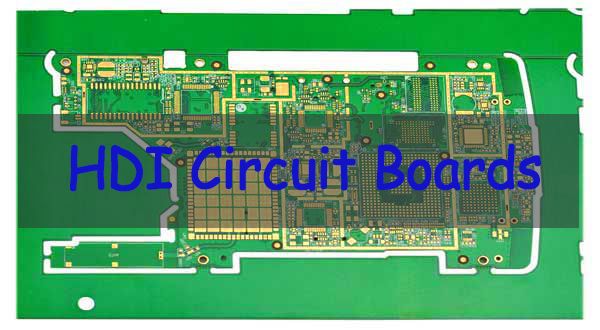
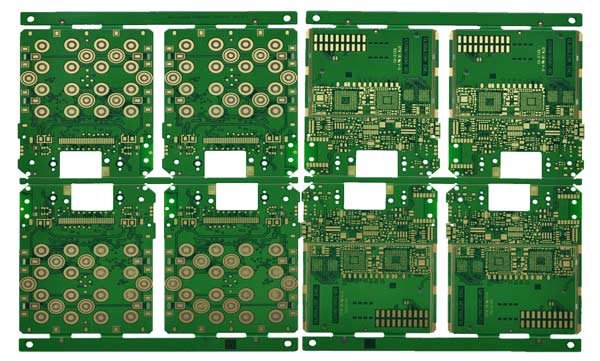
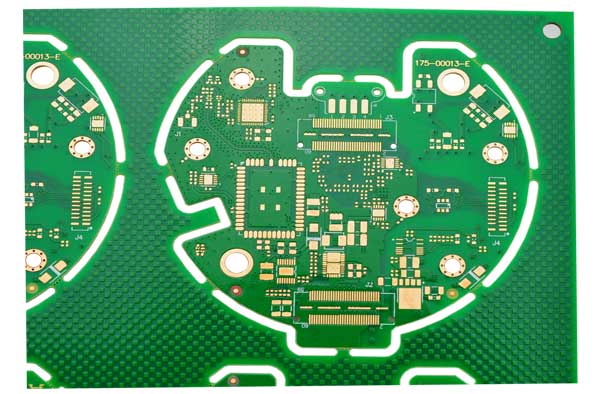
HDI printed circuit boards‚Äč are advanced multilayer boards that utilize high-density interconnect technology to accommodate more components in a smaller area, enabling the miniaturization and enhanced performance of modern electronics. This comprehensive guide will explore the intricacies of HDI PCB technology, its manufacturing process, and the critical importance of choosing a partner with full turnkey capability for your project’s success.
Navigating the complex world of advanced PCB procurement can be fraught with challenges. Are you struggling to balance high performance with tight project constraints? Common pain points include:
- Managing Sky-High Complexity:‚Äč HDI designs with microvias and multiple lamination cycles introduce significant manufacturing and design validation hurdles.
- Controlling Unpredictable Costs:‚Äč Quotes that spiral due to unforeseen process steps, material waste, or yield issues with delicate HDI structures.
- Suffering from Fragmented Supply Chains:‚Äč Coordinating separately with design houses, board fabricators, and assembly shops leads to communication gaps, finger-pointing, and delayed timelines.
- Ensuring Reliable Performance:‚Äč Anxiety over signal integrity in dense layouts and the long-term reliability of microvias under thermal and mechanical stress.
- Navigating Opaque Vendor Capabilities:‚Äč Difficulty verifying if a supplier truly has the specialized equipment and expertise for your specific HDI level and technology needs.
The most effective path to mitigating these risks is partnering with a manufacturer that offers genuine full turnkey capability. This means:
- Integrated Design Support:‚Äč Expert HDI PCB design‚Äč guidance from the start to prevent costly manufacturability issues.
- Transparent Cost Engineering:‚Äč Clear cost breakdowns and design-for-manufacturing (DFM) advice to optimize the HDI printed circuit boards price.
- Seamless Process Ownership:‚Äč A single point of accountability managing the entire flow from Gerber files to tested assemblies.
- Advanced Process Validation:‚Äč Rigorous testing protocols, including cross-sectioning and thermal cycling, for reliability assessment of microvias in HDI printed circuit boards.
- Demonstrable Technical Expertise:‚Äč Clear evidence of in-house advanced equipment and a proven track record with complex HDI builds.
At BEST Technology, we specialize in transforming these complex challenges into seamless solutions. As a professional HDI PCB manufacturer‚Äč with robust full turnkey services, we own and manage the entire process‚ÄĒfrom design review and prototyping to sophisticated fabrication, precise assembly, and rigorous testing. Our expertise ensures your high-density interconnect projects are not only manufacturable but also optimized for performance, cost, and reliability. For your next project, pls feel free to contact our experts at sales@bestpcbs.com.
