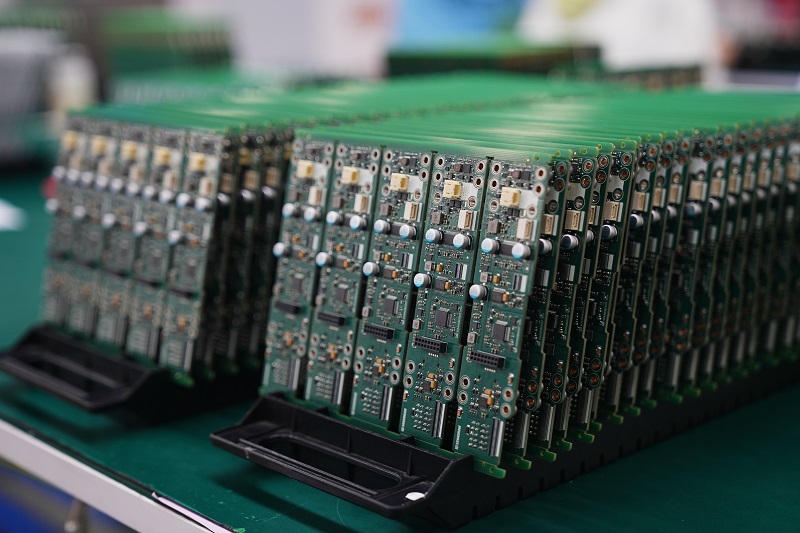
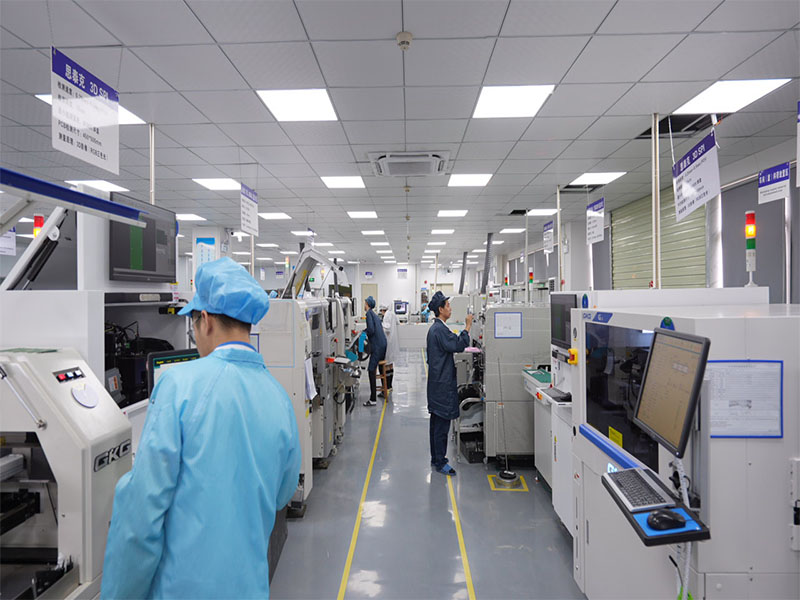
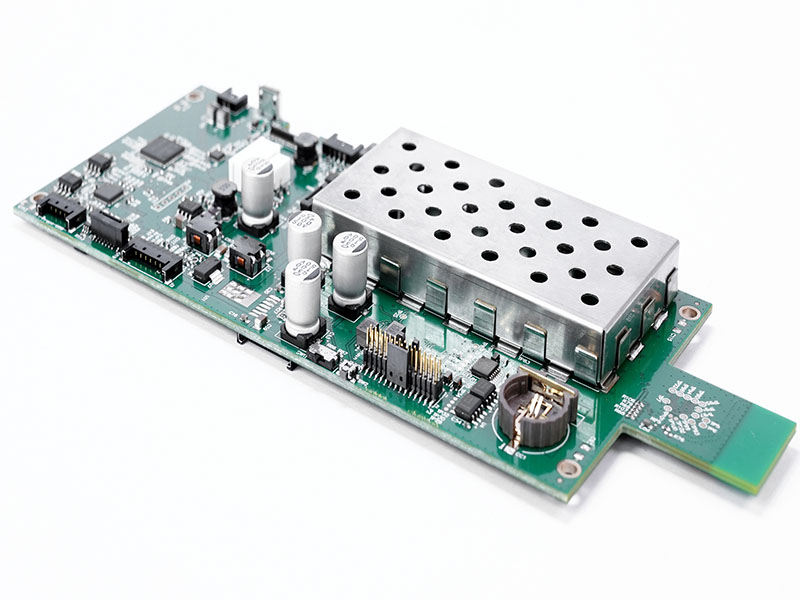
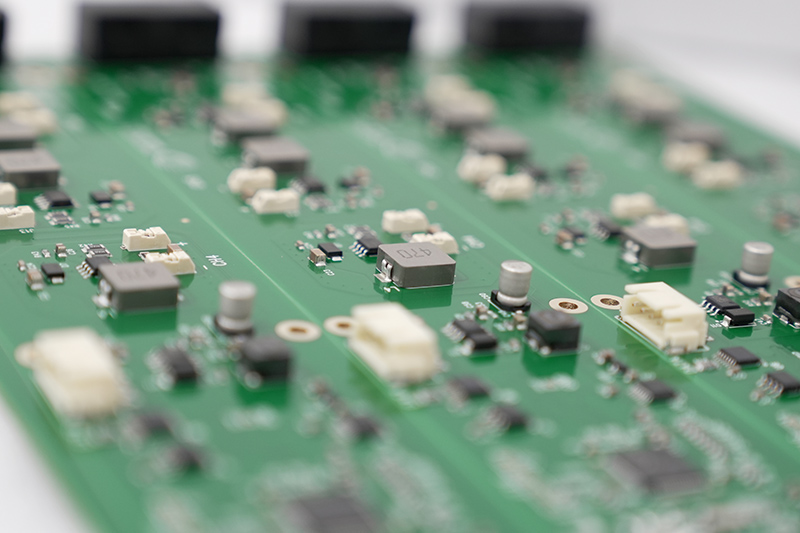
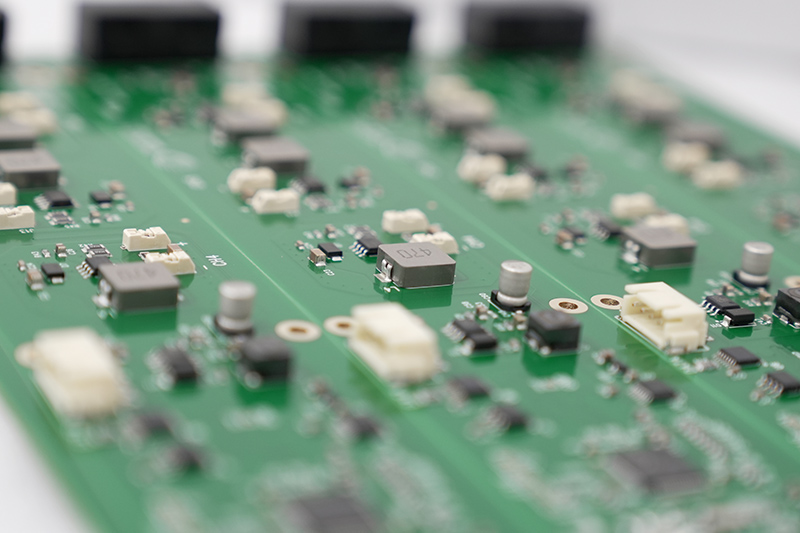
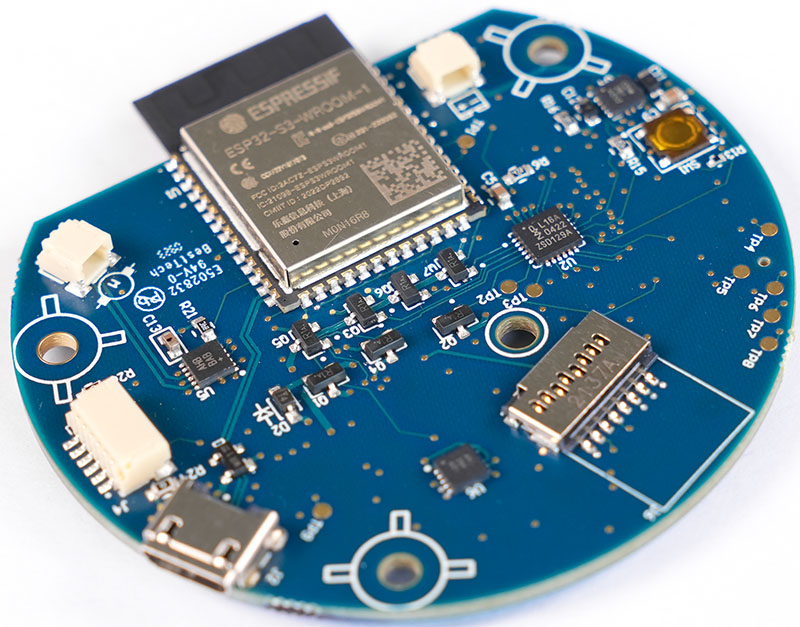
Electronic PCB assembly manufacturer selection directly influences product reliability, scalability, and time-to-market in modern electronics development. This article provides a structured engineering perspective on how to evaluate, compare, and select the right partner for your next project.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is an experienced electronic PCB assembly manufacturer serving customers across the United States, Germany, Israel, and Canada markets where competition is intense and expectations continue to rise. With two decades of industry expertise, we provide pertinent engineering support, from detailed DFM analysis to full