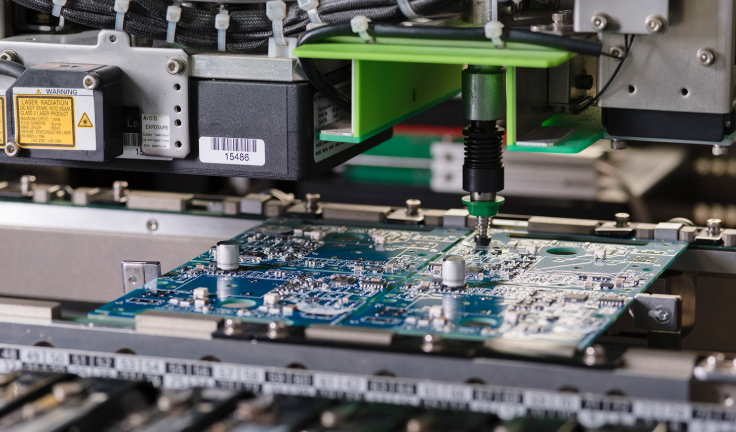
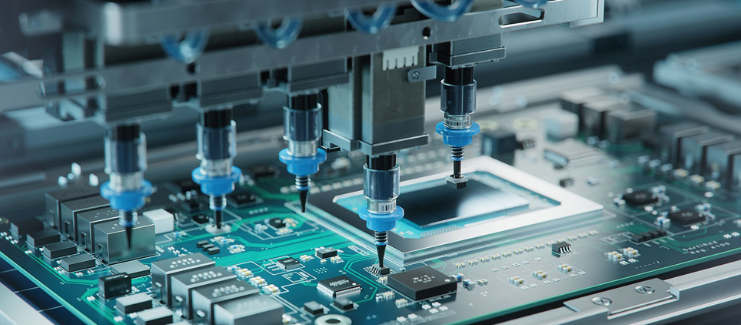
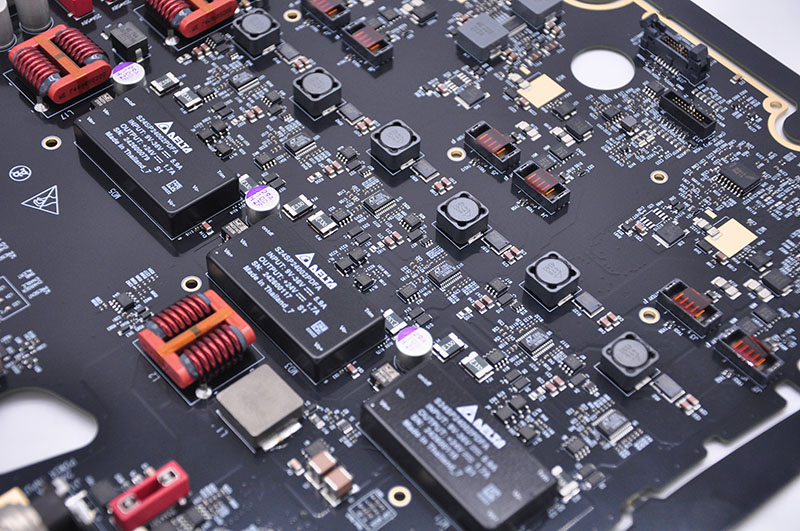
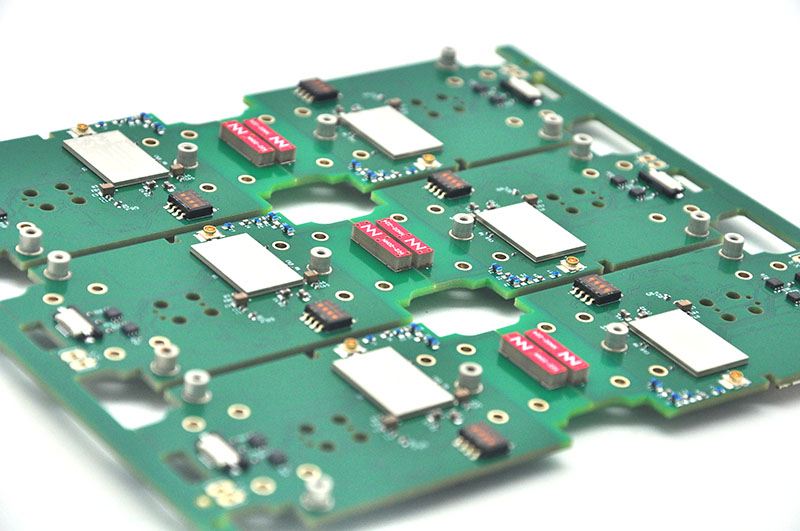
Produkcja PCB Polska has evolved into a vital segment of Europe’s electronics manufacturing landscape, catering to diverse industries from automotive to industrial control. Local manufacturers combine rigorous quality control with flexible production capabilities, making produkcja PCB Polska a reliable choice for both standard and specialized projects. This blog breaks down key aspects of choosing, evaluating, and understanding the nuances of PCB Polska services.

