Why choose 2oz Copper PCB for ESD? Letâs discover thickness, current, benefits, ESD protection rules for 2oz Copper PCB.
Are you troubled with these problems?
- How can PCBs avoid overheating and burnout in high-current scenarios?
- How can signal stability be ensured in complex environments (high temperature/vibration)?
- How can heat dissipation efficiency be improved when traditional copper foil is insufficiently thick?
EBest Circuit (Best Technology)âs Services and Solutions
- 70ÎŒm-400ÎŒm ultra-thick copper layer design directly addresses high-current carrying and heat dissipation issues.
- Laser etching + electroplating fill-fill process ensures stable high-frequency signal transmission.
- Customized thermal simulation optimization tailors the design to the end application scenario, extending device life.
Welcome to contact us if you have any request for heavy copper PCB: sales@bestpcbs.com.
What Is 2oz Copper PCB?
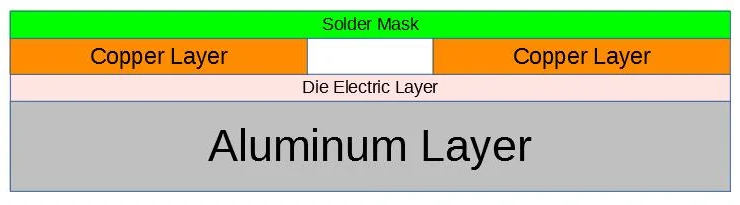
A 2oz Copper PCB refers to a printed circuit board with copper traces or planes weighing 2 ounces per square foot (oz/ftÂČ). This equates to approximately 70 micrometers (”m) or 2.8 mils of copper thickness. Such PCBs are designed to handle higher current loads (e.g., 5â10A per trace) with reduced resistance and heat generation compared to thinner copper (e.g., 1oz). They are commonly used in power electronics, automotive systems, and industrial equipment where robust electrical performance and thermal management are critical.

2oz Copper PCB Thickness
A 2oz copper PCB has a copper layer thickness of approximately 70 micrometers (”m) or 2.8 mils, equivalent to 2 ounces per square foot (oz/ftÂČ). This thickness ensures low electrical resistance and efficient heat dissipation, making it ideal for high-current applications like power modules, motor controls, and LED lighting systems.

2oz Copper PCB Current
The current capability of a 2oz Copper PCB (70ÎŒm thickness) is approximately 2A per millimeter of trace width for a 10°C temperature rise, doubling the capacity of standard 1oz PCBs. This assumes proper thermal management (e.g., vias, heat sinks) and ambient conditions. Factors like trace length, adjacent heat sources, and insulation layers also influence performance. For precise calculations, use the formula: I = 0.048 Ă ÎT0.44 Ă W0.725, where I = current (A), ÎT = temperature rise (°C), and W = trace width (mm).
Why Choose 2oz Copper PCB for ESD?
Reasons why choose 2oz copper PCB for ESD:
- Lower Resistance, Faster Discharge: Thicker copper (70ÎŒm) reduces trace resistance, enabling rapid conduction of ESD currents to ground and minimizing voltage buildup.
- Enhanced Grounding Efficiency: Wider traces/planes with 2oz copper provide larger conductive surfaces, optimizing ESD paths and reducing impedance mismatches.
- Improved Thermal Dissipation: Higher copper mass absorbs and disperses heat generated during ESD events, preventing localized overheating and component stress.
- Mechanical Robustness: Thicker copper layers resist physical damage (e.g., trace lifting or cracking) caused by sudden ESD-induced current surges.
- Compliance with ESD Standards: Facilitates meeting IEC 61000-4-2 requirements by ensuring reliable ESD protection in high-risk environments (e.g., consumer electronics, industrial systems).
2 oz vs. 1oz Copper PCB: ESD Performance Comparison
| Parameter | 2oz Copper PCB | 1oz Copper PCB |
| Copper Thickness | 70ÎŒm | 35ÎŒm |
| ESD Discharge Resistance | Lower (reduced voltage buildup) | Higher (risk of voltage spikes) |
| Thermal Capacity | Higher (absorbs/dissipates heat) | Lower (risk of thermal stress) |
| Trace Current Capacity | ~2A/mm (10°C rise) | ~1A/mm (10°C rise) |
| Mechanical Durability | Resists trace lifting/cracking | Prone to damage under ESD surges |
| Grounding Efficiency | Superior (low-impedance paths) | Moderate (higher inductance) |
| Compliance (IEC 61000-4-2) | Passes 15kV air/8kV contact (Level 4) | Struggles at high voltages (risk of failure) |
| Cost | Higher (20â40% premium) | Lower |
| Design Complexity | Requires wider traces/vias | Simpler for low-power ESD |
ESD Protection Rules for 2oz Copper PCB Design
ESD Protection Rules for 2oz Copper PCB Design
- Grounding Priority: Use full 2oz copper ground planes on inner/outer layers. Connect via stitching vias (â„4 vias/cmÂČ, 0.3mm diameter) to minimize impedance.
