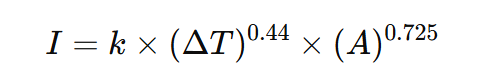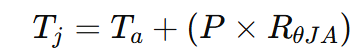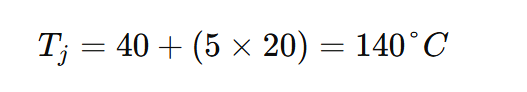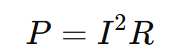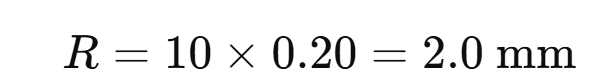Contract manufacturing electronic assembly is a strategic manufacturing model that helps OEMs turn PCB designs into finished, tested, and scalable electronic products with better speed, process control, and supply chain coordination. This article explains the engineering workflow, thermal calculations, sourcing integration, capability evaluation, production scaling, design support, electro-mechanical assembly, quality control, and global market landscape behind expedited electronic assembly services.
Common Customer Pain Points Often Look Like This:
- DFM issues are found too late and delay launch.
- PCB fabrication, sourcing, and assembly are split across too many vendors.
- Thermal and current limits are not verified early enough.
- Prototype success does not transfer smoothly into volume production.
- Supplier communication is slow when urgent changes happen.
How A Manufacturer Responds To Those Pain Points:
- Review Gerber, BOM, and assembly risks before release.
- Combine PCB fabrication, sourcing, and PCBA under one workflow.
- Validate thermal paths and current carrying capacity during engineering review.
- Build processes that support both low-volume and mass production.
- Use responsive project management for expedited service execution.
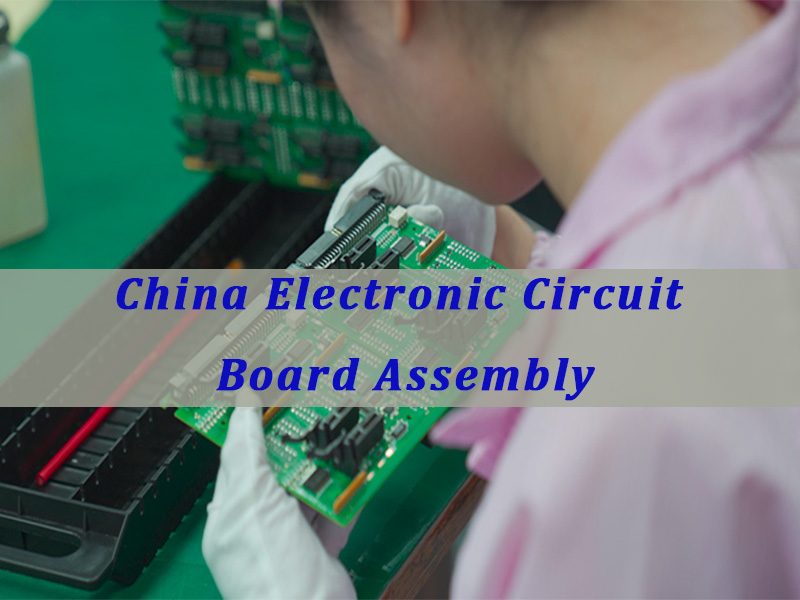
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is a professional PCB and PCBA manufacturer focused on prototype, low-volume, and medium-batch electronic products that require fast turnaround and dependable engineering support. We provide PCB fabrication, component sourcing, SMT, DIP, testing, and box-build integration with a practical engineering mindset, helping customers shorten development cycles while improving manufacturability and delivery reliability. For project support, pls feel free to contact us via sales@bestpcbs.com.

What Engineering Processes Are Included In Contract Manufacturing Electronic Assembly From DFM To Final Testing?
A strong contract manufacturing electronic assembly process is not just about placing parts on a PCB. It is a controlled engineering chain that starts with design review and ends with validated product output. For expedited service, each step must be linked clearly to the next.