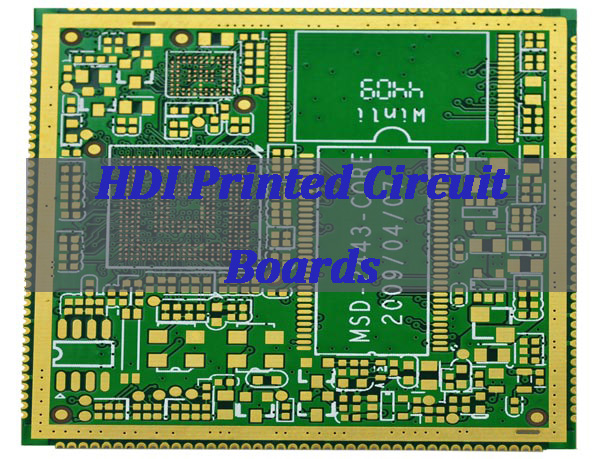
What are HDI Printed Circuit Boards?
HDI printed circuit boards are advanced PCBs designed for high wiring density and compact electronic systems. They rely on microvia technology, fine-line routing, and multilayer stackups to support complex interconnections within limited board space.
Key characteristics of HDI printed circuit boards include:
- High wiring density
Enables more signal routing and component placement in smaller board areas. - Microvia technology
Uses laser-drilled blind and buried vias, typically ‚ȧ 0.15 mm in diameter, to replace traditional mechanical through-holes. - Fine line width and spacing
Supports ultra-fine traces and tight spacing for high-density component layouts. - Advanced multilayer stackups
Incorporates sequential lamination and any-layer interconnect structures for greater design flexibility. - Improved signal integrity
Shorter interconnect paths and optional low-Dk/Df materials help maintain performance in high-speed designs. - Specialized manufacturing processes
Requires precision laser drilling, controlled lamination, and strict process control during the HDI PCB manufacturing process.
In summary, HDI printed circuit boards are not simply denser versions of standard PCBs. They represent a dedicated design and manufacturing approach that enables modern, high-performance electronic products with strict size and performance constraints.
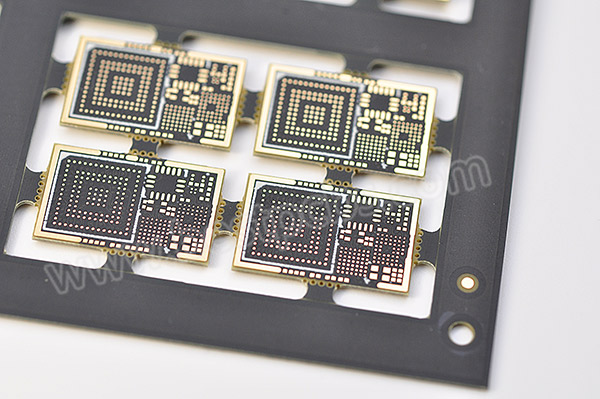
What Makes HDI Circuit Boards Different From Standard Multilayer PCBs?
While both are multilayer structures, HDI PCBs are fundamentally different in their construction and capabilities. Standard multilayer PCBs use mechanical drilling for through-hole vias, which limits density. HDI circuit boards, however, are defined by their use of microvias (typically with a diameter of less than 150¬Ķm), which allow for direct interconnections between adjacent layers, unlocking new routing possibilities.
| Feature | Standard Multilayer PCB | HDI PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Via Technology‚Äč | Primarily through-hole vias | Microvias, blind/buried vias |
| Line Width/Space‚Äč | Larger (e.g., ‚Č• 4 mil) | Finer (e.g., ‚ȧ 3 mil) |
| Pad Density‚Äč | Lower | Much Higher |
| Construction‚Äč | Fewer lamination cycles | Multiple sequential laminations |
| Key Benefit‚Äč | Cost-effective for simpler designs | Enables miniaturization & high-speed performance |
The distinction lies in the high density interconnect‚Äč approach, which provides superior electrical performance and design freedom, making it ideal for complex, space-constrained applications.
What Is the Structure of HDI Printed Circuit Boards?
The structure of HDI printed circuit boards‚Äč is not defined by a single, fixed stackup or manufacturing flow. Instead, HDI construction is highly flexible and is determined primarily by via requirements, drilling methods, and interconnection density. The layer structure and production sequence are customized to meet specific routing and component layout demands.
At the core of HDI PCB structure is the combination of multiple via types, each serving a different interconnection purpose:
- Laser-drilled blind vias
These microvias connect an outer layer to one or more adjacent inner layers. They are a defining feature of HDI printed circuit boards and enable high routing density while minimizing signal path length. - Mechanically drilled buried vias
Buried vias connect inner layers without reaching the outer surfaces. They support complex multilayer interconnections and help free surface area for fine-pitch components. - Mechanically drilled through holes
Through holes extend from the top layer to the bottom layer and are typically used for power distribution, grounding, or components that require mechanical strength.
