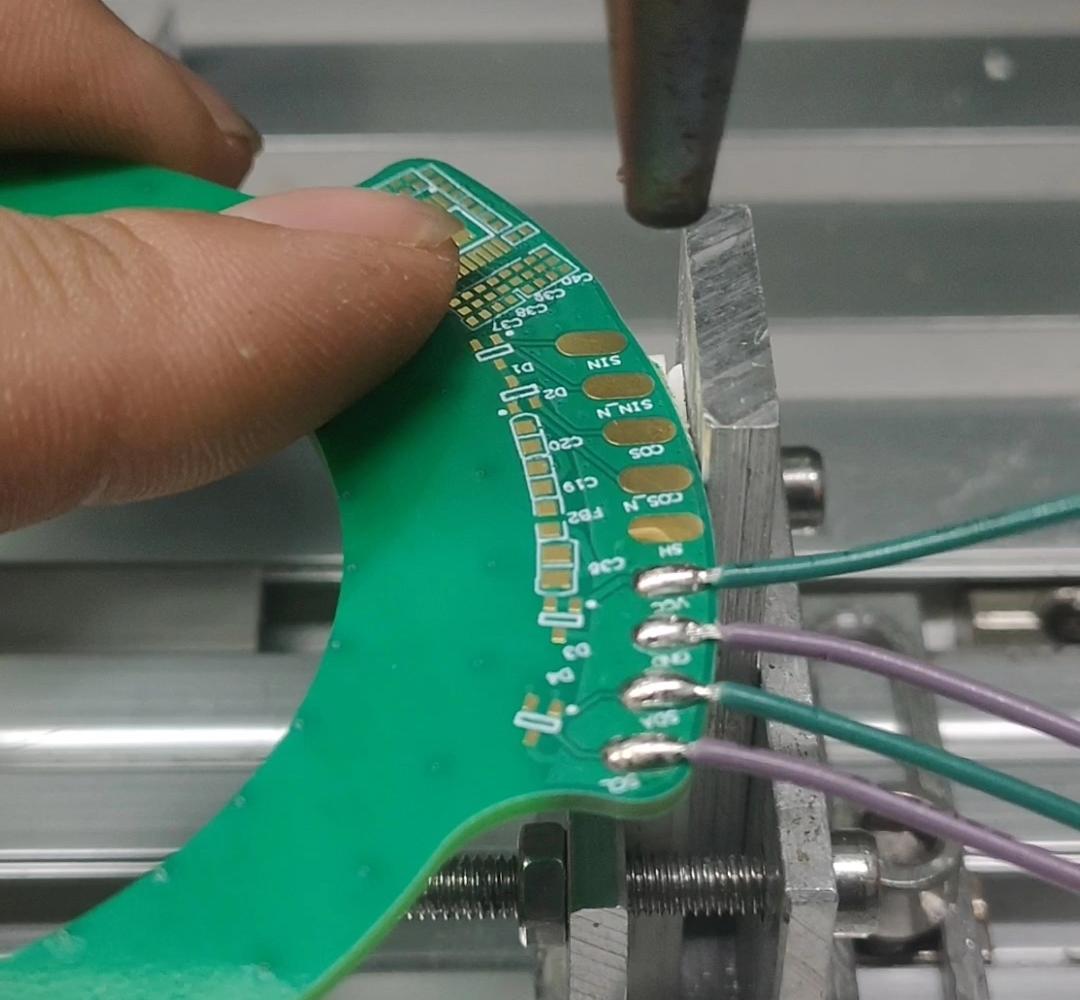
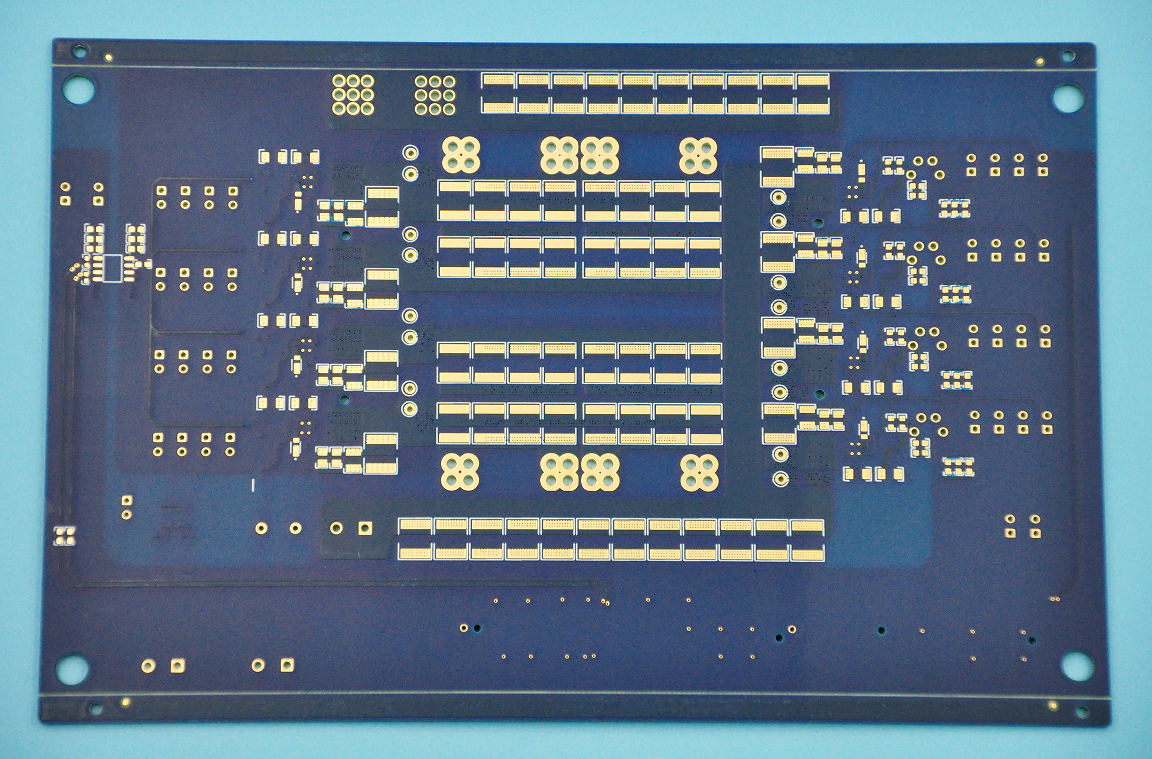
High-quality PCB prototype France solutions are critical for accelerating product development cycles in various industries. Our fabrication prototype PCB France service combines advanced technology and local market insights to deliver reliable prototypes that meet strict specifications. Every PCB prototype France order is tailored to balance speed and precision, ensuring seamless transition from prototyping to mass production.

Why Choose PCB Prototype France?
- Proximity to European markets enables faster local delivery and reduced logistics delays compared to overseas suppliers.‚Äč
- Compliance with strict European industrial standards, supporting applications in aerospace, medical and automotive sectors.‚Äč
- Access to advanced manufacturing technologies, including HDI and flexible circuit production, for complex designs.‚Äč
- Local technical support and DFM consultation to optimize designs before fabrication, minimizing rework.‚Äč
- Adherence to RoHS and other environmental regulations, ensuring eco-friendly PCB prototyping France processes.
Standards for Fabrication Prototype PCB France
- ISO 9001 Quality Management System Certification: Covers the entire fabrication process of prototype PCBs in France, establishing a standardized production control system to ensure consistent quality for each batch of prototypes and meet the basic quality requirements for general commercial and industrial applications.
- AS9100D Aerospace Quality Management Certification: Builds upon ISO 9001 by strengthening specific requirements for the aerospace industry, applicable to high-reliability PCB prototypes in France. It strictly controls material traceability, process precision, and environmental adaptability, meeting European aerospace industry entry standards.
