A BMS PCB board (Battery Management System Printed Circuit Board) is the essential protection and control system used in lithium battery packs, especially in 18650, Li-ion, LiPo, and LiFePO₄ applications. From simple consumer electronics to EV battery packs, the BMS PCB ensures safe charging, stable discharging, cell balancing, and real-time battery monitoring.
This guide covers everything you need to know about BMS PCBs—including how they work, types, key functions, how to choose the right board, how to test it, and why EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is a trusted BMS PCB manufacturer.

What Is a BMS PCB Board?
A BMS PCB board is an electronic circuit board designed to monitor, protect, and balance lithium battery cells. It ensures that the battery pack stays within safe operating limits, avoiding overcharging, over-discharging, overcurrent, overheating, and short circuits.
A typical BMS PCB contains:
- Protection IC
- MOSFET charge/discharge control
- Current shunt resistors
- Temperature sensors
- Balancing circuitry
- Communication chips (CAN, UART, RS485, Bluetooth, etc.)
- Thick-copper power traces
- Thermistors and connector interfaces
Because lithium batteries are highly sensitive to voltage and current fluctuations, a BMS PCB ensures that every cell operates safely and efficiently.
Types of BMS PCB Board
BMS PCBs come in several categories based on battery type, cell configuration, communication, and protection function.
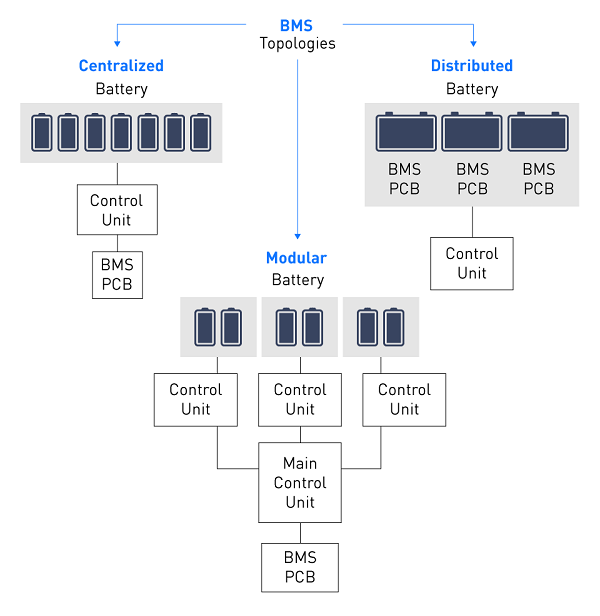
1. Based on Cell Configuration
- 1S BMS – single-cell lithium battery
- 2S–6S BMS – common for 18650 packs
- 7S–16S BMS – used in e-bikes, scooters
- 20S–24S and above – used in ESS and EV packs
2. Based on Balancing Method
- Passive balancing BMS (energy dissipated through resistors)
- Active balancing BMS (more efficient; redistributes energy between cells)
3. Based on Protection Function
- Basic protection boards (Over/Under-voltage, Overcurrent)
- Smart BMS (with Bluetooth, CAN, UART control, SOC/SOH monitoring)
4. Based on Application
- 18650 battery packs
- Power tools
- E-bike batteries
- Solar storage batteries
- Medical devices
What Does a BMS Board Do?
A BMS PCB board (Battery Management System PCB) is the central controller responsible for ensuring that lithium battery packs operate safely, efficiently, and reliably. Since lithium batteries are sensitive to voltage, current, temperature, and balancing differences, the BMS acts as an intelligent guardian that constantly supervises the entire pack. Its functions including:
1. Overcharge Protection
2. Over-Discharge Protection
3. Overcurrent & Short-Circuit Protection
4. Temperature Protection
5. Cell Balancing
6. Charging/Discharging Control
7. SOC/SOH Estimation (Smart BMS)
8. Communication & Data Reporting (for smart BMS)
These features make the BMS the “brain” of a lithium-ion battery pack.
How Does a BMS Board Work?