Because HDI printed circuit boards often rely on sequential lamination, the final structure may include multiple build-up layers, stacked or staggered microvias, and hybrid via combinations. As a result, each HDI design follows a drilling-driven structural logic, rather than a standardized process template.
In practice, the structure of HDI printed circuit boards is engineered around via architecture, layer interconnect strategy, and manufacturing feasibility, allowing designers to balance density, reliability, and performance in advanced electronic systems.
What Are the Blind Via Types in HDI Printed Circuit Boards?
In HDI printed circuit boards, blind vias are created primarily by laser drilling and are used to connect surface layers to inner layers without penetrating the entire board. Different blind via structures are selected based on layer count, routing density, and reliability requirements.
Common blind via types used in HDI printed circuit boards include:
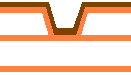
Microvia hole
Typically used in 1+N+1 HDI structures, microvias connect the outer layer to the adjacent inner layer. These vias are laser-drilled and are not copper-filled, making them suitable for simpler HDI designs with moderate density requirements.
Solid via hole (filled microvia)
Also applied in 1+N+1 structures, solid vias are laser-drilled microvias that require copper filling. The filled structure provides a flat surface for component pads and supports higher reliability and finer pitch components.

Staggered via hole
Used in second-order HDI, staggered vias consist of offset laser-drilled microvias on different layers. This structure reduces stress concentration and is commonly chosen for improved reliability in multilayer HDI designs.
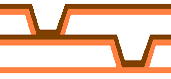
Stacked via hole
A key feature of high-density and any-layer HDI, stacked vias are vertically aligned laser-drilled microvias. These vias must be copper-filled to ensure mechanical strength and electrical continuity across multiple layers.

Skip via hole
Skip vias are laser-drilled microvias that connect non-adjacent layers, such as from layer 1 directly to layer 3, bypassing layer 2. This structure increases routing flexibility while maintaining surface density.

Step via hole
Step vias are co-located second-order laser vias that are not copper-filled. They are typically used in designs where surface planarity is less critical but routing density must still be increased.
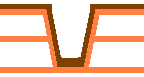
How to distinguish blind via structures in HDI designs:
- Whether the design is 1+N+1
This indicates the most basic HDI build-up structure, where laser-drilled blind vias connect the outer layers to the adjacent inner layers. - Whether the design is second-order HDI
Second-order HDI involves connecting to deeper layers using two sequential microvias, typically requiring either staggered or stacked via structures. - Staggered vs. stacked vias
The key distinction is whether the two microvias are vertically aligned.- Staggered vias are offset between layers.
- Stacked vias are directly aligned on the same vertical axis.
- Filled vs. non-filled vias
- Designs using via-in-pad, requiring high surface planarity or higher long-term reliability, typically require copper-filled vias.
- Vias that are not located in pads and are used in cost-sensitive designs may remain unfilled, depending on reliability requirements and manufacturing capability.
Each blind via type in HDI printed circuit boards serves a specific structural and electrical function. The selection depends on factors such as layer stackup, component pitch, signal integrity requirements, and manufacturing capability, making blind via design a critical part of HDI PCB engineering.
What Equipment Do HDI Printed Circuit Boards Factories Use for Microvias?
Producing reliable microvias requires specialized, high-precision equipment. A capable HDI printed circuit boards factory‚Äč invests in:
- UV or CO‚āā Laser Drilling Machines:‚Äč For ablating precise, small-diameter microvias (as small as 50¬Ķm).
- Advanced Direct Imaging (DI) Systems:‚Äč To expose ultra-fine line traces and spaces with high accuracy.
- Fully Automated Optical Inspection (AOI):‚Äč To detect minute defects in traces, spaces, and via pads.
- Electroless and Electrolytic Copper Plating Lines:‚Äč For uniform copper deposition into high-aspect-ratio microvias.
- Sequential Lamination Presses:‚Äč To build the multilayer structure with precise layer-to-layer registration.
This specialized toolset is non-negotiable for achieving the yields and quality required in the competitive HDI printed circuit board market.
How to Identify HDI Levels in HDI Printed Circuit Boards?
Identifying the HDI level of HDI printed circuit boards primarily depends on the via structure, rather than on trace etching or basic layer count. While routing processes for multilayer PCBs are largely similar to those used for single- or double-layer boards, the defining difference lies in how vias are formed and interconnected.
At a high level, PCB constructions can be classified into through-hole boards, first-order HDI, second-order HDI, and stacked HDI. Higher-order and any-layer HDI structures exist, but they are used far less frequently due to significantly higher cost and manufacturing complexity.