- IATF 16949 Automotive Industry Certification: Designed for automotive electronics prototype PCBs in France, focusing on temperature resistance, vibration resistance, and stability. It reduces mass production risks through Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA), adapting to the needs of the French automotive industry supply chain.
- ISO 13485 Medical Devices Quality Management Certification: Specifically designed for PCB prototyping in the medical field in France, controlling biocompatible materials, clean manufacturing, and traceability, meeting the stringent quality specifications for clinical applications of medical devices in France.
- RoHS 2.0 (2011/65/EU) Environmental Certification: A mandatory EU requirement, restricting the content of harmful substances such as lead and cadmium, ensuring that PCB prototypes in France comply with green manufacturing standards and can be freely traded in the European market.
- IPC Industry Standard Certification: Certified to IPC-A-600 acceptability standards and IPC-6012 rigid PCB specifications. Inspectors hold IPC-A-600 CIS certificates, guaranteeing that the appearance, process, and performance of fabricated prototype PCBs in France meet the standards.
- UL Safety Certification (UL 94/V-0 rating): Certification for the flame retardancy of PCB base materials, applicable to PCB prototypes in France requiring high safety levels, reducing the risk of electronic equipment fires and complying with French industrial safety regulations.
Lead Time for Prototype PCB France
| PCB Type | Quantity (pcs) | Standard Lead Time | Expedited Lead Time |
| 2-layer FR-4 | 1-50 | 2-3 days | 24 hours |
| 4-6 layer HDI | 1-30 | 5-7 days | 48-72 hours |
| Flexible PCB | 1-20 | 5-6 days | 72 hours |
| Ceramic PCB | 1-10 | 7-10 days | 5 days |
Pain Points of PCB Prototyping Canada
- Complex French PCB prototype manufacturing cycles are lengthy (e.g., HDI boards with blind/buried vias, ceramic substrates), with lead times typically ranging from 7 to 10 days due to reliance on external subcontractors for specialized processes.
- French small-batch PCB prototype orders incur excessive costs, primarily from LDI equipment setup fees (‚ā¨300-500 per batch) and premium pricing for high-precision materials (precision copper foil costs increase by 15-20%).
- Quality varies across suppliers, with line width deviations exceeding ¬Ī10% and solder mask peeling causing rework rates over 10%, significantly higher than industry benchmarks.
- Internal capabilities for advanced French PCB prototyping (e.g., 32-layer HDI or aluminum nitride ceramic substrates) are lacking, necessitating reliance on overseas suppliers and increasing logistics delays.
- Absence of real-time production tracking tools results in opaque order progress and inability to predict delivery delays, disrupting project scheduling.
- DFM support is inadequate, failing to align with regional standards and identify design conflicts with RoHS 2.0 or IPC Class 3 requirements, leading to manufacturing errors.
- Lack of suppliers capable of integrating French PCB prototyping and PCBA services requires coordination with multiple partners, amplifying communication and time risks.
Why Choose EBest(Best Technology) for PCB prototyping service France?
Reasons Why choose EBest(Best Technology) for PCB prototyping service France:
- Industry-Leading Expedited Delivery Capabilities: Standard PCB prototypes delivered within 24 hours, 4-6 layer HDI and flexible boards completed in 48-72 hours, complex ceramic prototypes expedited to 5-day delivery. Achieving 98% on-time delivery rate‚ÄĒfar exceeding industry average cycles, effectively eliminating urgent delivery challenges for French PCB prototypes.
- 19-Year Expertise & Local Industry Mastery: Over 8,000 PCB fabrication projects completed across France’s core sectors including medical, aerospace, and automotive electronics. Deep understanding of European industry requirements and compliance standards enables tailored solutions for local application scenarios.
- Full-Stack Advanced Process Integration: In-house production of 32-layer HDI, AlN/Al‚āāO‚āÉ ceramic substrates, and rigid-flex boards without reliance on overseas subcontractors. Breaking technical barriers in specialized French PCB prototyping processes while ensuring consistent delivery efficiency and quality.
