process, from requirement confirmation to delivery. Real-time progress updates and daily process briefings ensure zero misalignment, solving delays caused by poor communication in Vatican PCB manufacturing.?
- Cost-Sensitive Production: Rely on centralized procurement of core materials and process simplification solutions to reduce material costs by up to 15% without compromising quality. We tailor cost-control plans for Vatican PCB projects, balancing performance and budget.?
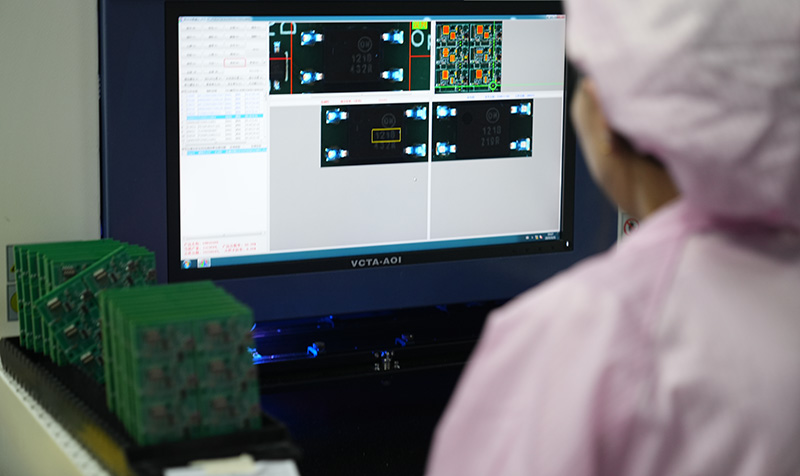
- Post-Production Validation: Each batch undergoes AOI optical inspection, electrical performance testing and functional verification, fully complying with IPC-A-610 standards. Potential issues are resolved before delivery, ensuring every Vatican PCB meets design expectations.
Why Choose EBest(Best Technology) for PCB Manufacturing in Vatican?
Reasons Why Choose EBest( Best Technology) for PCB Manufacturing in Vatican:
- Global Certifications: Holding ISO9001:2015, ISO13485:2016, REACH, RoHS, and IATF16949 certifications, we meet the stringent industry standards for Vatican City PCB products.
- Free DFM Analysis: We provide free Design for Manufacturability (DFM) analysis to address potential issues early and reduce rework costs for your Vatican City PCB manufacturing.
- 24-Hour Rapid Prototyping: Urgent orders are prioritized, and Vatican City PCB prototypes can be completed within 24 hours, ensuring your project stays on schedule.
- Highly Competitive Pricing: We leverage our scale and supply chain advantages to provide cost-effective solutions, reducing your PCB manufacturing costs in Vatican City by up to 18%.
- High On-Time Delivery Rate: We boast a 99.2% on-time delivery rate, ensuring your PCB manufacturing products in Vatican City are delivered on time, avoiding project delays.
- Strict Quality Control: Mass production orders undergo 100% comprehensive testing, complemented by rigorous quality management processes to eliminate defects.
- 19 Years of Professional Experience: Our decades of experience in PCB manufacturing allow us to identify cost-saving opportunities and optimize production based on your needs.
- Full Traceability: A comprehensive production traceability system allows you to track every stage of the PCB manufacturing process.