A BMS PCB operates by continuously monitoring voltage, current, and temperature. Here is the basic workflow:
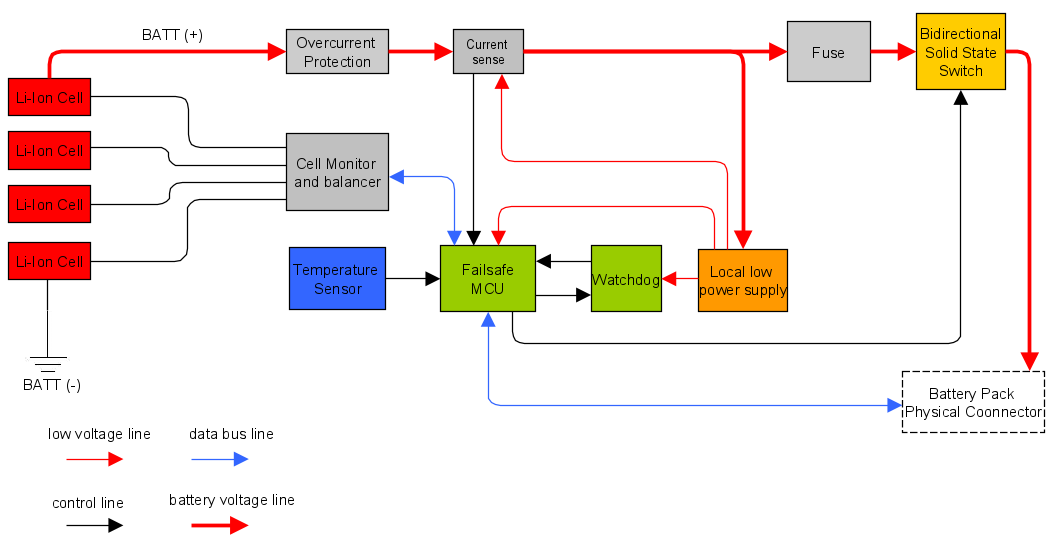
1. Voltage Sensing
Each cell’s voltage is monitored through sense lines to prevent overcharge/over-discharge.
2. Current Measurement
A shunt resistor or Hall sensor measures current passing through the pack.
3. MOSFET Switching
The BMS activates or deactivates charging/discharging MOSFETs to protect the battery.
4. Temperature Monitoring
Sensors detect overheating and disable charging/discharging if needed.
5. Balancing Circuit
If one cell becomes higher than others, balancing resistors bleed excess charge until all cells match.
6. Control Unit (in Smart BMS)
A microcontroller processes data and communicates via CAN, UART, RS485, etc.
The result is a stable, safe, efficiently managed battery system.
What Is the Difference Between PCM and BMS?
| Feature | PCM (Protection Circuit Module) | BMS (Battery Management System) |
| Basic Protection | ✔ Overcharge / Overdischarge / Overcurrent | ✔ Includes PCM features |
| Cell Balancing | ❌ Usually none | ✔ Supports balancing |
| Communication | ❌ None | ✔ CAN, UART, RS485, Bluetooth |
| Data Logging | ❌ No | ✔ SOC, SOH, temperature, cycles |
| Complexity | Simple | Advanced |
| Applications | Small electronics, 18650 packs | EVs, ESS, scooters, UPS |
PCM = basic protection
BMS = complete monitoring and management system
What Is a BMS PCB Used For?
A BMS PCB is used in all lithium-ion battery applications, such as:
- 18650 battery packs (flashlights, e-bikes, power tools)
- Electric vehicles (EV, HEV, PHEV)
- Energy Storage Systems (ESS)
- Solar battery systems
- UPS / backup power
- Drones, UAVs, robotics
- Medical devices
- Smart home appliances
- Portable electronics
- E-scooters and e-motorcycles
Any application requiring safe lithium battery operation needs a BMS PCB.
Can I Run a Lithium Battery Without a BMS?
No — it is unsafe to run a lithium-ion battery without a BMS.
Without protection, lithium batteries can experience:
- Overcharging → thermal runaway, fire, explosion
- Over-discharging → permanent battery damage
- Overcurrent → pack overheating
- Cell imbalance → capacity drop, premature aging
Using a lithium-ion battery without a BMS is highly dangerous and not recommended.
How to Choose a PCB BMS Protection Board?
Selecting the right PCB BMS protection board is crucial for safety, performance, and battery lifespan. Here’s a detailed guide to help you choose correctly:
1. Select Based on Battery Chemistry
Different lithium chemistries have distinct voltage requirements:
| Battery Type | Max Charge Voltage | Needs BMS? |
| Li-ion / NMC | 4.20V | ✔ Yes |
| LiPo | 4.20V | ✔ Yes |
| LiFePO₄ | 3.65V | ✔ Yes |
Using the wrong BMS for your chemistry may cause incorrect cutoff points.