Through-Hole Boards (Non-HDI)
Through-hole boards use a single via type that runs from the top layer to the bottom layer. All interconnections‚ÄĒboth outer and inner‚ÄĒare completed using mechanically drilled through holes that are subsequently copper plated.
The number of layers does not determine whether a board is HDI. A 2-layer PCB is typically a through-hole board, but many high-end products such as network switches or military electronics use 20-layer boards that are still entirely through-hole. Typical finished via diameters range from 0.2 mm to 0.3 mm, with smaller diameters increasing cost due to drill wear and slower drilling speeds.
First-Order HDI (1st-Order HDI)
A first-order HDI board is identified by the presence of one layer of laser-drilled microvias on each outer surface. These microvias usually have diameters around 0.1 mm and connect the outer layers to the adjacent inner layers.
Structurally, a common example is a 6-layer first-order HDI board, which can be viewed as a 4-layer through-hole core with one HDI build-up layer added to each side. The inner layers still rely on mechanical vias, while the outer layers use laser microvias.
Laser drilling only penetrates dielectric material and does not cut through copper, allowing precise via formation without damaging internal circuitry.
Second-Order HDI (2nd-Order HDI)
A second-order HDI board contains two layers of laser-drilled microvias on each side of the core. In practical applications, second-order HDI structures are most commonly found in 8-layer or higher designs, rather than in 6-layer boards.
There are two main second-order configurations:
- Staggered vias
The two layers of laser microvias are offset from each other. This approach is used because unfilled microvias cannot reliably support another laser via drilled directly on top. Staggered structures reduce process risk and are more cost-effective. - Stacked vias
In stacked structures, the laser microvias are vertically aligned. To make this reliable, the lower microvia must be copper-filled before drilling the upper microvia. This process is more complex and significantly more expensive but enables tighter routing density.
In terms of structure:
- A 6-layer second-order HDI board can be viewed as a 4-layer first-order board with an additional HDI build-up.
- An 8-layer second-order HDI board is effectively a 6-layer first-order board with another build-up layer added.
Any-Layer HDI
Any-layer HDI represents the highest level of HDI technology. Every layer is interconnected using laser-drilled microvias, and any layer can connect directly to any other layer.
This structure offers maximum routing freedom and density, making layout significantly easier for engineers. However, the cost is extremely high‚ÄĒoften more than ten times that of a standard through-hole board‚ÄĒso any-layer HDI is reserved for only the most compact and performance-critical designs.
In practice, HDI levels in HDI printed circuit boards are identified by answering three key questions:
- Are laser-drilled microvias present?
If not, the board is a through-hole design. - How many layers of microvias are used?
One layer indicates first-order HDI; two layers indicate second-order HDI. - Are the microvias staggered or stacked?
Staggered vias suggest cost-optimized second-order HDI, while stacked vias indicate higher-density, higher-cost designs.
By examining via type, drilling method, and build-up layer count, the HDI level of a printed circuit board can be accurately determined, independent of total layer count alone.
How Does HDI Technology in PCB Improve Signal Integrity?
HDI technology in PCB‚Äč is a cornerstone for high-speed digital and RF applications because it inherently enhances signal integrity (SI).
- Shorter Interconnect Paths:‚Äč Microvias enable more direct routing, reducing signal path length and propagation delay.
- Reduced Parasitics:‚Äč Smaller via stubs and pads lower parasitic inductance (L) and capacitance (C), minimizing unwanted signal reflection and attenuation.
- Better Impedance Control:‚Äč Finer lines and consistent dielectric layers allow for more precise control over characteristic impedance.
- Improved Power Integrity:‚Äč Dense via-in-pad technology provides low-inductance paths for power delivery networks (PDNs), reducing switching noise.
- Enhanced EMI/EMC Performance:‚Äč Tighter component placement and optimized grounding via microvias help contain electromagnetic interference.
These SI benefits make HDI printed circuit boards‚Äč essential for 5G, high-performance computing, and advanced automotive electronics.
HDI PCB Manufacturing Process Explained Step by Step
In HDI production, the ‚Äústep-by-step‚ÄĚ flow changes with the stackup and via strategy.
Example 1: 1+4+1 (B) Process Flow
(Two lamination cycles, with inner mechanical drilling and plating performed before the second lamination, then laser microvias after the second lamination.)
- Panel Cutting
- Inner Layer Imaging & Etching
- 1st Lamination (First Press)
- L2‚ÄďL5 Mechanical Drilling
- L2‚ÄďL5 Copper Plating
- L2‚ÄďL5 Inner/Outer Layer Circuit Formation (for the sub-structure)
- 2nd Lamination (Second Press)
- Laser Drilling (Microvias)
- Mechanical Drilling (Through Holes / Tooling Holes as required)
- Copper Plating (Via Metallization)
- Outer Layer Imaging & Etching
- Solder Mask Application
- ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold)
- Legend / Silkscreen Printing
- Profiling / Routing (Final Outline)
- Electrical Test (E-test)
- Final Inspection
- OQC (Outgoing Quality Control)
- Packing
- Warehouse Receiving (Stock-in)
Example 2: 1+4+1 (A) Process Flow
(Single lamination cycle, then laser drilling and standard downstream flow.)