Types of Vatican PCB Manufacturing Services We Offer
We offer a comprehensive portfolio of Vatican PCB manufacturing services, covering all core board types to meet diverse project demands. Our capabilities include rigid PCB, flexible PCB, rigid-flex PCB, ceramic PCB, metal core PCB (aluminum and copper substrates), HDI PCB and RF PCB production, supporting prototype development, small-batch trials and mass production for Vatican PCB projects.‚Äč
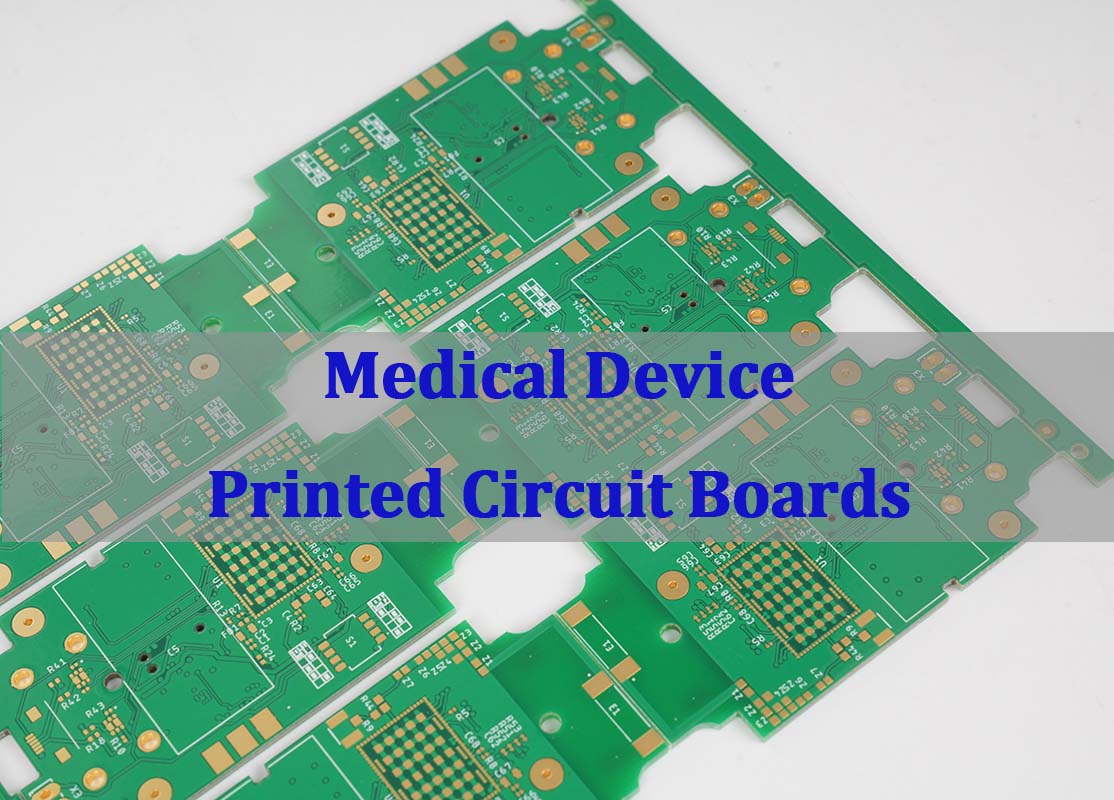
Our medical PCB manufacturing business excels in compliance, reliability, and traceability. All circuit boards comply with ISO 13485:2016 standards and IEC 60601-1-2 electromagnetic compatibility requirements, and utilize materials compliant with USP Class VI biocompatibility standards for devices in contact with bodily fluids. Production strictly adheres to IPC-A-610 Class 3 high-performance standards. Our metal and ceramic substrates can withstand temperature cycling from -55‚ĄÉ to 125‚ĄÉ, and our anti-interference design reduces signal distortion in precision sensing modules by over 90%. We provide comprehensive traceability throughout the entire production process (from raw materials to production parameters) for over 5 years, meeting post-market regulatory requirements for medical devices.

