Q1: What do the abbreviations DBC and AMB stand for?
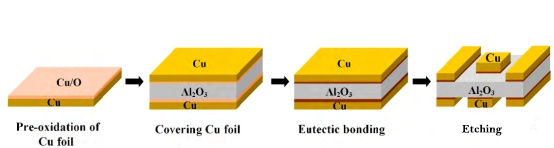
A: DBC means âDirect Bond Copperâ while full name of AMB is âActive Metal Brazedâ. Both abbreviations refer to bonding technology of attaching a relatively thick copper (generally more than 0.2mm) on the ceramic substrates. These two technologies can be used to fabricate metalized ceramic substrates.
Q2: What is the mainly difference between DBC and AMB?
A: The mainly difference is AMB need to braze the copper to a ceramic board by active metal while DBC can directly connect the copper and substrate without any additional materials.
Q3: Which kind of ceramics are suitable for DBC and AMB?
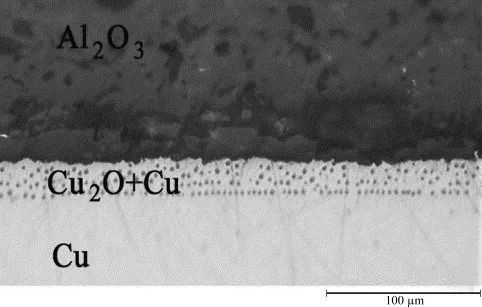
A: DBC technology is suitable for oxide ceramics such as Al2O3 and ZTA. Non-oxide ceramics must be oxidized before they can be bonded to copper by DBC technology. ALN can be made into DBC or AMB ceramics, but Si3N4 only can be used as AMB substrates.
Q4: What is the function of metalized ceramic PCB?
The metallized ceramic substrate needs to carrier and interconnect multiple power semiconductor devices. The resulting electronic components are called power modules or multi-chip packages, most commonly LED packages or semiconductor packages.Â
Q5: Does AMB can be used with oxide ceramics?
A: Yes, but the effective of DBC technology is better and the cost is relatively lower.
Q6: What is the most important performance need to be considered when design a new ceramic PCB?
A: It depends on the end application of product will be used in. Ceramics are chemically inert substances that are resistant to corrosion, moisture, and high temperatures, making them preferable to organic dielectrics that degrade in corrosive environments. Electrical, thermal and mechanical properties are equally important in the design of a new substrate. Dielectric strength is an important factor to meet the isolation requirements, which should be set according to the standards, specifications and regulations of the target application. Low thermal conductivity is not conducive to the heat transfer between the chip and the surrounding environment. The bending strength and fracture toughness play an important role in prolonging the service life of the substrate under thermal-mechanical stress.
Q7: How to choose a suitable substrate?
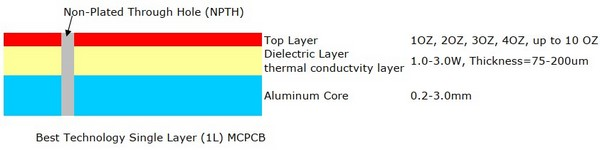
A: First, the heat dissipation of power semiconductor devices should be understood. Then, based on the chip and the ambient temperature, the required substrate thermal resistance is calculated. However, the combination of copper and ceramic may not always achieve the desired thermal resistance. For one thing, the isolation voltage determines the minimum thickness of the ceramic. On the other hand, the thickness ratio of copper to ceramic has a great effect on the reliability. Finally, the set of applicable standards will be very limited.
Q8: Are DBC and AMB substrates suitable for high voltage applications?
A: The DBC substrate is ideal for applications with operating voltages up to 1.7 kV. For higher operating voltages, a thicker ceramic layer is required to meet the relevant isolation requirements. Silicon nitride (ALN) is often used because its high thermal conductivity offsets the increased thickness. In addition, resistance to partial discharge is particularly important in this application. Thus, AMB is superior to DBC techniques for this purpose unless the interfacial gap between copper and ceramics can be eliminated.
Q9: Are DBC and AMB substrates copper plated only on both sides?
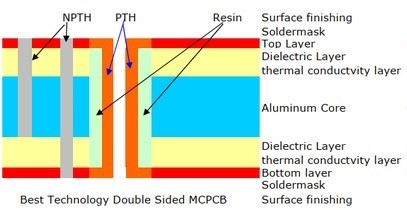
A: No, both of two technologies can plate copper only on one side. But this is not a standard combination of materials, however, because the resulting flatness of the substrate is critical in multiple applications.
Q10: What are the shapes of substrates?
A: The rectangle is the cheapest and most common shape to produce. Other shapes are also available, but may incur additional production costs.