- Panel Cutting
- Inner Layer Imaging & Etching
- Lamination (Pressing)
- Laser Drilling (Microvias)
- Mechanical Drilling (Through Holes / Tooling Holes as required)
- Copper Plating (Via Metallization)
- Outer Layer Imaging & Etching
- Solder Mask Application
- ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold)
- Legend / Silkscreen Printing
- Profiling / Routing (Final Outline)
- Electrical Test (E-test)
- Final Inspection
- OQC (Outgoing Quality Control)
- Packing
- Warehouse Receiving (Stock-in)
The practical difference between 1+4+1 (A) and 1+4+1 (B) is whether the build requires a staged sequence with an early drill-and-plate step before the second lamination. That staged approach adds process control points and complexity, which often affects lead time and cost.
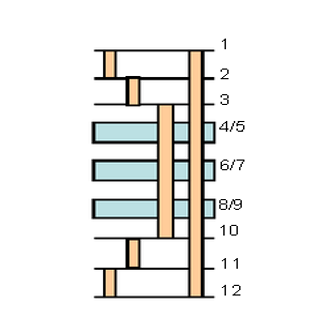
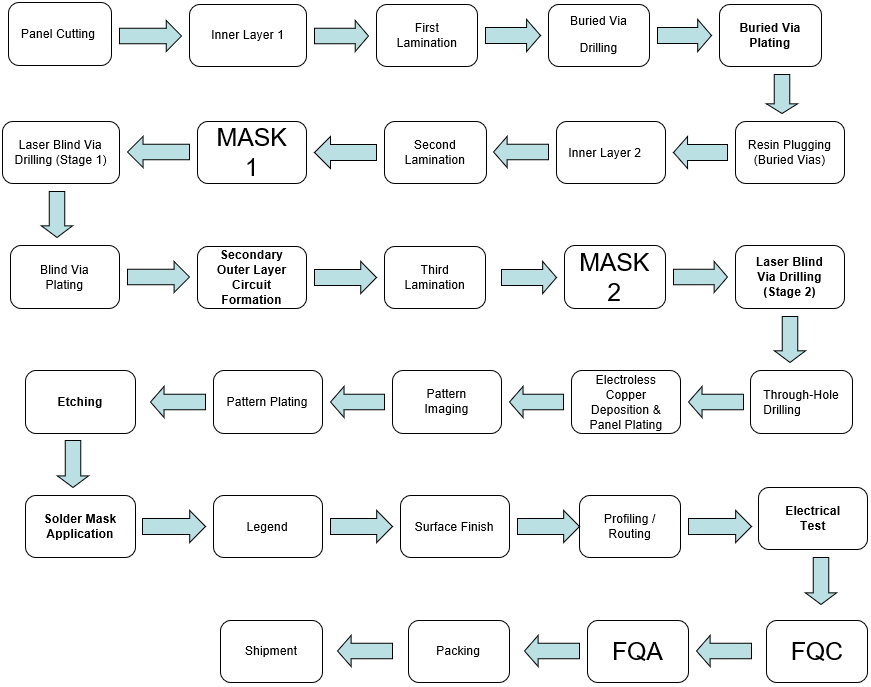
Example 3: 1+1+8+1+1 Process Flow
Using a 12-layer, double-lamination first-order HDI structure (1+1+8+1+1) as an example, the following briefly outlines the standard manufacturing process commonly used in the industry.
What Applications Use HDI Circuit Boards Most Frequently?
HDI circuit boards are most widely used in applications that demand high signal density, compact form factors, and reliable high-speed performance. As electronic systems continue to evolve toward higher integration and smaller footprints, HDI technology has become a foundational solution across several major industries.
Consumer Electronics and Smartphones
Smartphones remain the largest application segment for HDI circuit boards, accounting for more than half of total HDI demand. Modern smartphone mainboards rely heavily on HDI structures to support high pin-count processors, dense memory interfaces, and multi-antenna RF layouts within extremely limited space.
HDI enables fine line routing, multi-layer interconnects, and compact board stacking, making it essential for slim device profiles and advanced functionality. Wearable electronics further extend this demand, using HDI and embedded via technologies to significantly reduce PCB area.
PC, Consumer Computing, and High-Performance Devices
PCs, tablets, and other consumer computing products represent a rapidly expanding HDI application area. As processors become more powerful and interfaces move toward higher speeds, HDI circuit boards are increasingly adopted to meet routing density and signal integrity requirements.
