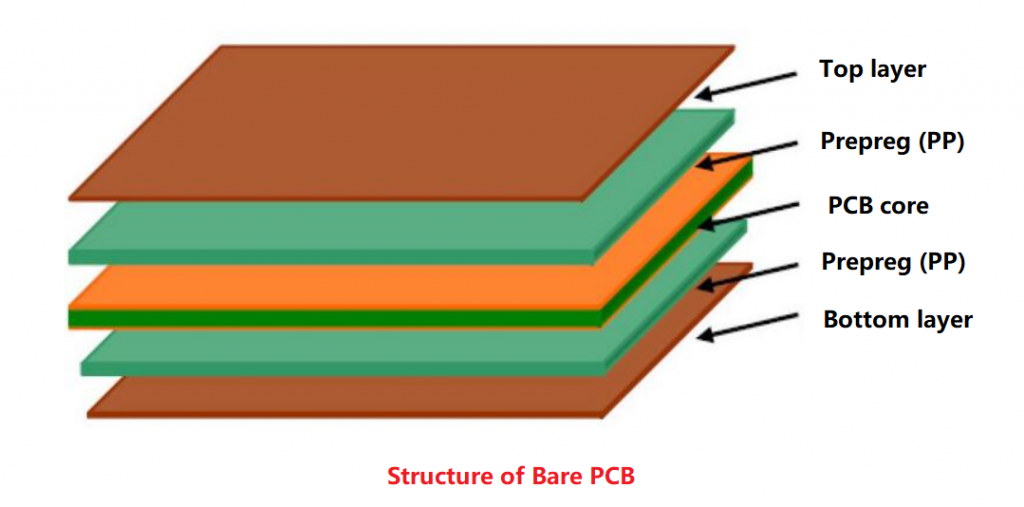
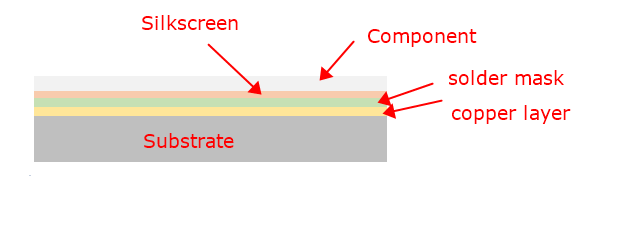
Copper thickness has a very important impact on the performance of PCB, and PCBs with different copper thicknesses also have very different applications. The fundamental reason why copper is widely used in circuit board manufacturing is its electrical conductivity, so different copper thicknesses correspond to different electrical conductivities. In addition, copper also has low resistance and thermal stability.
Why fill PCB with copper?
The main purpose of using copper to fill PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is to improve the electrical conductivity of the circuit board, enhance mechanical strength and stability, protect the circuit board from oxidation or corrosion, and improve heat dissipation capabilities. ā
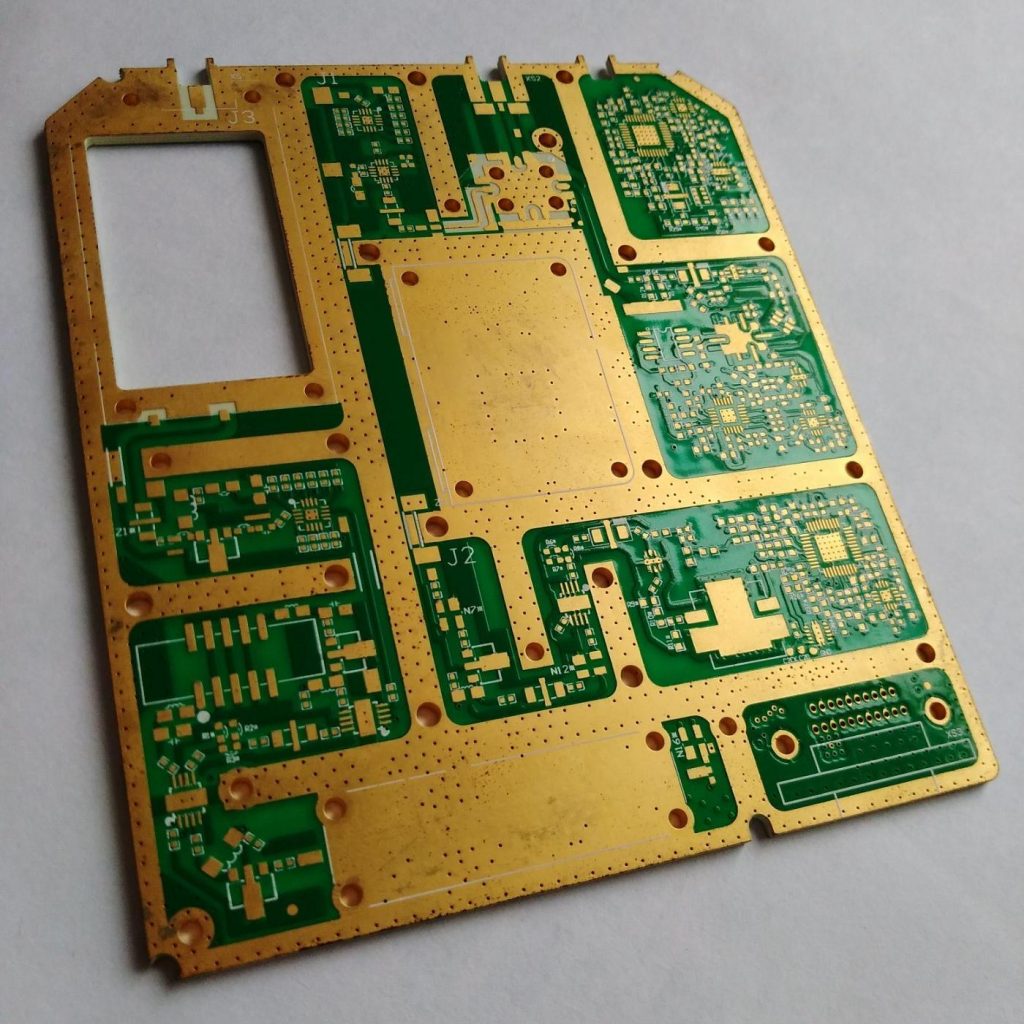

As an excellent conductive material, copper plays a vital role in PCB design. By covering the surface of the PCB with copper foil, the conductive performance of the circuit board can be significantly improved and the connection between various components can be ensured to be more stable and reliable.
Copper foil itself has high mechanical strength and stability, which can effectively prevent PCB from being damaged or deformed due to the influence of the external environment. The corrosion resistance of copper foil can also protect the circuit board from oxidation or corrosion, thereby extending the service life of the circuit board and ensuring its stability and reliability during work.
Since metal has good electrical and thermal conductivity, copper coating can increase the heat dissipation surface area of the PCB, help distribute heat evenly, and prevent the generation of local high-temperature areas. This can not only reduce local heat concentration, but also reduce the temperature gradient of the heat source and improve heat dissipation efficiency.
To sum up, the role of copper-filled PCB is multi-faceted. It can not only improve the conductivity and mechanical stability of the circuit board, but also protect the circuit board from environmental influences, while enhancing the heat dissipation capacity and ensuring the stable operation of electronic equipment. and long-term useā.
Is a thicker PCB copper better?
The copper thickness of PCB is not as thick as possible, but the appropriate copper thickness needs to be selected according to the design requirements and actual application of the circuit board. ā
The importance of copper thickness in PCB manufacturing cannot be ignored because it directly affects the conductive performance, heat dissipation performance, mechanical strength and signal integrity of the circuit board. Proper copper thickness can provide good electrical and thermal conductivity while ensuring the reliability and stability of the circuit board.
Although an excessively thick copper layer can improve current carrying capacity and heat dissipation performance, it will also increase cost and weight, which may lead to serious glue flow and increased processing difficulty. Therefore, when selecting copper thickness, factors such as circuit board design requirements, application environment, and cost need to be comprehensively considered.