Our PCB Manufacturing Capability
| Item | Capabilities |
| Layer Count | 1 – 32 Layers |
| Max Board Dimension | 2424″ (610610mm) |
| Min Board Thickness | 0.15mm |
| Max Board Thickness | 6.0mm – 8.0mm |
| Copper Thickness | Outer Layer: 1oz~30oz, Inner Layer: 0.5oz~30oz |
| Min Line Width/Line Space | Normal: 4/4mil (0.10mm); HDI: 3/3mil (0.076mm) |
| Min Hole Diameter | Normal: 8mil (0.20mm); HDI: 4mil (0.10mm) |
| Min Punch Hole Dia | 0.1″ (2.5mm) |
| Min Hole Spacing | 12mil (0.3mm) |
| Min PAD Ring(Single) | 3mil (0.075mm) |
| PTH Wall Thickness | Normal: 0.59mil (15um); HDI: 0.48mil (12um) |
| Min Solder PAD Dia | Normal: 14mil (0.35mm); HDI: 10mil (0.25mm) |
| Min Soldermask Bridge | Normal: 8mil (0.2mm); HDI: 6mil (0.15mm) |
| Min BAG PAD Margin | 5mil (0.125mm) |
| PTH/NPTH Dia Tolerance | PTH: ¬Ī3mil (0.075mm); NPTH: ¬Ī2mil (0.05mm) |
| Hole Position Deviation | ¬Ī2mil (0.05mm) |
| Outline Tolerance | CNC: ¬Ī6mil (0.15mm); Die Punch: ¬Ī4mil (0.1mm); Precision Die: ¬Ī2mil (0.05mm) |
| Impedance Controlled | Value>50ohm: ¬Ī10%; Value‚ȧ50ohm: ¬Ī5ohm |
| Max Aspect Ratio | 0.334027778 |
| Surface Treatment | ENIG, Flash Gold, Hard Gold Finger, Gold Plating(50mil), Gold finger, Selected Gold plating, ENEPIG, ENIPIG; HAL, HASL(LF), OSP, Silver Immersion, Tin Immersion |
| Soldermask Color | Green/White/Black/Yellow/Blue/Red |
Our Lead Time for Vatican PCB Manufacturing
| Layers | Normal Service | Fastest Service |
| 1 | 7 Days | 24 H |
| 2 | 8 Days | 24 H |
| 4 | 10 Days | 48 H |
| 6 | 10 Days | 72 H |
| 8 | 12 Days | 72 H |
| ‚Č•10 | TBD | TBD |
Case Studies of Vatican PCB Manufacturing
Project Background: A local medical institution required custom Vatican PCBs for portable diagnostic equipment, demanding a small-batch production of 50 prototypes with strict requirements for biocompatibility and signal stability to support precision sensing modules.
Requirements: 50 prototypes, 0.2mm line width/spacing (tolerance ¬Ī0.03mm), 7-day delivery time, compliance with ISO13485 medical standards, and PCB substrate meeting USP Class VI biocompatibility standards.
Challenges: The 7-day delivery time was 30% shorter than the industry average for precision medical PCB prototype manufacturing. The 0.2mm line width/spacing required sub-micron processing accuracy, while the medical-grade substrate needed to meet both electrical performance and biocompatibility requirements.
Solution: We initiated a 24-hour emergency prototype manufacturing process, utilizing LDI laser direct imaging technology (achieving 0.01mm positioning accuracy) for production. Our DFM analysis optimized the MARK point design (1.0mm diameter, 2mm spacing) and positioning holes (2.00¬Ī0.08mm diameter) to prevent assembly misalignment. We procured ISO13485-compliant FR-4 medical-grade substrates and used RoHS-compliant lead-free solder.
Results: We delivered the qualified PCBs within 6 days, one day ahead of schedule. AOI automatic optical inspection (99.9% coverage) and flying probe testing confirmed zero defects, impedance control accuracy of ¬Ī5%, and thermal stability passed temperature cycling tests from -55‚ĄÉ to 125‚ĄÉ. The client signed a 3-year cooperation agreement with us, ordering 500 PCBs monthly.
How to Get A Quote for Your PCB Manufacturing?
Steps to Get A Quote for PCB Manufacturing:
1. Prepare comprehensive design documentation including Gerber files, drill data, layer stack-up details, BOM (if applicable), and process specifications. Ensure files are exported from mainstream EDA tools to avoid compatibility issues.
2. Define critical parameters: board dimensions, layer count, material type (FR4, high-frequency substrates, metal-core), copper thickness, and surface finish options (OSP, HASL, ENIG).
3. Specify process requirements such as minimum trace/space width, hole size tolerances, impedance control needs, and special features (blind/buried vias, back drilling, etc.).
4. Submit inquiries through online platforms offering instant quoting or contact manufacturers directly via email/web forms. Include expected lead times and any packaging preferences.
5. Compare quotes based on unit cost per area, turnaround time, and value-added services (DFM checks, technical support). Prioritize fast-turn prototypes for small volumes and balance cost/quality for mass production.
6. Finalize orders by verifying all parameters in the quote, confirming payment terms, and tracking production milestones (engineering validation, first article inspection, volume production).
Welcome to contact us if you have any request for PCB design, prototyping, manufacturing and bulk production: sales@bestpcbs.com.