This segment has grown to roughly one-third of overall HDI demand, driven by compact laptops, high-performance computing modules, and emerging AI-enabled consumer devices.
Automotive Electronics and ADAS Systems
Automotive electronics, particularly ADAS and intelligent vehicle platforms, are a fast-growing HDI application. Vehicle systems require HDI circuit boards to support synchronized multi-sensor signal processing, high-speed data transmission, and stable operation under thermal stress and vibration.
HDI technology enables reliable high-density interconnects for camera modules, radar systems, and in-vehicle infotainment, making it a critical component in the transition toward autonomous and intelligent vehicles.
Communication Infrastructure and 5G Equipment
HDI circuit boards are widely used in 5G base stations and communication equipment, where high-frequency, low-loss signal transmission is essential. These systems require fine-line HDI layouts to support large antenna arrays, RF front-end integration, and high-speed signal processing.
The increasing complexity of 5G infrastructure continues to push higher layer counts and tighter precision requirements, accelerating HDI adoption in telecom applications.
Medical Electronics and Healthcare Devices
Medical electronics represent a smaller but high-value HDI segment. Advanced imaging systems, implantable medical devices, and portable diagnostic equipment rely on HDI circuit boards to achieve miniaturization, high reliability, and precise signal acquisition.
HDI flexible and rigid-flex structures are particularly important in medical applications where space constraints and signal accuracy are critical.
AI Servers and Emerging High-Growth Segments
AI servers and data-center hardware are emerging as one of the fastest-growing HDI application areas. The need for ultra-high interconnect density, high-speed signal integrity, and multilayer routing has made HDI circuit boards a key enabler for advanced computing platforms.
As AI workloads and server architectures continue to evolve, higher-order HDI and any-layer HDI solutions are increasingly replacing traditional PCB designs.
In summary, HDI circuit boards are most frequently used in:
- Smartphones and consumer electronics
- PCs, tablets, and high-performance consumer devices
- Automotive electronics and ADAS systems
- 5G communication infrastructure
- Medical and healthcare electronics
- AI servers and advanced computing hardware
Across these applications, HDI technology plays a central role in enabling miniaturization, high-speed performance, and system-level integration, making it one of the most important PCB technologies in modern electronics manufacturing.
What Capabilities Should You Expect From an HDI PCB Manufacturer?
When selecting an HDI PCB manufacturer, particularly one claiming full turnkey capability, it’s crucial to understand the specific advanced technological competencies they must possess. A true specialist in high density interconnect‚Äč must demonstrate proficiency far beyond standard PCB fabrication. Based on our internal process capabilities at BEST Technology, here are the definitive capabilities you should expect from a leading HDI PCB manufacturer.
An advanced HDI printed circuit board supplier‚Äč must be able to deliver on the following key areas to ensure your HDI printed circuit boards‚Äč meet the highest standards of performance, miniaturization, and reliability:
- Precision Microvia Fabrication & Sequential Build-Up:
- Laser Drilling Mastery:‚Äč The capability to consistently drill microvias with diameters down to 0.070mm (limit) or 0.10mm (standard), a fundamental requirement for what is HDI PCB. This includes controlling the depth-to-diameter ratio precisely.
- Complex Lamination Expertise:‚Äč Proficiency in executing multi-stage sequential lamination processes (1+N+1, 2+N+2, etc.) with exceptional layer-to-layer registration (alignment tolerance ‚ȧ0.13mm standard, ‚ȧ0.10mm limit). This is critical for building reliable any-layer HDI printed circuit boards.
- Ultra-Fine Line & Space Imaging:
- Sub-4mil Resolution:‚Äč The ability to reliably manufacture extremely fine traces and spaces. For outer layers, this means achieving 3.5/4mil (standard) or even 3/3mil (limit). On inner layers, capabilities extend to 3/3mil (standard) or 2.5/2.5mil (limit), which is essential for high density PCB‚Äč designs requiring maximum component density.
- Controlled Etching:‚Äč Maintaining tight etch tolerances (e.g., ¬Ī1mil for lines ‚ȧ5mil) to ensure geometric accuracy and consistency.
- Advanced Impedance Control:
- Dielectric Management:‚Äč Precise control over insulation layer thickness (minimum 0.076mm standard) and material properties to achieve consistent electrical characteristics.
- Targeted Impedance Performance:‚Äč Delivering specified impedance values (e.g., 50ő©, 100ő© differential) with tight tolerances (¬Ī5ő© for <50ő© impedance, standard), which is vital for maintaining signal integrity in high-speed HDI technology in PCB‚Äč applications.
