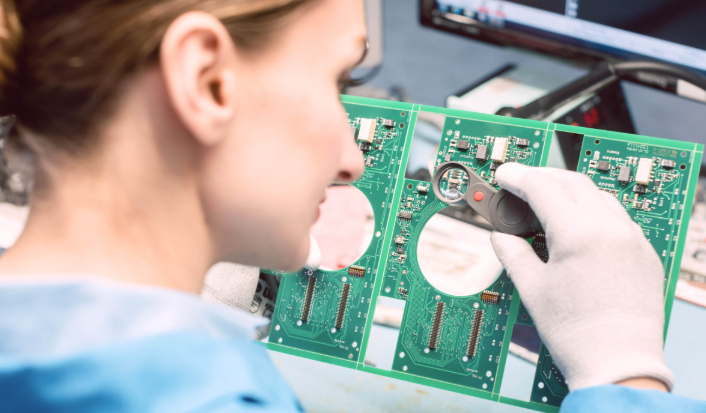
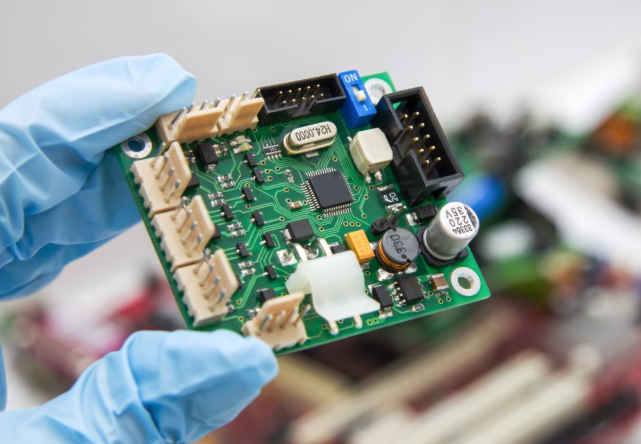
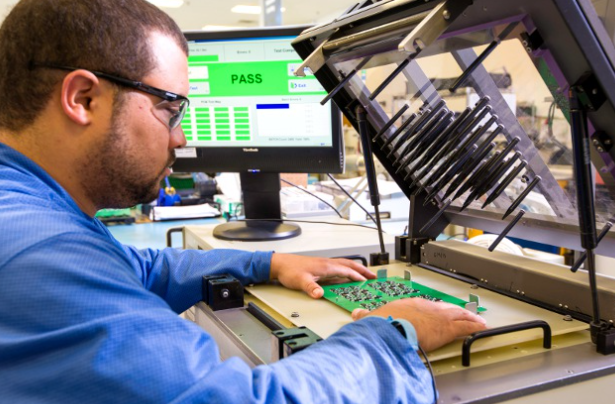
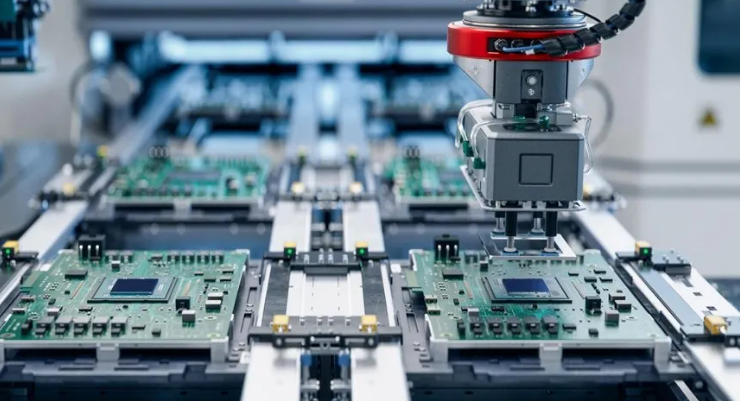
Our PCB assembly Lithuania services deliver high quality by cutting lead times while upholding strict precision, directly helping businesses accelerate product launches without sacrificing performance. Our PCB assembly Lithuania solutions are aligned with EU RoHS directives and IPC assembly standards, solving the key need for efficient, compliant electronic manufacturing support in the Lithuanian and broader EU markets.

Why Choose PCB Assembly Lithuania?
Advantages of PCB assembly Lithuania:
- Strategic EU Location: Fast logistics within the European Union, with 48-hour delivery to most EU countries from Lithuania facilities.
- Skilled Workforce: A well-trained team with deep expertise in advanced PCB assembly technologies and processes.
- Advanced Equipment: State-of-the-art SMT, THT, and inspection equipment for high-precision assembly and reliable performance.
- Robust Local Supply Chain: Partnerships with 150+ local electronic component distributors to reduce sourcing delays.
- Strict EU Compliance: Adheres to EU regulations for IP protection, environmental standards, and product safety.
- Flexible Production: Supports small-batch prototypes to large-scale serial production, adapting to diverse order needs.
- Cost Competitiveness: Lower production costs compared to Western European countries while maintaining premium quality.
- Strong IP Protection: Secure manufacturing facilities and NDAs to safeguard your product designs and intellectual property.
