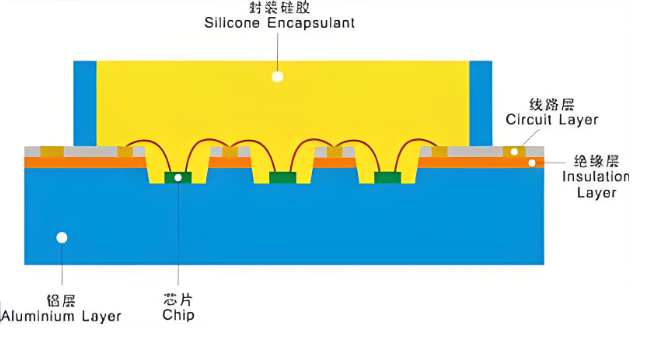
China MCPCB LED board suppliers are now offering more flexible, fast, and dependable solutions to global lighting brands. Whether you’re a startup or scaling up, choosing the right Chinese PCB manufacturer makes a real difference. In this blog, weâll go through the core questions customers usually ask and how a reliable partner like EBest Circuit (Best Technology) can simplify the buying experience.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) provides high-quality China MCPCB LED boards and delivers trustworthy and reliable LED PCB assembly services to the very large market. We are most trustworthy in optimizing our supply chain, offering high-mix MCPCB LED boards selections, achieving high yield, maintaining a stable manufacturing process, ensuring short lead times, providing fast after-sales service, and preserving quality consistency.
There are some well-known brands that make a long-term relationship with us. And we still maintain a high customer retention rate. If you would like to inquire about any MCPCB LED boards, our team is always available to discuss your project details by phone or email and provide viable solutions. Our phone number is +86-18923412995. Email sales@bestpcbs.com is also ok. You can also talk to us online via this link.

Who Provides China MCPCB LED Board?
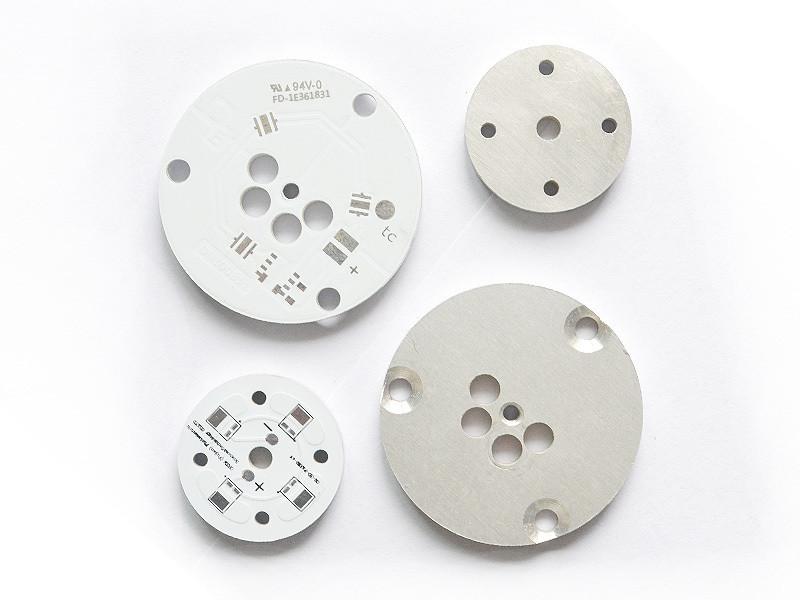
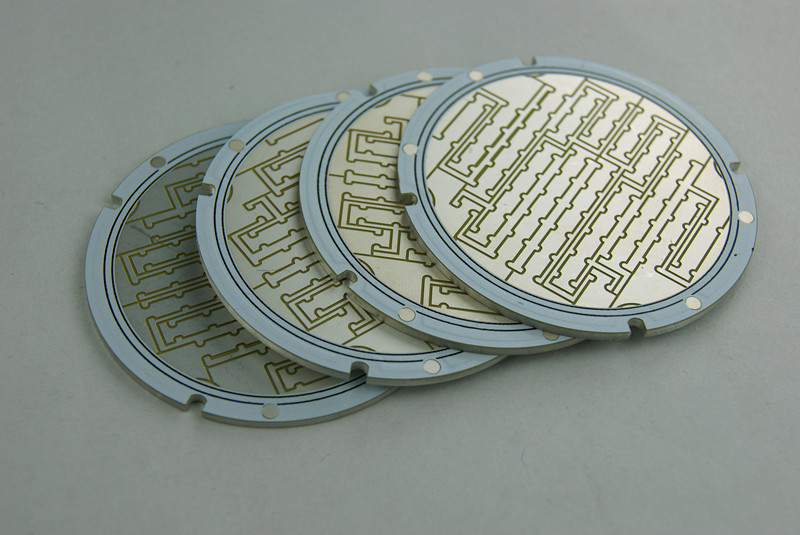
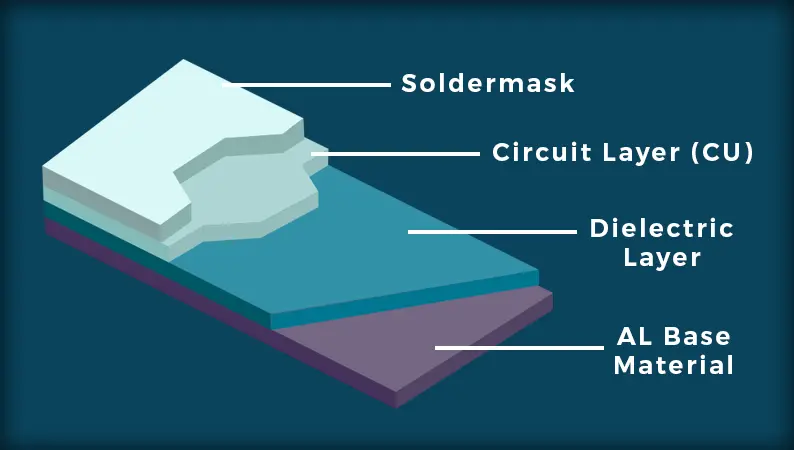