Typical Engineering Flow
| Stage | Main Task | Core Output |
|---|---|---|
| DFM Review | Check manufacturability risk | DFM comments |
| BOM Review | Verify parts, alternates, lifecycle | BOM optimization |
| PCB Fabrication Prep | Confirm stack-up, finish, panelization | Fabrication release |
| SMT/DIP Process Setup | Define stencil, fixture, profile | Process package |
| Assembly Execution | Mount, solder, inspect | Assembled PCBA |
| Testing | AOI, X-Ray, ICT, FCT | Test records |
| Final Inspection | Verify workmanship and labeling | Shipment approval |
Key Engineering Elements
- DFM Review: pad design, spacing, via structure, solder mask clearance, fiducials, panel strategy.
- BOM Validation: availability, substitute control, package consistency, MPN conflicts, EOL exposure.
- Process Engineering: stencil thickness, reflow profile, wave or selective solder settings, fixture design.
- Inspection Planning: AOI rules, X-Ray criteria, critical polarity checkpoints, hidden joint control.
- Functional Verification: ICT, flying probe, FCT, burn-in where required.
Why This Matters In Expedited Service
- Early DFM reduces rework loops.
- BOM review prevents last-minute sourcing failures.
- Process setup improves first-pass yield.
- Testing protects outgoing quality.
- Documented flow supports repeat orders.
In practical terms, electronics assembly contract manufacturing works best when engineering, purchasing, production, and QA are aligned from day one. That alignment is what turns a rush order into a controlled build rather than a reactive one.
How To Calculate Thermal Dissipation And Current Carrying Capacity In Contract Manufacturing Electronic Assembly Designs?
For expedited builds, thermal and electrical validation cannot be treated as a late-stage check. In contract manufacturing electronic assembly projects, overheating, trace overload, and poor heat spreading can quickly undermine reliability even if assembly quality looks fine.
1) Thermal Resistance Calculation
A simple thermal model begins with:
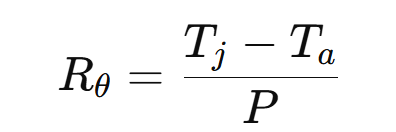
Where:
- (R_{\theta}) = thermal resistance (°C/W)
- (T_j) = junction temperature
- (T_a) = ambient temperature
- (P) = power dissipation (W)
Example:
If a device has a junction limit of 125°C, ambient is 45°C, and power is 4 W:
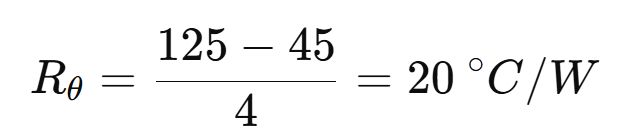
That means the full thermal path from junction to air must stay at or below 20°C/W.
2) PCB Trace Current Carrying Capacity
A widely used engineering expression based on IPC practice is:
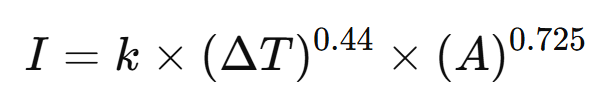
Where:
- (I) = allowable current
- (\Delta T) = temperature rise
- (A) = conductor cross-sectional area
- (k) = layer constant
Quick Design Factors
| Factor | Higher Value Effect | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Copper Thickness | Increases current capacity | Better for power lines |
| Trace Width | Lowers resistance | Reduces temperature rise |
| Copper Plane Area | Improves heat spread | Better thermal stability |
| Thermal Vias | Moves heat vertically | Helps hot components |
| Airflow | Improves cooling | Lowers junction temp |
What Engineers Should Check
- Power components near thermal bottlenecks
- Copper thickness on high-current nets
- Internal vs external trace conditions
- Via-in-pad or thermal via arrays under power packages
- Safe margin between actual and allowable temperature rise
An experienced electronic assembly contract manufacturer does not only assemble what is drawn. It also flags thermal imbalance, copper weakness, and layout risks before they become field failures. That is especially important in power supplies, motor control boards, LED drivers, telecom modules, and industrial control systems.