During the PCB design and manufacturing process, the optimal copper thickness should be selected based on specific application requirements and cost considerations to achieve optimal circuit performance, heat dissipation, and mechanical strengthā.
How thick is the copper on a 1 ounce copper PCB?
The thickness of 1 ounce of copper on a PCB is 35 microns. ā
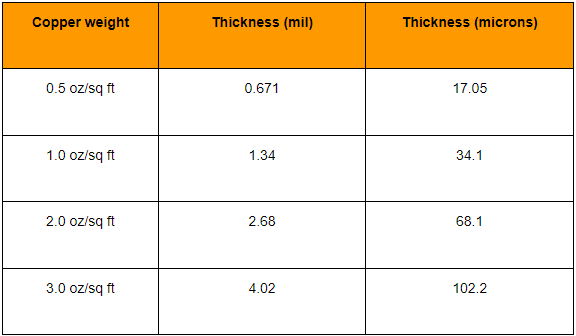
In the PCB industry, ounces (oz) are the unit used to express copper foil thickness, not weight. Specifically, the thickness of 1oz of copper refers to the thickness achieved by spreading 1oz of copper evenly over an area of 1 square foot.
According to different information, the thickness of 1oz copper can be obtained by different calculation methods, but the generally accepted value is that 1oz copper is equal to 1.4mil (milliinch), which is equivalent to 35 microns. Therefore, whether in international standards or practical applications, the thickness of 1oz copper on PCB is usually considered to be 35 microns.
In addition, the copper thickness of the PCB has a direct impact on the circuit boardās current carrying capacity, heat dissipation, reliability and other performance indicators. Commonly used PCB copper thickness specifications include 1oz, 2oz, 3oz, 4oz, 5oz, 6oz, etc., which correspond to different copper layer thicknesses. The copper layer thickness of 1oz is 35 microns, 2oz is 70 microns, and so on, 6oz is 210 microns. . These specifications provide the basis for selecting different copper thicknesses based on specific application needs to meet different electrical performance and physical requirements.
What is the conventional PCB copper thickness?Thick copper plate, FPC
āRegular PCB copper thickness is 1oz (35Ī¼m). When the thickness of the copper foil reaches or exceeds 2oz, such a PCB board is defined as a thick copper board; for flexible circuit boards (FPC), the copper thickness also has different specifications, for example, 0.5oz copper thickness is used for flexible circuit boards is being manufactured. ā
In PCB manufacturing, the choice of copper thickness is determined based on specific application requirements. Common copper thickness classifications include:
1. ā1oz copper thickness: ā
This is the most common and standard copper foil thickness and is widely used in everyday electronic devices and general applications. 1oz (ounce) means 1 ounce of copper foil weighs 1 square foot. In the PCB manufacturing process, 1 ounce corresponds to a copper foil thickness of approximately 35 microns, which has good electrical and thermal conductivity.
2. ā2oz copper thickness: ā
Copper foil of this thickness is usually used in circuits that require higher current carrying capabilities, such as power amplifiers, high-power LEDs, etc. 2oz copper thickness corresponds to a copper foil thickness of approximately 70 microns, which has better performance in electrical conductivity and heat dissipation than 1oz copper thickness.
3. ā0.5oz copper thickness: ā
This thinner copper foil thickness is suitable for some light and small electronic products, such as electronic watches, mobile phones, etc. 0.5oz (18Ī¼m) copper foil is suitable for equipment that has strict requirements on circuit board size and weight.
How to choose PCB copper thickness?
Choosing PCB copper thickness depends primarily on the board’s purpose, current requirements, signal integrity requirements, cost budget, and manufacturing process capabilities.
1. āCircuit board usage and current requirementsā: For circuit boards that need to handle large currents, such as power boards, it is recommended to use thicker copper foil, such as 2oz (about 70Ī¼m) or 3oz (about 105Ī¼m). For signal transmission, a copper thickness of 1oz (~35Ī¼m) is usually sufficient. Ordinary double-sided boards generally use 1oz copper thickness, while multi-layer boards generally use 1/2oz, 1/3oz copper thickness for the inner layer, and 1oz, 1/2oz, 1/3oz copper thickness for the outer layer.