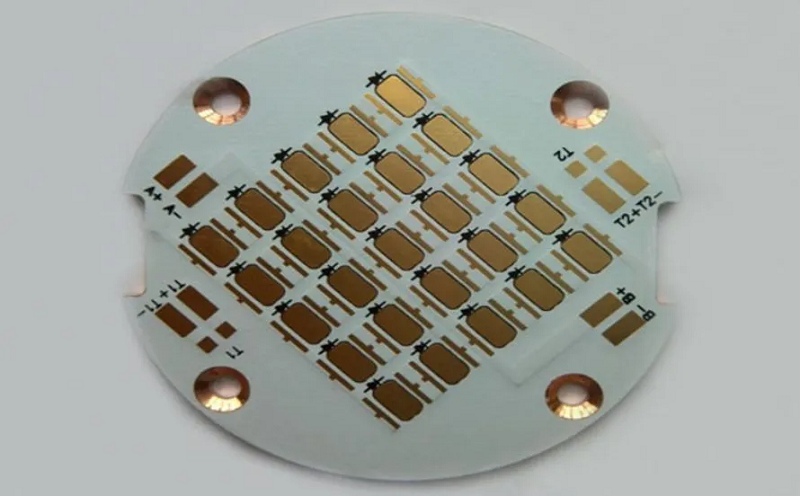
There are hundreds of Chinese PCB manufacturers, but only a few specialize in MCPCB LED boards. These boards, made with metal core bases like aluminum or copper, need professional manufacturing. Reliable suppliers like EBest Circuit (Best Technology) focus on high-precision drilling, consistent thermal conductivity, small-batch support, lead time reduction, and complete material traceability. Our strength lies in combining fabrication with engineeringâso you donât just get a board, you get a well-designed, ready-to-use solution.

What Is China MCPCB LED Board Price?
China MCPCB LED board price depends on size, copper thickness, layer count, and surface finish. Smaller boards with standard specs may cost as low as $0.20 per piece. More advanced types like high-wattage copper-core boards cost more. But what truly matters is not just low pricingâitâs the value. EBest Circuit (Best Technology) offers reasonable pricing thanks to bulk raw material sourcing and automatic MES tracking. We help you control costs while meeting strict technical demands.
What Are the Advantages of Buying MCPCB LED Board from Chinese PCB Manufacturers?
There are clear benefits of working with Chinese PCB manufacturers:
- Speed:Â Fast quoting, short lead times, and on-time shipping.
- Cost efficiency:Â Lower labor and material costs reduce your expenses.
- Technical support: Experts help you with MCPCB design suggestions before production.