In short, thermal dissipation and current capacity calculations help convert a fast build into a reliable one. Speed without thermal validation is fragile. Speed with engineering discipline is scalable.
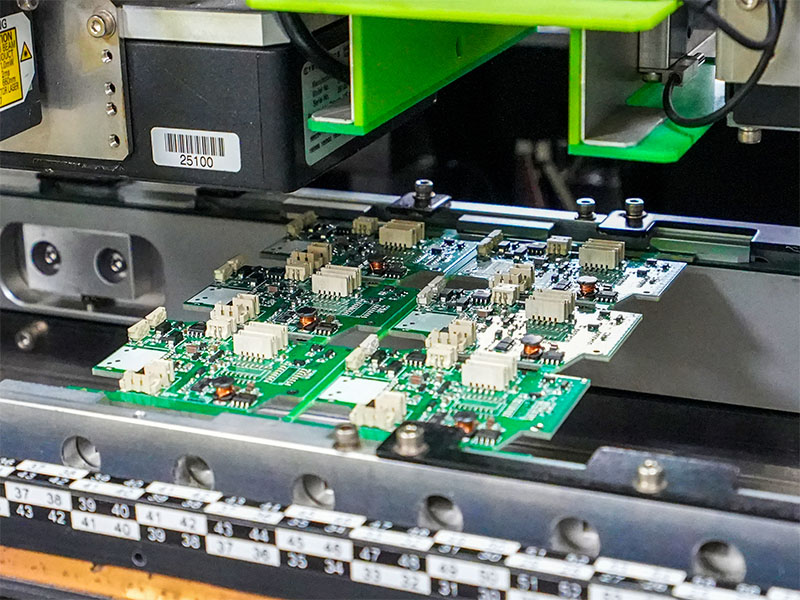
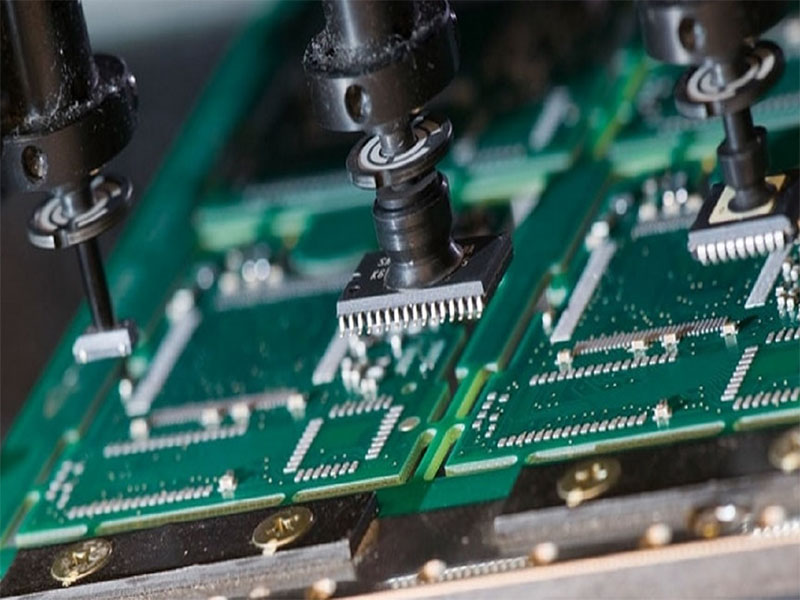
How Do Electronic Assembly Contract Manufacturers Handle PCB Fabrication, Component Sourcing, And PCBA Integration?
Customers often struggle when PCB fabrication, procurement, and assembly are managed by separate vendors. A mature electronic assembly contract manufacturer reduces that friction by integrating the full chain into one coordinated workflow.