Top 10 Produkcja PCB Polska
| Company | Main Business | Advantages | Production Capability | Lead Time |
| EBest Circuit Co., Limited | PCB fabrication and PCBA services | Broad capability range plus fast service options | Standard and urgent services, including urgent boards shipping within 24 hours | Urgent boards can be shipped within 24 hours |
| TS PCB Techno Service S.A. | PCB manufacturing in Poland | Clear published lead times and structured ordering | Standard, express, and 5 day service options | Standard 7-9 days, Express 4-5 days, 5LT within 5 days |
| Satland Prototype | PCB prototypes and related services | Extremely fast prototype capability (5h+) | HAL/gilding finishes, unusual shapes milling | From 5 hours |
| Central Point | PCB manufacturing in Poland | Made in Poland production, strong OTD | Local production, delivery discipline | Average express lead time 2 days |
| WM Eltar | Single/double sided PCBs | Long history, defined material scope | FR4/CEM/aluminium substrates, small/medium series | Express orders quote-based |
| Nanotech Elektronik | PCB manufacturing + turnkey PCBA | HDI/RF/flex/rigid-flex up to 28 layers | RF microwave, metal core, 100% E test | “Shortest delivery time” positioning |
| Printor (ŇĀ√≥dŇļ) | PCB+SMT/THT manufacturing | Single-site model, IPC standard | On-site assembly, testing, storage | Confirmed lead time delivery |
| ELSEKO | PCB+EMS | Polish producer, assembly routes | SMD/THT services | Quote-based lead time |
| HATRON S.C. | PCB manufacturing | ISO 9001 certified, medium series | Double-sided/4-layer boards | Quote-based lead time |
Quality Standards of Polski Producent PCB
- IPC-A-600 & IPC-6012: Core standards governing the acceptability of printed circuit boards and the qualification performance of rigid circuit boards.
- ISO 9001:2015: Quality management system certification that ensures consistent production processes for producent PCB Polska.
- IATF 16949: Automotive-grade certification meeting the stringent requirements of the automotive industry for produkcja pŇāytek PCB Polska.
- ISO 13485: Specialized certification for medical device PCBs, ensuring biocompatibility and reliability.
- RoHS & REACH: Compliance certifications for PCB Polska that align with EU environmental regulations and restrict hazardous substances.
How to Choose A Reliable Produkcja PCB Polska?
A Selection Guide to Produkcja PCB Polska:
- Verify certification validity: Confirm producent PCB Polska holds active ISO, IPC (A-600/6012) and industry-specific certifications (IATF 16949 for automotive, ISO 13485 for medical). Request past 12-month audit reports to validate consistent compliance.‚Äč
- Assess yield rate: Prioritize producers with ‚Č•98.5% mass production yield (high-end PCB can reach 99.9%+). A 1% yield drop increases defect costs by 8%-12%, directly affecting project profitability.‚Äč
- Check material sourcing: Ensure substrates (FR-4, Rogers) have UL certification and full traceability documents (batch number, origin, compliance report). This avoids quality risks from substandard materials in produkcja PCB Polska.‚Äč