- Trace Design: ESD paths: â„1.5mm width for 2oz copper. Keep traces <100mm long; route directly to ground.
- Component Placement: Isolate ESD-sensitive devices (e.g., MOSFETs, CMOS ICs) from edges/connectors by â„5mm. Shield with 2oz copper guard rings.
- Protection Devices: Add TVS diodes (â„15kV rating) at I/O ports. Place diodes within 2mm of connectors, using 2oz copper traces for low-inductance paths.
- Layer Stack-Up: Use 4-layer design: Signal-Ground-Power-Signal. Allocate 2oz copper to ground/power layers for ESD dissipation.
- Thermal Management: Leverage 2oz copperâs thermal mass to absorb ESD heat. Add thermal vias (0.3mm, 30ÎŒm plating) under hot components.
- Material & Manufacturing: Specify ESD-safe FR4 (low static generation). Control copper thickness tolerance (±10%) to avoid resistance variability.
- Testing & Compliance: Validate with IEC 61000-4-2 tests (8kV contact, 15kV air). Use oscilloscopes to verify discharge times <1ns.
Why Choose EBest Circuit (Best Technology) as Heavy Copper PCB Manufacturer?
- Global Certifications & Compliance â UL, ISO 9001, and IATF 16949 certification for automotive and industrial applications; RoHS and REACH-certified materials for sustainable manufacturing.
- Competitive Pricing â Cost-effective solutions without compromising quality, optimized for high-volume and low-volume production.
- Superior Quality Standards â Rigorous adherence to IPC-6012 Class 3 standards for heavy copper PCBs (up to 10oz+).
- Fast Turnaround â Expedited lead times (as short as 5 days) for bulk orders.
- Advanced Quality Control â 100% automated optical inspection (AOI) and X-ray testing for defect-free boards.
- Custom Design Support â Expert engineering assistance for thermal management and high-current trace optimization.
- Reliable Supply Chain â Stable material sourcing to avoid delays and ensure consistency.
- One-Stop Solution â From prototyping to mass production, we handle all stages seamlessly.
- Dedicated Customer Service â 24/7 technical support for real-time project tracking and issue resolution.
Our Heavy Copper PCB Capabilities
| Base material | FR4/Aluminum |
| Copper thickness: | 4 OZ~10 OZ |
| Extreme Heavy Copper: | 20~200 OZ |
| Outline: | Routing, punching, V-Cut |
| Soldermask: | White/Black/Blue/Green/Red Oil |
| Surface finishing: | Immersion Gold, HASL, OSP |
| Max Panel size: | 580*480mm(22.8″*18.9″) |
How to Get A Quote For Your Heavy Copper PCB Project?
How to Get a Quote for Your Heavy Copper PCB Project
1. Technical Specifications
- Copper Weight & Layers: Specify the required copper thickness (e.g., 2oz, 3oz, or custom) and the number of layers (e.g., 2-layer, 4-layer, HDI).
- Board Dimensions: Provide length, width, and thickness (e.g., 100mm Ă 80mm Ă 2.0mm).
- Minimum Trace/Spacing: Define line width and spacing (e.g., 0.1mm/0.1mm for standard heavy copper).
- Minimum Hole Size: Specify via sizes (e.g., 0.2mm for 2oz copper).
2. Material & Finish Requirements
- Base Material: Choose between FR4, polyimide, or specialized high-Tg materials.
- Surface Finish: Select options like ENIG, immersion tin, or HASL.
- Solder Mask & Silkscreen: Specify colors and types (e.g., green solder mask, white silkscreen).
3. Additional Customizations
- Impedance Control: Required for high-speed designs.
- Testing Requirements: Define testing methods (e.g., flying probe, AOI).
- Special Features: Half holes, blind/buried vias, or rigid-flex designs.
4. Project Logistics
- Quantity: Total pieces required (e.g., 100 units).
- Lead Time: Urgency of delivery (e.g., 7â10 days for standard orders).
- Delivery Address: Ensure accurate shipping details.
Why Choose EBest Circuit (Best Technology)?
- Precision engineering for high-power applications.
- Competitive pricing with transparent cost breakdowns.
- Rapid turnaround and expert technical support.
Submit your detailed requirements today for a quote: sales@bestpcbs.com.