Integrated Workflow Structure
- PCB Fabrication: stack-up review, surface finish selection, impedance control, panelization, fabrication release.
- Component Sourcing: approved vendor purchasing, lead-time control, alternates management, shortage response.
- PCBA Assembly: SMT, THT, reflow, wave/selective soldering, cleaning, inspection, testing.
- Logistics Coordination: incoming material control, line kitting, build scheduling, traceable shipment release.
What Good Integration Looks Like
| Area | Poor Coordination Result | Integrated Result |
|---|---|---|
| PCB + BOM Timing | Idle assembly line | Synchronized material arrival |
| Shortage Handling | Last-minute delay | Approved alternates ready |
| Engineering Change | Document mismatch | Controlled ECO execution |
| Build Planning | Mixed priorities | Clear production scheduling |
Practical Benefits
- Fewer handoff errors.
- Faster feedback between sourcing and engineering.
- Shorter turnaround for prototypes.
- Better traceability from bare board to final assembly.
- Easier root-cause analysis when issues appear.
This is where electronic assembly contract manufacturing becomes more than a purchasing model. It becomes an execution model. For expedited service, that execution discipline is often the difference between an on-time build and a delayed launch.
What Manufacturing Capabilities Should You Evaluate In Electronic Assembly Contract Manufacturing Partners?
Not all partners that offer electronic assembly contract manufacturing have the same engineering depth or production fit. A useful evaluation should go beyond brochure language and focus on capability that affects yield, lead time, and product consistency.
Capability Checklist
- PCB Range: layer count, material system, copper weight, HDI, impedance control.
- Assembly Range: fine-pitch SMT, BGA, QFN, THT, mixed technology, double-sided assembly.
- Inspection Tools: AOI, X-Ray, SPI, flying probe, ICT, FCT.
- Production Flexibility: prototype, NPI, low-volume, repeat batch, mass production.
- Traceability System: lot control, barcode tracking, process records, test history.
- Engineering Support: DFM, DFA, BOM review, alternate recommendation, process optimization.
Fast Screening Table
| Capability | Why It Matters |
|---|---|
| Fine-Pitch SMT | Supports dense modern designs |
| BGA/X-Ray | Controls hidden solder joints |
| Prototype + Volume | Enables growth path |
| Material Sourcing Team | Reduces shortage risk |
| Test Engineering | Improves outgoing reliability |
| Process Traceability | Supports regulated industries |
Questions Worth Asking
- Can the supplier support both quick-turn NPI and stable repeat production?
- Can it manage difficult packages and mixed assembly processes?
- Does it provide engineering feedback before production starts?
- How does it respond to shortages and urgent ECOs?
- What evidence does it provide for quality control?
A reliable partner in electronics assembly contract manufacturing should make your product easier to launch, easier to scale, and easier to control. If it only offers placement capacity without engineering support, the risk remains with the customer.
How Does Electronics Contract Manufacturing Assembly Support Low Volume Prototyping And Mass Production?
One of the biggest challenges in electronics contract manufacturing assembly is moving smoothly from prototype to scale. A rushed prototype may prove function, but it does not automatically prove manufacturability. Good contract assembly service bridges both stages with process continuity.
Low-Volume Prototype Priorities
- Fast engineering review
- Manual or semi-automated flexibility
- Rapid material substitution handling
- Frequent revision support
- Quick debug feedback
Mass Production Priorities
- Stable approved BOM
- Standardized work instructions
- Line balancing and fixture planning
- Yield monitoring
- Controlled logistics and replenishment
Comparison Table
| Build Type | Main Goal | Typical Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Prototype | Verify design | Speed and flexibility |
| Pilot Run | Validate process | Repeatability |
| Mass Production | Deliver volume | Stability and cost control |
How A Good Manufacturer Supports Both
- Keeps the same engineering data structure from NPI to production.
- Records process settings that can be reused later.
- Captures defects early and feeds them back to design.
- Builds scalable sourcing plans around real demand.