2. Determine the Number of Series Cells (S Count)
A BMS must match the battery pack’s series number:
| Pack | BMS Needed |
| 3S (11.1V) | 3S BMS |
| 4S (14.8V) | 4S BMS |
| 7S (24V) | 7S BMS |
| 10S (36V) | 10S BMS |
| 13S (48V) | 13S BMS |
| 16S (60V) | 16S BMS |
3. Choose Continuous Discharge Current Rating
BMS current rating must exceed your maximum load.
| Application | Suggested Current |
| Power banks | 3–10A |
| Tools / drones | 20–45A |
| E-bikes | 20–35A |
| E-scooters | 40–60A |
| ESS / inverter | 80–200A+ |
High current BMS PCBs require wide copper traces and heavy copper layers (2–10 oz).
4. Pick Balancing Type
- Passive balancing → economical, good for small/medium packs
- Active balancing → high efficiency, ideal for EV and solar storage
Choose based on expected lifetime and precision needed.
5. Decide Whether You Need Smart Communication
Choose Smart BMS if you need:
- Real-time monitoring
- CAN communication with motor controller
- Bluetooth APP
- RS485 for energy storage
- SOC/SOH estimates
If not required, a simpler PCM or basic BMS is enough.
6. PCB Structure Requirements
For reliable high-power protection boards, a proper PCB structure is essential:
- High TG material (TG ≥150°C)
- Thick copper (2–4 oz or higher)
- Reinforced pads for MOSFETs
- Wide trace routing for current paths
- Good thermal dissipation design
- ENIG finishing for stable bonding
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) specializes in heavy-copper PCBs designed specifically for BMS modules.
7. Safety Certifications
Depending on product category/status:
- UL
- CE
- RoHS
- IEC62133
- UN38.3
Choosing a compliant BMS PCB manufacturer enable to reduce risks and improves product reliability.
How to Test the BMS PCB Board?
Testing a BMS PCB board is crucial to ensure it performs safely and reliably before being integrated into a lithium battery pack. A well-designed Battery Management System must accurately sense voltages, manage current, protect against faults, and communicate with other system components. Below are 5 essential BMS PCB testing methods, each commonly used in manufacturing and engineering validation.
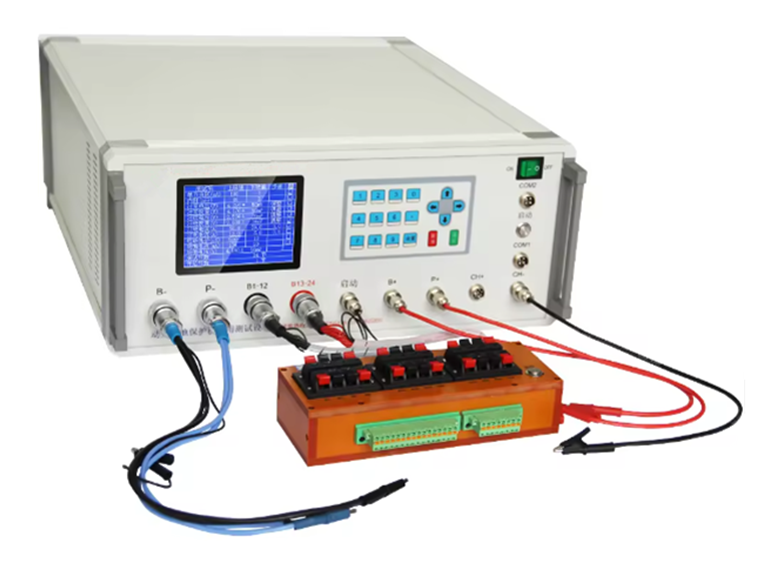

1. Visual Inspection (Surface & Solder Joint Check)
Purpose: Identify obvious defects before powering the board.
How it works:
Technicians use AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) or manual magnification tools to check:
- Solder bridge, cold solder joints
- Component orientation errors
- Missing or misplaced components
- PCB surface damage, cracks, or contamination
This step ensures the board is physically ready for electrical testing and prevents short circuits during power-up.
2. Continuity & Insulation Test (Shorts and Opens Test)
Purpose: Verify PCB traces, vias, and components are correctly connected.