2. Signal integrity requirements: For high-density interconnect (HDI) boards or high-frequency circuits, thinner copper foil may be required to reduce parasitic effects and ensure signal integrity.
3. āCost considerationsā: The thicker the copper foil, the higher the cost is usually.
4. Environmental factors: For PCBs in extreme working environments (such as high temperature, high humidity or high vibration environments), the thickness of the copper foil may need to be adjusted to enhance the stability and durability of the circuit.
In summary, selecting PCB copper thickness is a process that comprehensively considers multiple factors and needs to be determined based on specific application scenarios and design requirements.
What is the difference between different copper thicknesses on PCB?
āThe main differences between different copper thicknesses on PCBs are their conductive properties, load-bearing capacity, anti-interference performance, cost and manufacturing difficulty. ā
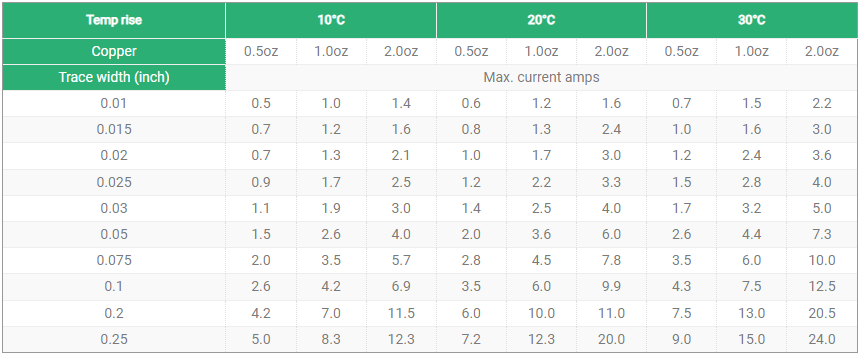
āOuter copper thicknessā is commonly used for circuit board routing and connections, and its selection depends on the application requirements and design needs of the circuit board. The outer copper thickness range is generally between 1-5oz, and the more common ones are 1oz, 2oz, 3oz and 4oz. The thicker the outer copper layer, the stronger the circuit board’s load-bearing capacity, and the better its anti-interference performance and electrical conductivity. But at the same time, the increase in the thickness of the outer copper layer will also lead to an increase in cost and manufacturing difficulty.
āInner layer copper thicknessā is used for internal connections and signal transmission of the circuit board, and its selection also depends on the application requirements and design needs of the circuit board. The thickness of the inner copper layer generally ranges from 0.5-2oz, with the more common ones being 0.5oz, 1oz, and 2oz. If the circuit board needs to transmit high-speed signals, a larger inner copper thickness should be selected. The increase in the thickness of the inner copper layer will also lead to an increase in cost and manufacturing difficulty.
āCopper Thickness StandardāAccording to international standards, the copper thickness of PCB boards can be divided into standard copper thickness (such as 1oz and 2oz) and non-standard copper thickness (such as 0.5oz, 3oz and 4oz). In practical applications, some special PCB boards may require higher copper thickness, such as high-power LED lights, electronic high-frequency circuits, etc.
To sum up, the choice of different copper thicknesses is to meet specific circuit board design needs, including conductive performance, anti-interference performance and other requirements. At the same time, the choice of copper thickness also needs to consider aspects such as cost and manufacturing difficulty.
Conclusion:
By controlling the thickness of copper on the PCB to meet different usage requirements, applications that require large currents will naturally require PCBs with thicker copper foils. However, PCBs that require thicker copper foils are a great test of the capabilities of PCB manufacturers. BEST Technology has accumulated rich production experience in the PCB manufacturing industry and has many years of manufacturing experience for PCBs with different copper thicknesses. We can meet any PCB copper thickness requirements.