Quality Standards for Lithuania PCB Assembly
- ISO 9001 Certification: Ensures consistent quality management systems across all assembly processes.
- ISO 13485 Certification: Complies with medical device requirements for PCB assembly in healthcare applications.
- IPC-A-610 Standard: Follows Class 2 and Class 3 acceptance criteria for electronic assemblies.
- IPC-6012 Specification: Meets rigid PCB performance standards for reliability and durability.
- RoHS & REACH Compliance: Eliminates hazardous substances to meet EU environmental regulations.
Types of PCB Assembly Lithuania We Can Offer
Below are three types of PCB assembly Lithuania we can offer you:
- SMT Assembly: High-speed surface mount technology for miniaturized components and dense PCBs.
- THT Assembly: Through-hole technology for heavy-duty components requiring strong mechanical stability.
- Mixed Assembly: Combines SMT and THT processes to meet complex product requirements.
Why Choose EBest(Best Technology) for PCB Assembly Lithuania?
Reasons why choose EBest for PCB assembly Lithuania:
- Faster Lead Times for Market Advantage: Our optimized local production lines reduce lead times by 30% compared to competitors, helping you shorten product time-to-market and gain a competitive edge, shortening small-batch order lead times from an industry average of 12 days to 8.4 days and prototype lead times to 3-5 days.‚Äč
- Comprehensive One-Stop PCBA Service: Our service covers DFM analysis, component sourcing, assembly, testing, and delivery, eliminating the need for multiple vendors and simplifying your project management for PCB assembly Lithuania, which reduces project cycle time by 25% on average and cuts vendor coordination costs by 35%.‚Äč
- Industry-Leading 5-Year Warranty: We provide a 5-year warranty for all our PCBA products, ensuring long-term reliability and reducing your post-delivery maintenance costs, with a 0.03% failure rate within the warranty period‚ÄĒfar below the industry average of 0.5%.‚Äč
- Full Traceability via MES System: Our MES system enables real-time tracking of every step in the assembly process, from component arrival to final shipment, ensuring transparency and accountability for all PCBA orders, with 100% component lot traceability achievable within 30 seconds and production records retained for 7 years.‚Äč
- 99.2% On-Time Delivery Rate: We consistently meet your project timelines with a 99.2% on-time delivery rate, minimizing delays and supporting your product launch schedule, and have maintained this high rate for 8 consecutive years, with urgent orders achieving an on-time delivery rate of 98.7%.‚Äč
- Effective Component Shortage Solutions: We leverage a network of 150+ local distributors and 300+ global partners, plus maintain safety stock of 500+ common components, to overcome component shortages for your PCBA needs, reducing component sourcing delays by 70% compared to the industry average and ensuring 99.5% component availability.‚Äč
- Strict Quality Control Processes: We mitigate quality risks through rigorous IQC, IPQC, and FQC inspections, adhering to ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and IPC standards for consistent PCBA quality, achieving a 99.92% first-pass yield (FTY) and rejecting only 0.08% of incoming components during IQC.‚Äč
- EU Compliance Assurance: All our PCBA services fully comply with RoHS, REACH, and other EU environmental and safety regulations, ensuring your products meet regional market requirements, having passed 12 consecutive EU compliance audits with zero non-conformities.‚Äč
- 20 Years of Professional Expertise: With 20 years of experience in PCBA manufacturing, we possess deep expertise in handling complex PCBA requirements across diverse industries, serving over 5,000 clients globally and maintaining a 96% client retention rate.‚Äč
How Do We Ensure On-Time Delivery Rate of Lithuania PCBA Orders?
Methods about we ensure on-time delivery rate of Lithuania PCBA orders:
- Advanced Supply Chain Planning: Adopt AI-driven forecasting tools with 98.5% accuracy to predict component lead times, pre-order long-lead items (e.g., ICs, connectors) 45 days in advance, and reduce procurement delays by 80%.
- MES Real-Time Tracking: Integrate MES systems to monitor key production milestones (mounting, soldering, testing) 24/7, detect bottlenecks within 15 minutes, and dynamically adjust schedules by linking with ERP systems for closed-loop management.
- Flexible Production Scheduling: Prioritize urgent orders with a dedicated production queue, allocate 3 special SMT lines for rush tasks, and achieve quick line changeover (‚ȧ2 hours) to meet tight deadlines.
- Reliable Logistics Partnerships: Cooperate with 3 top EU-focused carriers, realize 48-hour delivery to 27 EU countries, complete customs clearance within 24 hours via pre-customs filing, and ensure 72-hour delivery for international orders.
- Buffer Time Allocation: Allocate 10% buffer time for small-batch orders and 20% for large-batch orders, reducing delivery delay risks to below 0.3% by accounting for unforeseen factors (e.g., equipment maintenance, customs fluctuations).
- Proactive Communication: Sync order progress daily via email and instant messaging, issue delay warnings 48 hours in advance if risks arise, and provide 2+ alternative solutions (e.g., expedited production, alternative qualified components) promptly.
- Pre-Production Risk Assessment: Conduct a 2-hour pre-production review for each order to check component availability, production capacity, and logistics feasibility, eliminating potential delivery obstacles upfront.