- Broad Material & Surface Finish Portfolio:
- High-Performance Substrates:‚Äč Access to and proven experience with a wide variety of materials, including standard FR4 (normal, medium, and high TG), high CTI materials, and specialized high-frequency/low-loss laminates (e.g., Rogers, Taconic series), catering to demanding applications in the HDI printed circuit board market.
- Diverse Surface Treatments:‚Äč Offering a comprehensive range of surface finishes such as ENIG, Immersion Tin/Silver, OSP, Hard/Soft Gold, and ENEPIG to meet various assembly requirements and component specifications.
- Integrated Full-Turnkey Services:
- Proactive Design Support (DFM):‚Äč Providing expert engineering feedback during the design phase to optimize for manufacturability, performance, and HDI printed circuit boards price‚Äč considerations.
- Seamless Fabrication-to-Assembly Flow:‚Äč Managing the entire process under one roof, from HDI PCB manufacturing process‚Äč execution to precision SMT/BGA assembly, ensuring quality, traceability, and faster time-to-market.
- Rigorous Testing & Validation:‚Äč Implementing thorough testing protocols, including electrical testing (flying probe, ICT), AOI, and functional testing, to guarantee the reliability of complex HDI assemblies.
In summary, a premier HDI printed circuit board supplier‚Äč with full turnkey capability integrates these sophisticated technologies and services. BEST Technology’s detailed process capabilities, as reflected in our manufacturing specifications, underscore our commitment to delivering the highest quality HDI printed circuit boards‚Äč for the most challenging applications. We possess the advanced infrastructure, technical expertise, and integrated services necessary to transform your complex HDI designs into successful, high-performance products.
How to Choose a Reliable HDI Printed Circuit Board Supplier?
Choosing the right HDI printed circuit board supplier‚Äč is a strategic decision. Follow this checklist:
- Audit Technical Certifications:‚Äč Look for ISO 9001, IATF 16949 (automotive), and relevant industry-specific certifications.
- Review Their Portfolio:‚Äč Examine case studies or samples of similar complexity (HDI level, layer count, material).
- Evaluate Communication:‚Äč Assess their responsiveness, engineering support, and willingness to provide HDI printed circuit boards quotes‚Äč with clear breakdowns.
- Request a Facility Tour/Virtual Audit:‚Äč Verify their equipment (laser drillers, DI machines) and process controls.
- Check Supply Chain Stability:‚Äč Ensure they have strong relationships with material suppliers to mitigate shortage risks.
- Discuss Prototype & Volume Scalability:‚Äč Confirm they can support both rapid prototyping and volume production. Thorough vetting separates true technical partners from basic board vendors.
HDI Printed Circuit Boards Price Factors and Cost Considerations
The HDI printed circuit boards price‚Äč is influenced by multiple, often interrelated, factors. Understanding them helps in budget planning and design optimization.
- HDI Level/Complexity:‚Äč More sequential laminations (Level 2, 3, any-layer) drastically increase cost.
- Layer Count & Board Size:‚Äč More layers and custom sizes use more material and process time.
- Material Type:‚Äč Standard FR-4 vs. high-speed/low-loss or halogen-free materials.
- Minimum Feature Size:‚Äč Tighter trace/space and smaller microvia diameters require more precise (and expensive) processes.
- Surface Finish:‚Äč ENIG, ENEPIG, or hard gold are costlier than HASL.
- Quantity & Lead Time:‚Äč Prototype quantities have higher unit costs; expedited turnarounds incur premiums.
A trusted manufacturer will work with you to find the most cost-effective design path without compromising critical performance.
How Is the HDI Printed Circuit Board Market Evolving With AI and 5G?
The HDI printed circuit board market‚Äč is undergoing a fundamental transformation, shifting from a cycle driven primarily by consumer electronics miniaturization to one powered by the high-performance demands of artificial intelligence (AI) and ubiquitous 5G connectivity. This evolution is not merely a growth in volume but a strategic upgrade in technology, value, and application focus, creating new high-growth segments and reshaping competitive dynamics.
1. Market Overview: From 5G Build-out to an AI-Powered Future
The market trajectory clearly illustrates this shift. In 2023, the global HDI board market, valued at approximately 8.5 billion with China accounting for4210 billion, growing at a rate of 9.2%, primarily fueled by AI servers and automotive electronics. This is moving the industry’s focus from volume to advanced capability, as seen in the rising proportion of Any-layer HDI, projected to reach 28% by 2025.
2. Primary Growth Drivers: A Confluence of Megatrends
The demand surge is coming from multiple, synergistic frontiers:
- AI Server Demand Explosion:‚Äč This is the most potent driver. AI training chips (e.g., NVIDIA H100) require HDI boards with 20+ layers, with per-unit value reaching 3-5 times that of traditional servers. The global market for HDI in AI servers is forecast to surpass $2.5 billion by 2025. This creates intense demand for boards that support heterogeneous integration technologies‚Äč like 2.5D/3D packaging and can manage thermal loads from chips consuming over 1000W.