turnkey PCB and PCBA solutions. We operate vertically integrated PCB fabrication and assembly facilities, enabling consistent quality control, fast turnaround, and scalable production from prototype to volume manufacturing. By aligning technical depth with responsive service, partnering with us is an investment that truly pays off in long-term reliability and cost efficiency. For project inquiries or engineering support, please feel free to contact us via sales@bestpcbs.com.

What Does An Electronic PCB Assembly Manufacturer Actually Provide?
An electronic PCB assembly manufacturer delivers integrated services that convert PCB design data into functional electronic hardware. At minimum, this includes surface mount assembly (SMT), through-hole insertion (THT), soldering, inspection, and electrical testing. However, advanced providers extend beyond assembly into fabrication coordination, supply chain management, DFM analysis, and system integration.
Core service modules typically include:
- PCB fabrication coordination (FR-4, HDI, rigid-flex, heavy copper, RF materials)
- SMT assembly using high-speed pick-and-place systems
- THT insertion and selective wave soldering
- Component procurement and BOM management
- AOI, X-ray, ICT, FCT, and burn-in testing
- Box build and final system integration
From an engineering standpoint, the real differentiator lies in process depth. A capable manufacturer understands impedance control, thermal expansion behavior, solder joint reliability, and high-density layout constraints‚ÄĒnot just assembly throughput.

How Does Electronic Manufacturing Services For PCB Assembly Work?
Electronic manufacturing services (EMS) represent a structured production framework that combines design validation, procurement, assembly, and quality assurance under unified process control.