- Turnkey service:Â From prototyping to mass production and assembly.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) stands out with in-house DFM checking, thermal simulation tools, and a full testing line including flying probe, AOI, and X-ray inspection. We are a qualified MCPCB LED board factory, compliant with ISO 9001, ISO 13485, IATF 16949, AS9100D, UL, REACH, RoHS. That ensures reliability, not just savings.
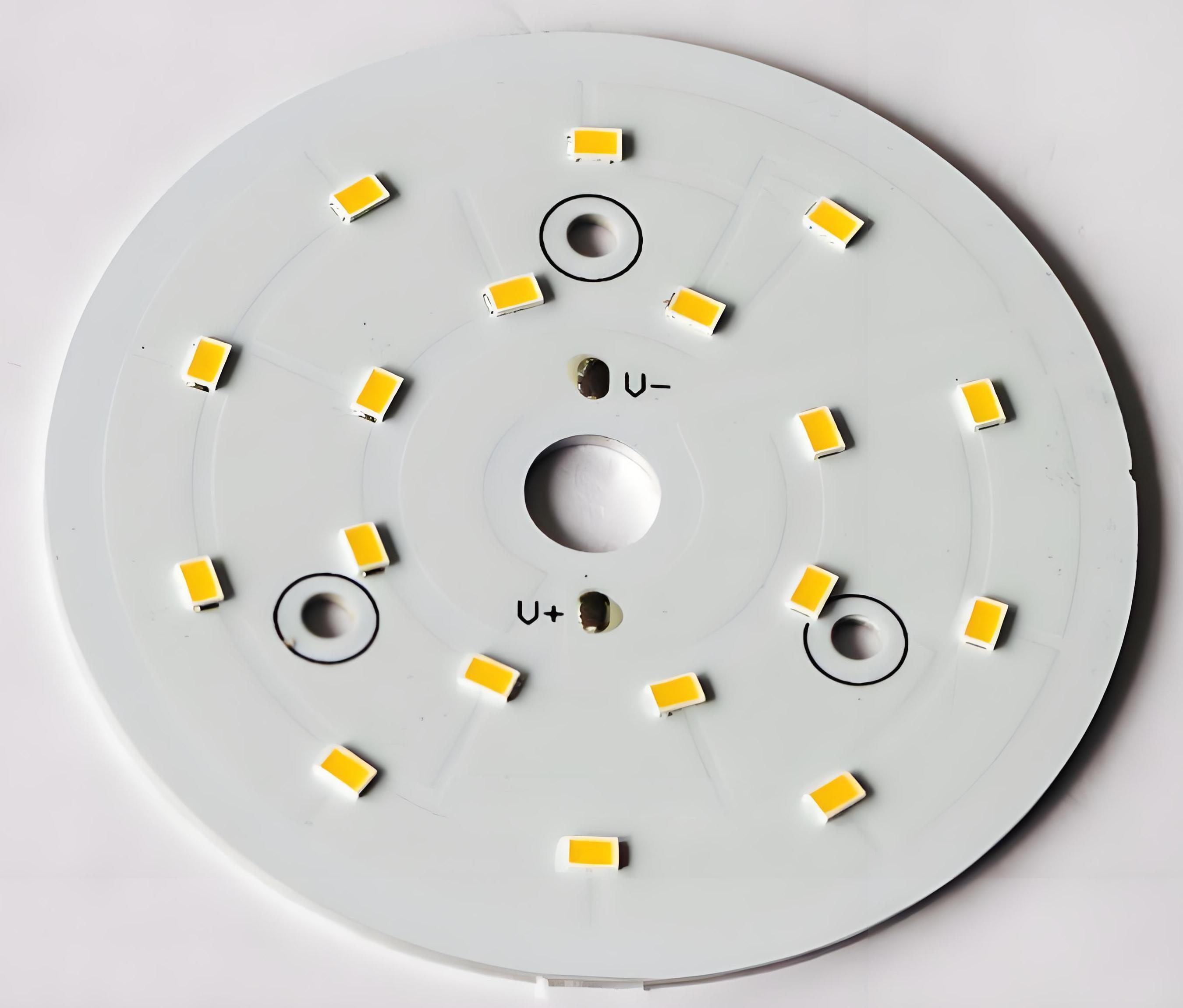
Where to Use China MCPCB LED Board 12V?