- Automotive Electronics Penetration:‚Äč Advanced Driver-Assistance Systems (ADAS) and smart cockpits are drastically increasing HDI content per vehicle from 1-2 pieces to 5-8 pieces. The automotive segment’s share of the HDI market is expected to rise from 15% to 25% by 2025, demanding ultra-high reliability.
- Accelerated 5G & Data Center Infrastructure:‚Äč The rollout of Massive MIMO antennas and the upgrade to 800G optical modules in data centers require high-frequency, high-speed HDI boards‚Äč with extremely fine line widths/spaces (below 20¬Ķm) and ultra-low signal loss, pushing the limits of manufacturing processes like mSAP.
3. Application Shift: Beyond the Smartphone Core
While smartphones‚Äč remain the dominant application, accounting for 58% of demand, the future growth engine is demonstrably elsewhere. The combined share of PC/consumer electronics (30%) and automotive electronics (7%)‚Äč highlights HDI’s expanding role in computing and automotive intelligence. The 42% non-smartphone segment represents a vast technology substitution space, where high-end HDI is progressively replacing traditional PCBs, a process that will continue to deepen.
4. Technological and Supply Chain Transformation
The requirements of AI and 5G are forcing a comprehensive upgrade across the HDI PCB manufacturing‚Äč ecosystem:
- Technology Trends:‚Äč Line/space is advancing toward 30/30¬Ķm, and the penetration of SLP (Substrate-Like PCB) technology is increasing.
- New Capabilities Required:‚Äč Manufacturers must master advanced thermal management (embedded copper blocks, metal cores), supply ultra-low-loss materials for high-frequency applications, and build full turnkey capabilities‚ÄĒfrom collaborative design and simulation to full-scale production and testing‚ÄĒto meet the stringent demands of clients like NVIDIA.
In summary, the HDI printed circuit board market‚Äč is decisively evolving from enabling device miniaturization to becoming the critical backbone of the AI and 5G infrastructure. Growth is being driven by high-value, high-complexity applications in AI servers, autonomous vehicles, and advanced communications, which in turn are triggering a wave of technological innovation and supply chain restructuring. Manufacturers that can master advanced processes like Any-layer HDI, ultra-fine line imaging, and integrated thermal management, while providing comprehensive full turnkey‚Äč solutions, are positioned to lead the next phase of the industry’s evolution.
In conclusion, HDI printed circuit boards‚Äč are the foundational technology enabling the miniaturization, high speed, and reliability of today’s most advanced electronic devices. This guide has explored their design, manufacturing, applications, and the critical factors in selecting a manufacturing partner. Success in this complex domain hinges on collaboration with a supplier that offers genuine full turnkey capability‚ÄĒseamlessly integrating design support, advanced fabrication, precise assembly, and rigorous testing under one roof. BEST Technology is committed to being that partner, providing the expertise and end-to-end service to bring your most ambitious HDI projects to life with efficiency. For a consultation or quote, please contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com.
FAQs
What Are the Benefits of HDI PCB?
- HDI PCBs offer significantly higher wiring density compared to traditional multilayer boards. By using microvias, fine line/space routing, and build-up layers, HDI technology enables smaller board size, lighter weight, and higher component integration. HDI PCBs also improve signal integrity by shortening interconnect paths and reducing parasitic effects, making them well suited for high-speed and high-frequency designs.
What Is Ultra HDI PCB?
- Ultra HDI PCB refers to advanced, high-order HDI designs that go beyond standard first- or second-order HDI. These boards typically feature ultra-fine line widths, very small laser microvias, multiple build-up layers, and in many cases stacked or any-layer interconnect structures. Ultra HDI is commonly used in smartphones, AI hardware, and other applications where extreme miniaturization and routing density are required.
What Are the Four Tiers of HDI?
The four tiers of HDI are usually classified by the number of build-up layers and microvia levels:
- Tier 1 (First-Order HDI) ‚Äď One layer of laser microvias on each side of the core (e.g., 1+N+1).
- Tier 2 (Second-Order HDI) ‚Äď Two layers of microvias, using staggered or stacked via structures.
- Tier 3 (Higher-Order HDI) ‚Äď Three or more microvia layers, supporting much higher routing density.
- Tier 4 (Any-Layer HDI) ‚Äď Every layer can be interconnected with laser microvias, offering maximum design flexibility at the highest cost.
What Does 1 HDI Mean?
- ‚Äú1 HDI‚ÄĚ typically means a first-order HDI PCB, which uses one build-up layer of laser-drilled microvias on each side of the core. This structure is commonly expressed as 1+N+1 and represents the entry level of HDI technology, balancing higher density with controlled manufacturing cost.