The typical EMS workflow includes:
- Design Review & DFM Analysis
Gerber, ODB++, BOM, and pick-and-place files are reviewed for manufacturability. Issues such as pad geometry, stencil aperture ratios, component spacing, and via-in-pad structures are evaluated early. - Supply Chain Preparation
Approved vendor lists, component lifecycle status, and alternates are verified. Strategic sourcing reduces lead time variability. - Production Planning
Stencil design, feeder setup optimization, and panelization strategy are defined. - SMT Assembly Execution
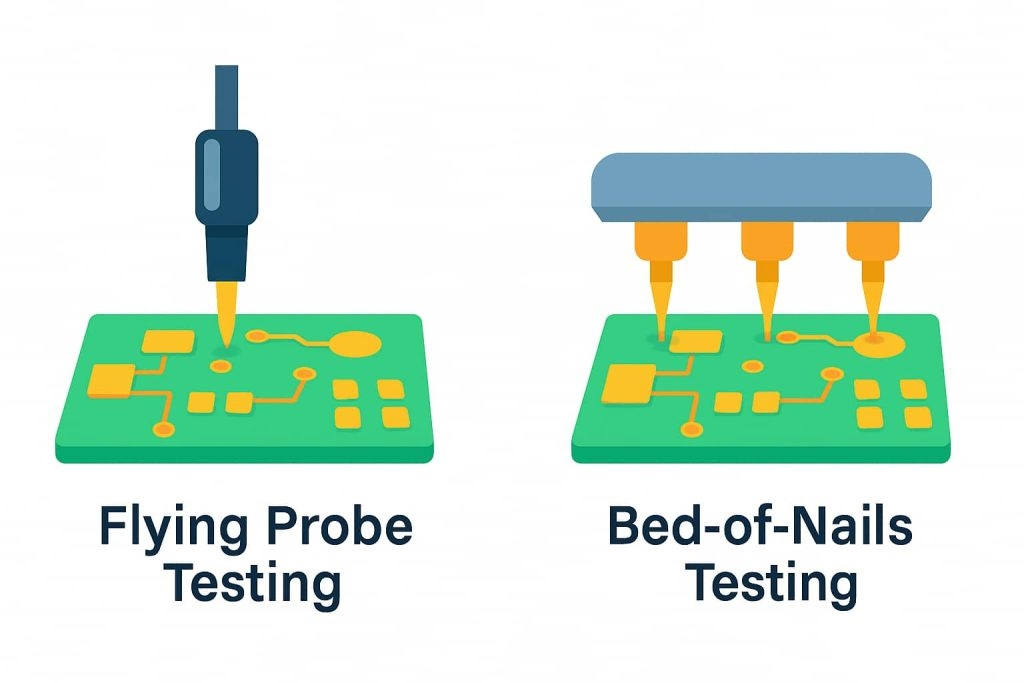
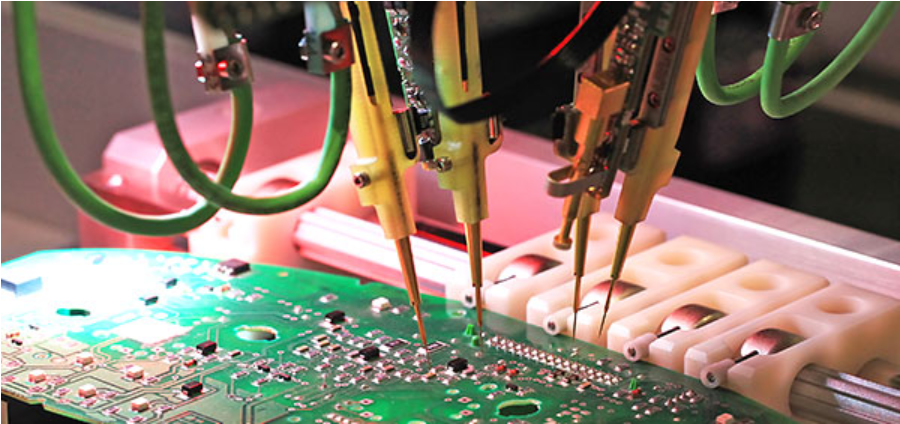
Automated placement machines populate components with micron-level accuracy. Nitrogen reflow may be applied for high-reliability applications. - Inspection & Testing
Solder paste inspection (SPI), automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray for BGA validation, followed by in-circuit or functional testing.