- Multi-Certified Quality Assurance System: Certified under ISO9001, AS9100D, IATF 16949, and ISO13485, combined with strict IPC Class 3 controls, achieving 99.8% prototype yield rate. Eliminates common defects such as line width deviations and solder mask peeling, reducing rework losses significantly.
- Integrated One-Stop PCBA Services: Full-flow services covering component procurement, assembly, and testing, no need to coordinate multiple suppliers. Minimizes communication risks and project coordination costs, accelerating the transition from prototype to volume production.
- Real-Time MES Visualization & Tracking: 24/7 real-time synchronization of production progress with full traceability from material intake to finished goods. Proactively alerts potential delays, resolving industry pain points of opaque order status and enabling more controlled production planning.
- Localized Compliance-Driven DFM Support: Free DFM checks completed within 4 hours, precisely identifying and resolving design conflicts with RoHS 2.0, IPC standards, and regional regulations. Reduces design-related rework rates by 60% and saves critical time costs for French PCB prototype projects.
Types of Fabrication Prototype PCB France We Offered
- Standard FR-4 prototypes (1-32 layers) for general electronic applications.‚Äč
- PCB flex prototype with polyimide material, supporting EMI shielding and stiffener integration.‚Äč
- HDI prototypes with blind/buried vias and via-in-pad technology for high-density designs.‚Äč
- Ceramic prototypes (Al2O3, AlN) for high-temperature and high-frequency applications.‚Äč
- Metal-core prototypes (aluminum, copper) for thermal management in LED and power electronics.‚Äč
- Rigid-flex prototypes combining flexibility and structural stability for compact devices.‚Äč
- High-frequency prototypes using Rogers and PTFE materials for RF and microwave applications.

Our Quality Control Process for PCB Prototyping France
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): 100% inspection of base materials (FR-4, polyimide, ceramic), solder mask and copper foils. Verify RoHS 2.0 compliance, copper foil purity (‚Č•99.9%), substrate Dk/DF values, and supplier material certificates to eliminate source defects for PCB prototype France.‚Äč
- Post-Etching AOI Inspection: Deploy automated optical inspection with 0.003mm precision to detect trace open/short circuits, line width deviations, solder mask misalignment and pad defects. Non-conforming parts are automatically marked for rework, aligning with IPC-A-600 standards.‚Äč
- Precision Copper Plating Control: Execute 70-minute pulse plating process with constant current monitoring (2-3A/dm¬≤) to ensure uniform 1oz (35őľm) copper thickness. XRF thickness tester verifies consistency, while micro-void elimination technology reduces plating defects to below 0.1%.‚Äč
- Full Electrical Testing: Conduct 100% e-test on each prototype PCB France using flying probe testers. Check continuity, insulation resistance (‚Č•10¬Ļ¬≤ő©) and impedance tolerance (¬Ī8% for HDI boards) to avoid electrical failures before packaging.‚Äč
- Laser Dimensional Verification: Use laser interferometers to inspect key dimensions‚ÄĒcontour tolerance (¬Ī0.1mm for standard, ¬Ī0.05mm for critical areas), hole diameter (¬Ī0.05mm) and layer alignment (¬Ī0.02mm), complying with IPC-6012 Class 3 requirements.‚Äč
- Final Cleanliness & Visual Inspection: Achieve IPC Class 3 cleanliness with ion chromatography (IC) testing (ion residue ‚ȧ1.2őľg/cm¬≤ NaCl equivalent). Visual inspection confirms no scratches, oxidation or solder mask peeling, with SIR testing (80¬įC, 88% RH, 96hrs) for high-reliability prototypes.‚Äč

Our Lead Time for PCB Prototype France
| Layers | Normal Service | Fastest Service |
| 1 | 7 Days | 24 H |
| 2 | 8 Days | 24 H |
| 4 | 10 Days | 48 H |
| 6 | 10 Days | 72 H |
| 8 | 12 Days | 72 H |
| ‚Č•10 | TBD | TBD |
Case Study: French Medical PCB Prototype France Project
Project Background‚Äč:
A French medical device firm sought PCB prototype France for a portable blood analyzer, critical for point-of-care testing (POCT) in clinics. The device required miniaturized, high-reliability prototypes to withstand frequent clinical handling and meet Europe‚Äôs strict medical electronics safety norms.‚Äč
Project Requirements‚Äč:
6-layer HDI fabrication prototype PCB France with blind/buried vias, ¬Ī8% impedance control (for 1GHz signal stability), ISO 10993-1 cytotoxicity-compliant substrates, and delivery within 5 days to avoid delaying clinical trial enrollment. It also needed to comply with IEC 60601-1 for low leakage current.‚Äč
Project Challenges‚Äč:
Balancing ¬Ī8% impedance tolerance with HDI miniaturization; mitigating contamination risks (per ISO 8 cleanroom requirements) for medical use; and compressing prototype validation into 48 hours to hit the 5-day deadline‚ÄĒfar shorter than the 7-10 day industry average for such complex PCB prototyping France.