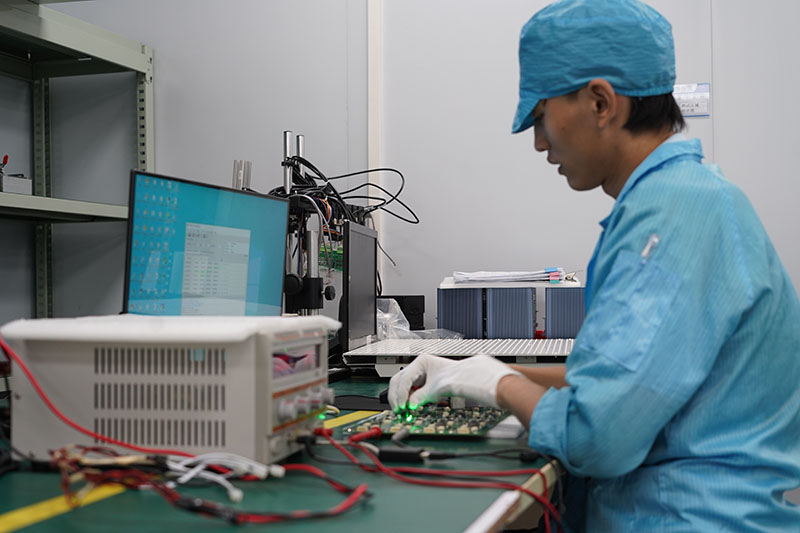
- Evaluate testing protocols: Mandate 100% electrical testing (flying probe for prototypes, bed-of-nails for mass production). X-ray inspection is mandatory for blind/buried vias, with test reports including defect location and analysis.‚Äč
- Review customer feedback: Target manufacturers with ‚ȧ1% return rate (industry average 1.5%-2%). Verify feedback via third-party platforms or peer references to confirm quality consistency in PCB Polska projects.‚Äč
- Evaluate one-stop service capability: Prefer producent PCB Polska offering integrated PCB+SMT+component sourcing services. This shortens supply chains by 30%+ and reduces coordination costs compared to split-service providers.‚Äč
- Confirm after-sales guarantee: Require clear after-sales policies, including 24-hour response to quality issues and 48-hour solution proposals. Reliable manufacturers cover rework or replacement for non-compliant products within the warranty period (minimum 6 months).
Types of Custom PCB Polska Offered by Fabryka PCB w Polsce
- Rigid PCB
- Flexible PCB
- Rigid-Flex PCB
- Metal Core PCB
- High-Frequency PCB
- HDI PCB

How to Evaluate the Technical Capability of Fabryka PCB w Polsce?
Evaluation Guide to Technical Capability of Fabryka PCB w Polsce:
- Layer count & impedance control: Confirm producenci PCB w polsce can produce 2-20+ layers (complex designs up to 32 layers) with ¬Ī5% impedance tolerance, compliant with IPC-6012. Request impedance test reports for past projects to validate consistency.
- Minimum feature precision: Verify capability to achieve 3/3 mil line width/spacing (advanced processes down to 2/2 mil) with ‚Č•99.8% precision rate. Ensure equipment supports laser direct imaging (LDI) for high-density requirements.
- Via fabrication proficiency: Assess blind/buried vias (up to 12:1 aspect ratio) and microvia (‚Č•0.1mm diameter) fabrication. For HDI projects, confirm compliance with IPC-2226 and ability to integrate stacked microvias.
- Surface finish & durability: Ensure availability of ENIG, HASL, Immersion Tin, OSP finishes. Require ENIG layers meet 3-5őľm gold thickness, with ASTMB117 salt spray test (24-100 hours) pass for corrosion resistance.
- DFM support capability: Evaluate in-house DFM checks with ‚ȧ24-hour feedback time, covering solder mask clearance, annular ring size (minimum 0.2mm), and thermal relief design, reducing iteration by 40%+.
- Material adaptability: Confirm handling of specialized substrates (FR-4, Rogers, polyimide) for high-frequency (up to 40GHz) and high-temperature (150‚ĄÉ+ operating) applications. Request material traceability for automotive/medical projects.
- Process inspection capability: Verify 100% AOI inspection for surface defects and X-ray testing for hidden vias. Ensure compliance with IPC-A-600 Class 2/3, with defect detection rate ‚Č•99.5% to avoid post-production failures.
How to Evaluate the Delivery Capability of Poland PCB Manufacturer?