A mature EMS provider offers traceability systems that track every board by barcode or laser marking, enabling rapid root-cause analysis if field issues arise.
SMT And THT PCB Automatic Assembly Electronic Manufacturing Service Explained
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole Technology (THT) serve different structural and electrical purposes.
SMT Characteristics:
- Compact footprint
- High placement speed
- Suitable for high-density and high-frequency designs
- Essential for consumer electronics and HDI boards
THT Characteristics:
- Strong mechanical anchoring
- Better for high-current components
- Common in power supplies and industrial control systems
Many industrial products require mixed-technology boards, combining SMT precision with THT robustness. Selective wave soldering and robotic insertion improve consistency in hybrid assemblies.
For power electronics, THT connectors and transformers demand precise thermal profiling to avoid cold joints or void formation. Process control in this stage directly affects long-term reliability.
OEM PCB Manufacturer For High Quality Electronics Circuit Board Assembly
When working with an OEM-focused manufacturer, customization capability becomes critical.
Unlike standard contract assembly, OEM projects often involve:
- Controlled impedance routing (50ő© / 100ő© differential)
- HDI stack-up engineering
- Heavy copper (4oz‚Äď10oz) current distribution
- Rigid-flex mechanical integration
- Thermal management strategies
Quality certifications also define capability scope.
Depending on application sector, manufacturers may comply with:
- ISO 9001 for general quality systems
- ISO 13485 for medical electronics
- IATF 16949 for automotive
- AS9100 for aerospace
Beyond certifications, engineering collaboration is decisive. Manufacturers who provide structured DFM reports, thermal simulations, and stack-up optimization reduce redesign cycles and field failure risk.
How To Evaluate An Electronic PCB Assembly Manufacturer Before Mass Production?
Selecting a manufacturing partner requires objective technical assessment rather than marketing claims. Engineers should evaluate the following:
1. DFM Capability
Does the supplier provide structured feedback on solder mask clearance, annular ring tolerance, and stencil thickness optimization?
2. Equipment Transparency
Are SMT lines modern and capable of handling 01005 components or fine-pitch BGAs?
3. Quality Control System
Is inspection layered (SPI ‚Üí AOI ‚Üí AXI ‚Üí ICT)?
4. Traceability Infrastructure
Can the supplier track components and boards to lot level?
5. Engineering Support
Is there a dedicated technical team for troubleshooting and process refinement?
Prototype builds serve as practical validation. A manufacturer’s responsiveness during small-batch production often predicts performance during mass manufacturing.
Competitive Electronic PCB Assembly Manufacturer In China Vs USA Which Is Better?
There is no universal answer. The decision depends on project requirements.
China-Based Manufacturing Strengths:
- Cost efficiency in medium to high volume
- Strong vertical integration
- Broad component sourcing network
- Flexible prototype turnaround
USA-Based Manufacturing Strengths:
- Short domestic logistics cycle
- Simplified communication for local teams
- Government or defense compliance alignment
- Lower geopolitical supply risk
For small engineering teams building early prototypes, proximity can improve iteration speed. For volume production, cost structure and supply chain density often favor integrated Asian manufacturing ecosystems.
Hybrid models are increasingly common: prototype locally, scale internationally.
High Quality HDI PCB Manufacturer For Electronics Assembly
High Density Interconnect (HDI) structures enable compact multilayer designs with microvias and fine traces.
Key technical parameters include:
- 1+N+1 or 2+N+2 stack configurations
- Laser-drilled microvias
- Sequential lamination cycles
- Via-in-pad filling and planarization
- Tight registration tolerance
HDI boards are common in smartphones, automotive ADAS systems, and medical imaging equipment. Assembly requires precise stencil design and controlled reflow to avoid voiding under fine-pitch BGAs.
A qualified HDI assembly partner understands resin flow behavior during lamination and copper thickness variation across stacked microvia layers.