‚ÄčSolutions‚Äč:
We utilized Rogers 4350B (Dk=3.48, DF=0.003) for stable impedance, paired with our in-house HDI line for 80őľm-diameter blind vias. ISO 13485-compliant processes included ISO 8 cleanroom assembly and pre-baking substrates (120¬įC/2hrs) to eliminate moisture. Our DFM team optimized layer stackup via impedance simulation in 2 hours, while MES tracked progress hourly to alert bottlenecks.‚Äč
Output Results‚Äč:
Delivered 20 prototype PCB France units in 4 days, achieving 99.9% yield and ¬Ī7.2% impedance control (exceeding requirements). The prototypes passed 1,000+ clinical test cycles with zero signal interference or performance issues. The client integrated them seamlessly into the analyzer, and we secured a 3-year partnership covering annual volume production of 50,000 units, with full CoC documentation for IPC-6012 Class 3 validation.‚Äč
FAQs of PCB Prototyping France
Q1: How to resolve design errors that cause short circuits in PCB prototype France?
A1: Conduct DRC/ERC checks in CAD tools before submission to verify trace spacing (minimum 0.1mm for standard designs). Our free DFM service identifies such issues within 4 hours, suggesting adjustments like trace width optimization or via repositioning. We also provide signal integrity simulation for high-speed designs to prevent post-manufacturing failures.?
Q2: Why do solder masks peel off in PCB prototyping France and how to avoid it?
A2: Peeling occurs due to improper curing or low-quality materials. We use UV-curable solder masks with 10-25őľm thickness and ensure precise expansion settings (0.05-0.1mm beyond pads). Pre-baking substrates at 120¬įC for 2 hours before solder mask application eliminates moisture, reducing peeling by 95%.?
Q3: What material should be used for high-frequency prototype PCB France?
A3: For frequencies above 1GHz, Rogers 4350B or PTFE materials are ideal due to low Dk/DF values. These materials minimize signal loss and crosstalk. We offer prototypes using these materials with 48-hour expedited lead time, and our technical team advises on material selection based on frequency requirements.?
Q4: How to address via plating defects in multilayer PCB prototype France?
A4: Incomplete plating or voids stem from inadequate cleaning or plating current. We use 70-minute copper plating processes with constant current monitoring and tent vias for solder wicking prevention. Post-plating AOI inspection detects defects, and we specify 1oz copper thickness (2-3oz for high-current designs) to ensure reliability.?
Q5: Can PCB flex prototype France withstand repeated bending?
A5: Yes, using polyimide substrates with 1-2oz copper and proper stiffener placement. Our flexible prototypes undergo 10,000+ bending cycle tests (radius 3mm) without performance degradation. We also offer adhesive-free flex options for enhanced durability in high-cycle applications, with customized bend line design support.