How it works:
Using a multimeter or flying-probe tester, engineers check:
- Shorts between power rails
- Open circuits on balancing lines
- Proper grounding and isolation between channels
This test eliminates wiring errors that could cause BMS malfunction or overheating.
3. Cell Voltage Detection Accuracy Test
Purpose: Ensure the BMS measures each cell’s voltage correctly.
How it works:
A variable DC power source simulates individual battery cells. The tester adjusts voltage (e.g., 2.5V → 4.2V for Li-ion cells) and compares:
- Actual input voltage
- BMS measurement output (through UART/CAN/I²C or display)
Acceptable deviation is usually ±5–10 mV for quality BMS boards.
Accurate detection is crucial for safe charging and balancing.
4. Protection Function Test (OVP, UVP, OCP, SCP)
Purpose: Confirm the BMS triggers proper protection responses.
How it works:
Engineers simulate fault conditions:
- Over-voltage protection (OVP): Gradually raise simulated cell voltage until BMS disconnects charging.
- Under-voltage protection (UVP): Lower cell voltage until BMS cuts off discharging.
- Over-current protection (OCP): Apply load current beyond spec to check if the MOSFET shuts off.
- Short-circuit protection (SCP): Momentarily create a low-resistance path to verify BMS reacts instantly.
5. Balancing Function Test (Active/Passive Balance Check)
Purpose: Verify that the BMS can equalize cell voltages.
How it works:
Setting slight voltage differences between simulated cells. The BMS should under one of below situations:
- Activate resistance bleeding (passive balance)
- Transfer energy between cells (active balance)
Engineers measure:
- Balance current
- Trigger threshold
- Balance response time
Balancing tests ensure better battery lifespan and capacity utilization.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology)’s BMS PCB Manufacturing Service
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is a professional BMS PCB board and PCB & PCBA manufacturer with over 18 years of experience, providing high-reliability battery protection boards for lithium battery companies worldwide.
Why Choose EBest Circuit (Best Technology) for BMS PCB?
✔ 2–10 oz heavy-copper BMS PCBs
✔ High-TG board materials specialized for high-current
✔ IPC Class 2 & Class 3 manufacturing
✔ SMT + through-hole assembly for BMS MOSFETs/ICs
✔ 100% functional testing
✔ Customized 1S–30S BMS PCB solutions for 18650, LiFePO4, NMC
Industries We Support
- E-bike & scooter battery manufacturers
- Energy storage system providers
- Drone and UAV companies
- Power tool manufacturers
- Custom lithium battery pack makers
If you need BMS PCB prototype, small batch, or mass production, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) provides fast turn-around and engineering support.
FAQs
1. What type of BMS do I need for 18650 batteries?
Choose a BMS based on your pack configuration (1S–13S), your total continuous current (5A–60A for standard packs), and whether you need balancing or communication. A BMS PCB protection board for 18650 should match the battery chemistry and voltage thresholds.
2. Does BMS drain the battery?
Yes, but only slightly. A typical BMS has very low standby current (10–100 µA), which minimally affects overall battery life. High-quality BMS PCBs have optimized low-power designs to reduce parasitic drain.
3. What is a BMS PCB board used for?
A BMS PCB board is used to protect, monitor, and manage lithium-ion battery packs. It prevents overcharge, over-discharge, overcurrent, overheating, and cell imbalance. BMS PCBs are commonly used in 18650 battery packs, e-bikes, EVs, solar systems, UPS units, drones, and portable electronics.
4. What is balancing in a BMS?
Balancing ensures all cells in a series pack maintain equal voltage. This prevents weak cells from becoming overstressed, improves efficiency, and extends battery lifespan. Balancing can be passive (bleeding excess charge) or active (redistributing charge).
5. Why is my BMS cutting off power?
Your BMS may cut off power due to:
- Overcurrent
- Short circuit
- Over-discharge
- Overcharge
- High temperature
- Cell voltage imbalance
6. How long does a BMS last?
A high-quality BMS PCB typically lasts 5–10 years, depending on usage, heat exposure, component quality, and environment. Industrial-grade BMS modules can last even longer.
7. What happens if a BMS fails?
If a BMS fails, the battery may overcharge, over-discharge, or overheat. This can lead to permanent cell damage or dangerous thermal runaway. Therefore, quality manufacturing and thorough testing are essential for preventing BMS failure.