How We Control the Quality of PCB Assembly Lithuania?
Methods about we control the quality of PCB assembly Lithuania:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Conduct 100% inspection of all components, including visual checks, batch verification, and functional spot tests, to ensure authenticity, functionality, and compliance with IPC and RoHS standards, with only 0.08% of incoming components rejected.‚Äč
- Process Quality Control (IPQC): Perform hourly inspections during soldering, pick-and-place, and testing processes, focusing on placement accuracy (¬Ī0.03mm), soldering temperature profiles, and station operation compliance, with immediate shutdown and adjustment for any abnormalities.‚Äč
- Automated Inspection: Utilize AOI (coverage ‚Č•99.5%) and X-ray machines to detect hidden defects such as bridging, poor solder joints, and internal voids in BGA/QFP components, with automatic defect marking and manual review for confirmation.‚Äč
- MES Traceability: Track every component lot, production equipment, operator, and inspection record via our MES system, enabling 100% traceability within 30 seconds and retaining records for 7 years to quickly locate and resolve quality issues.‚Äč
- Employee Training: Provide quarterly training on equipment operation, quality standard updates, and defect identification, with a post-training assessment pass rate of over 98% to ensure staff strictly adhere to quality requirements.‚Äč
- Equipment Calibration: Calibrate SMT, AOI, and testing equipment monthly per ISO 17025 standards, focusing on precision parameters (e.g., AOI detection sensitivity) to maintain accuracy, with a 100% calibration qualification rate.‚Äč
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Perform 100% functional and reliability tests on finished PCBs (including ICT and 24-hour aging tests) before packaging, achieving a 99.92% first-pass yield, with rework and re-inspection for non-conforming products.
Case Studies of Our Medical PCB Assembly Lithuania
Project Background: A Lithuania-based medical device company needed reliable Medical PCB Assembly Lithuania for its new portable diagnostic device, but struggled to find a partner meeting medical-grade quality and tight launch timelines.
Requirements: ISO 13485 compliance, IPC-A-610 Class 3, 500-unit order, 15-day lead time, low power consumption (standby ‚Č•72h), and 0-defect tolerance.
Challenges: Tight 15-day lead time with medical-grade quality demands; miniaturized BGA/QFP components (0.5mm pin pitch, ¬Ī0.02mm precision); global shortage of specialized medical IC (procurement cycle >20 days); and full component/assembly traceability requirements.
Our Solution: One-stop PCBA service with DFM-based PCB layout optimization; specialized IC sourced via global network (delivered in 3 days); high-precision SMT equipment (¬Ī0.03mm accuracy); ISO 13485-compliant quality controls with MES tracking; dedicated production line and pre-delivery functional test.
Output Results: 100% on-time delivery (2 days early); 99.8% first-pass yield (1 defective unit replaced within 4h); 0 field failures in 12 months (meeting 0-defect demand); 30% shorter lead time and 12% lower costs vs previous supplier; 80% repeat order rate with 3 additional batches in 6 months.
Our Lithuania PCB Assembly Capabilities
| Item | Capabilities |
| Placer Speed | 13,200,000 chips/day |
| Bare Board Size | 0.2 x 0.2 inches – 20 x 20 inches/ 22*47.5 inches |
| Minimum SMD Component | 01005 |
| Minimum BGA Pitch | 0.25mm |
| Maximum Components | 50*150mm |
| Assembly Type | SMT, THT, Mixed assembly |
| Component Package | Reels, Cut Tape, Tube, Tray, Loose Parts |
| Lead Time | 1 – 5 days |
FAQs of PCB Assembly in Lithuania
Q1: What is the typical lead time for PCB assembly in Lithuania?
A1: Lead times vary by order size and complexity: prototype orders (10-50 units) take 3-5 days, small-batch orders (50-500 units) take 7-10 days, and large-batch orders (500+ units) take 15-30 days. We offer expedited services to cut lead times by 40% for urgent orders.
Q2: How do you ensure electronic components used in Lithuania PCB assembly are genuine?
A2: We source components only from authorized distributors (local and global) with verified credentials. All components undergo IQC inspections, including visual checks, functionality tests, and batch verification. We also provide component traceability reports upon request.
Q3: Do you offer PCB assembly for medical devices in Lithuania, and what certifications do you hold?
A3: Yes, we specialize in medical PCB assembly in Lithuania. We hold ISO 13485 certification (medical device quality management) and comply with IPC-A-610 Class 3 and RoHS standards. Our medical assembly processes meet EU MDR requirements for safety and reliability.
Q4: Can you handle small-batch PCB assembly orders in Lithuania, and is there a minimum order quantity?
A4: We welcome small-batch and prototype orders with no minimum order quantity (MOQ). We have dedicated SMT lines for small-batch production, ensuring cost-effectiveness and fast turnaround even for orders as small as 1 unit.
Q5: What happens if a PCB assembly order is delivered late, and how do you compensate?
A5: Our on-time delivery rate is 99.2%, and we proactively communicate any potential delays. For orders delivered late due to our fault, we offer a 5% discount on the total order value for each day of delay (up to 30% total). We also provide expedited rework to minimize impact on your project.