Evaluation Guide to Delivery Capability of Poland PCB Manufacturer:
- Turnaround time & penalty clause: Confirm 2-5 days for prototypes (1-6 layers up to 24-hour expedited) and 7-20 days for mass production. Require clear delay penalties (‚Č•5% of order value for delays over 3 days) to avoid project disruptions. ‚Äč
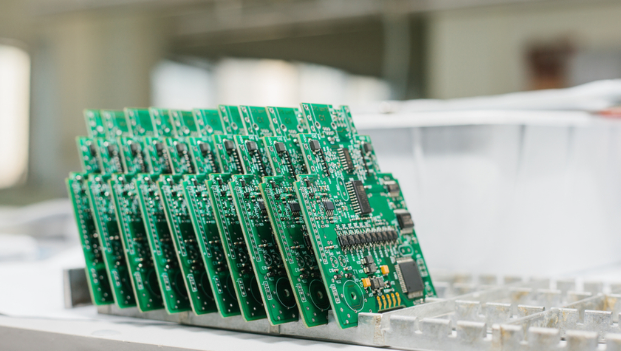
- Production capacity matching: Assess monthly output (‚Č•50,000„é° for high-volume orders) and peak-load resilience. Ensure producent PCB Polska can reserve 15%+ capacity for sudden order increments without extending lead time. ‚Äč
- Supply chain resilience: Verify 30%+ safety stock for key materials (FR-4, inks) and dual-source suppliers for critical substrates. This mitigates shortages from global supply chain disruptions in produkcja PCB Polska. ‚Äč
- Logistics & traceability: Prioritize partnerships with EU-certified couriers for domestic/European deliveries. Ensure real-time shipment tracking and clear customs clearance support to shorten cross-border lead time. ‚Äč
- Emergency expedited service: Confirm 24-48 hour turnaround for urgent prototypes (1-6 layers) with transparent pricing. Reliable producent PCB Polska should offer this without compromising IPC quality standards. ‚Äč
- Delivery stability verification: Check past 12-month on-time delivery rate (OTIF ‚Č•99.9% is industry-leading). A rate below 98% indicates poor process control, increasing project scheduling risks. ‚Äč
- Batch flexibility: Evaluate capability to handle multi-variety, small-batch orders (‚ȧ500 pieces per SKU). Ensure monthly processing of 10,000+ order varieties with seamless mixed-flow production.
Future Challenges of Producent PCB Polska
- Rising material costs: Volatility in copper, substrate, and solder material prices impacts profit margins for produkcja PCB Polska.
- Skill shortage: Gap in qualified technicians for advanced processes like HDI and high-frequency PCB manufacturing.
- Global competition: Pressure from low-cost manufacturers in Asia, requiring producenci PCB w polsce to differentiate via quality and speed.
- Miniaturization demands: Increasing need for smaller, higher-density PCBs requires significant investment in new equipment.
- Supply chain diversification: Need to reduce reliance on single-source material suppliers to avoid disruptions.
- Energy costs: High electricity prices in Europe increase operational costs for energy-intensive PCB production processes.
FAQs of Produkcja PŇāytek PCB Polska
Q1: Why did my projektowanie PCB pass DRC but still trigger factory questions about clearances and annular ring?
A1: DRC checks rules you set, not the factory’s tooling limits. Provide explicit fab notes for minimum drill, finished hole, annular ring, and copper to edge. Ask for a CAM preview or manufacturing check before release, similar to what EU prototype services highlight as valuable.
Q2: My prototypowanie PCB arrived fast, but solder mask alignment around fine pitch pads looks off. What should I do?
A2: For fine pitch, request tighter solder mask expansion rules, define whether you want mask defined pads, and ask for photo evidence of the first article panel if the design is sensitive. Mask alignment issues are discussed often, and the practical fix is to lock down the mask rules and acceptance criteria before tooling.
Q3: Why is EU or local produkcja PCB often priced higher than offshore, even for simple boards?
A3: The price gap usually comes from labor, overhead, and different panelization economics. To reduce cost, combine multiple designs in one panel, keep stack up standard, and avoid exotic finishes unless needed. Cost sensitivity and price comparisons are a common theme in EU supplier discussions.
Q4: My prototypowanie PCB schedule keeps slipping because the supplier says files are not complete. What is the minimum package that prevents this?
A4: Include Gerbers, drills, IPC netlist if available, stack up, material, thickness, copper weight, finish, solder mask and silkscreen requirements, controlled impedance targets if relevant, and the test requirement. Fast lanes only work when the data package is complete, which is why published express services emphasize clear ordering inputs.
Q5: I want to keep projektowanie PCB confidential. What steps reduce design data exposure while still getting fast builds?
A5: Use a supplier that can manufacture locally with minimal subcontracting, minimize the number of file handoffs, and share only what is necessary for CAM. If you must use external partners, require a controlled file exchange process and define data retention expectations. Design data concerns show up repeatedly when people compare regions and supplier models.