China MCPCB LED board 12VÂ is widely used in LED lighting systems. You’ll find them in:
- LED ceiling lamps
- Swimming Pool Light
- Street lighting
- Backlight modules
- Automotive LED systems
- Medical devices
12V MCPCBs are stable, easy to integrate, and safe for both indoor and outdoor use. EBest Circuit (Best Technology) supports customization in wattage, dimensions, and surface coating so customers can build to spec with no worries.

Where to Get MCPCB Design?
MCPCB design plays a key role in thermal control and product life. If the layout is poor, LEDs overheat or fail. Many buyers donât have in-house engineers, so they turn to manufacturers. EBest Circuit (Best Technology) provides one-on-one design guidance with quick CAD reviews and thermal modeling support. Whether you want a single-layer or complex structure, our team helps optimize the circuit to match your exact requirements.
How to Ensure Quality of MCPCB Board Buy from Chinese PCB Manufacturers?
When you buy an MCPCB board from a Chinese supplier, you’re not just looking for specs on paperâyou want dependable and repeatable quality. At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we follow strict IPC standards and use a MES system to track every production step. Full material traceability is built into our process to avoid mix-ups and ensure consistency.
We understand that many buyers have had issues beforeâpoor plating, misaligned drilling, or weak thermal bonding. To address these concerns, we carry out a full range of quality checks, including:
- 100% electrical testing to verify open and short circuits
- Solderability tests to confirm pad surface finish integrity
- Insulation resistance measurement to ensure safety in high-voltage applications
- Thermal aging tests, following a standard of 85°C at 85% RH for 1000 hours, to assess long-term stability under harsh environments
- Thermal resistance (Rth) tests, critical for MCPCB performance, to verify heat dissipation efficiency
- X-ray inspection, especially for boards with buried vias or inner layer bonding, to detect voids or misalignment inside the structure
We also provide complete test reports for your approval before final shipment. This way, you know exactly what quality level you’re getting.
Why Choose EBest Circuit (Best Technology) for Your Dependable China PCB Manufacturer?
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) doesnât just sell boards. We solve problems. Many customers come to us because they struggled with vague communication, poor DFM checks, or unstable lead times elsewhere. Hereâs how we help:
- Fast response:Â Quotes in 4 hours, engineering reply in 12 hours.
- Clear tracking:Â MES system shows real-time production status.
- Certifications:Â ISO 9001, IATF 16949, ISO 13485, and AS9100D.
- Flexibility:Â Low MOQ, urgent builds, and trial runs supported.
- Full transparency:Â From stack-up to material sourcing.
- One-stop service: We provide material procurement, MCPCB design, MCPCB prototype, mass production, and MCPCB assembly service under one roof.
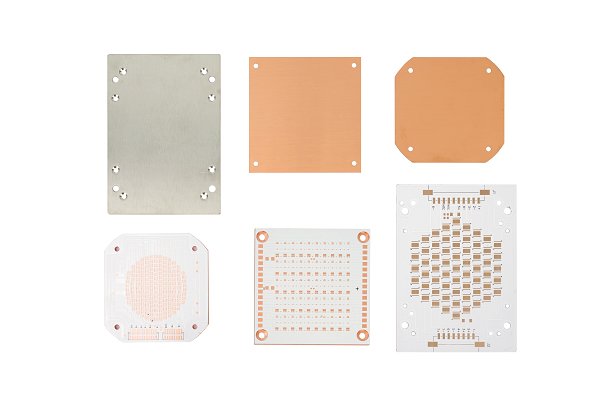
- Customization: No matter whether you need single-layer MCPCB, two-layer MCPCB, multi-layer MCPCB, COB MCPCB, double-sided MCPCB, or IMS PCB, we present support without any MOQ.
We take quality control seriously. For example, our X-ray checks verify LED solder joints inside aluminum MCPCBs. Our team supports multiple marketsâautomotive, aerospace, medical, and general lighting. You can always reach out to our teams for any concerns. Our sales engineers possess strong technical knowledge, allowing them to address your issues directly. When you encounter difficulties, our sales team will provide you with the appropriate answers and solutions without making you wait for responses from the engineers.
To summarize, if youâre tired of delays, unclear specs, or inconsistent product quality, then itâs time to try a new partner. At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we offer not just China MCPCB LED board manufacturing but a whole process of support. From smart design to final shipment, weâre here to back you up. For more information or if you would like to send us any inquiry, please send us an email through the contact form at the bottom of our Contact Page.