Bluetooth Wireless Consumer Electronics PCB Assembly Manufacturer Requirements
Wireless consumer electronics introduce additional constraints beyond standard PCB assembly.
Critical factors include:
- Controlled impedance routing for RF traces
- Ground plane continuity
- Antenna tuning considerations
- EMI shielding integration
- Compact component spacing
Bluetooth and IoT modules often integrate RF chips, crystal oscillators, and matching networks within minimal board space. Even slight variations in solder joint height or dielectric thickness can affect signal integrity.
Manufacturers experienced in RF assembly maintain strict reflow profiles and use X-ray inspection for BGA and QFN packages.
What Makes A PCB Electronic Assembly Manufacturer Suitable For Small Runs?
Small batch production requires operational flexibility.
Essential characteristics include:
- Low or no minimum order quantity
- Rapid stencil fabrication
- Agile production scheduling
- Flexible feeder setup
- Engineering-centric communication
Unlike mass production lines optimized for scale, high-mix low-volume facilities prioritize setup efficiency and process adaptability.
For startups or R&D teams, this responsiveness significantly reduces development cycle duration.
Electronic PCB Assembly Manufacturers And Quality Control Standards
Quality management defines long-term reliability.
Typical layered inspection process:
- SPI (Solder Paste Inspection) ‚Äď Verifies paste volume and alignment.
- AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) ‚Äď Detects placement defects.
- AXI (X-ray Inspection) ‚Äď Validates hidden solder joints.
- ICT (In-Circuit Testing) ‚Äď Checks electrical continuity.
- FCT (Functional Testing) ‚Äď Simulates real operating conditions.
- Burn-In Testing ‚Äď Identifies early-life failures.
Process documentation, statistical process control (SPC), and failure mode analysis (FMEA) enhance predictability.
Manufacturers with structured quality gates deliver consistent yields across production lots.
PCB Assembly And Electronics Manufacturing In Key U.S. Regions
Regional manufacturing clusters across the United States serve different industry verticals.
- California ‚Äď Aerospace, semiconductor, and advanced electronics
- Texas ‚Äď Industrial control and energy systems
- Ohio ‚Äď Automotive and automation
- North Carolina ‚Äď Telecom and medical devices
Local EMS providers often emphasize rapid prototyping and regulatory alignment. However, cost structures vary significantly depending on labor rates and facility overhead.
For global product launches, engineers frequently compare regional production to integrated international manufacturing networks.

To conclude, choosing the right electronic PCB assembly manufacturer requires structured evaluation of engineering depth, quality discipline, and supply chain maturity. Modern electronics production is not simply about placement speed or labor cost. It is about integrated process control‚ÄĒfrom DFM validation to final functional testing.
Whether you are developing a high-density HDI platform, a Bluetooth consumer device, or an industrial power controller, alignment between design intent and manufacturing capability determines long-term reliability.
By prioritizing technical collaboration, traceability, and scalable production infrastructure, engineering teams can significantly reduce risk while accelerating product commercialization. For project evaluation, DFM review, or turnkey PCB+PCBA support, please feel free to reach out to our engineering team at sales@bestpcbs.com. We would be glad to assist you with your upcoming project.
FAQs About Electronic PCB Assembly Manufacturer
What is the difference between PCB fabrication and PCB assembly?
Fabrication produces the bare board structure. Assembly mounts components onto that structure.
How long does electronic PCB assembly take?
Prototype assembly typically ranges from 3‚Äď10 days depending on component availability and complexity.
What certifications should a manufacturer have?
ISO 9001 is baseline. Automotive, medical, and aerospace projects require specialized compliance certifications.
Can small batch assembly meet industrial standards?
Yes. Quality standards apply regardless of volume if process controls are maintained.
What files are required for turnkey PCB assembly?
Gerber or ODB++, BOM, pick-and-place data, assembly drawings, and testing requirements.