- Aligns inspection depth with product risk and stage.
This is why contract manufacturing electronics assembly is valuable for OEMs that expect growth. It is not just about assembling todayâs boards. It is about building a repeatable path from first article to mature production.
What Engineering Services Are Provided In Contract Design And Manufacturing Electronic Assembly Projects?
In contract design and manufacturing electronic assembly projects, the supplier may contribute far more than assembly labor. The right engineering service can reduce redesign cycles, improve reliability, and speed up qualification.
Common Engineering Services
- DFM and DFA review
- BOM optimization
- Alternate component evaluation
- PCB stack-up suggestion
- Thermal and current path review
- Panelization support
- Test point planning
- Fixture and stencil design
- Process profile development
Service Breakdown
| Service | Value To Customer |
|---|---|
| DFM Review | Prevents fabrication and assembly defects |
| BOM Optimization | Improves availability and cost stability |
| Thermal Review | Reduces overheating risk |
| Test Planning | Makes debugging and validation easier |
| Process Setup | Improves yield on first build |
Where This Helps Most
- New product introduction
- Mixed-technology boards
- Dense PCBs with thermal load
- Long-lead or shortage-prone BOMs
- Products needing fast release
A supplier that supports contract design and manufacturing electronic assembly well is acting as an engineering extension of the customer, not just a production stop. For expedited service, that shared engineering effort saves time where it matters most: before material is committed and before defects multiply.
What Is Electro-Mechanical Assembly For Electronics Contract Manufacturing And Where Is It Used?
Electro-mechanical assembly for electronics contract manufacturing refers to the integration of electronic assemblies with mechanical elements such as enclosures, harnesses, connectors, switches, fans, brackets, displays, and power modules. It takes the product from board level toward system level.
Typical Scope
- PCB + enclosure integration
- Cable and wire harness assembly
- Connector installation
- Mechanical fastening
- Display and HMI integration
- Fan, sensor, and power module mounting
- Final box-build and system test
Common Applications
- Industrial control units
- Medical devices
- Telecom equipment
- EV charging modules
- Security systems
- Consumer electronics
- Embedded control products
Typical System-Level Benefits
- Fewer assembly handoffs.
- Better fit between PCB and housing.
- Lower shipping and handling damage risk.
- Simpler final product logistics.
- More complete outgoing testing.
When OEMs need more than bare PCBA, this service becomes highly practical. It is especially useful when cable routing, connector access, thermal layout, or final mechanical packaging affects field performance.
How Does Contract Manufacturing Electronics Assembly Ensure Quality And Supply Chain Stability?
For expedited orders, quality and supply chain stability must move together. A fast build with weak sourcing control creates shortage risk. A well-sourced build with weak process control creates field risk. Strong contract manufacturing electronics assembly addresses both.
Quality Control Structure
- Incoming material inspection
- SPI for solder paste consistency
- AOI after SMT
- X-Ray for BGA and hidden joints
- ICT or flying probe for electrical checks
- Functional test for product behavior
- Final visual and packaging inspection
Supply Chain Stability Methods
- Approved vendor lists
- Alternate part strategy
- Lifecycle monitoring
- Safety stock for repeat projects
- Lot traceability
- Shortage escalation process
Condensed Control Table
| Control Area | Stabilizing Method |
|---|---|
| Material Quality | Incoming IQC |
| Solder Process | SPI + profile control |
| Hidden Joints | X-Ray inspection |
| Functional Confidence | ICT/FCT |
| Part Shortages | AVL + alternates |
| Traceability | Barcode and batch records |
What Customers Should Expect
- Transparent shortage communication.
- Evidence-based quality records.
- Controlled handling of substitutions.
- Repeatable build documentation.
- Fast response when corrective action is needed.
This is where electronics assembly contract manufacturing shows its real value. It protects both the schedule and the shipment quality. In expedited service work, those two goals must be managed together, not separately.
Who Are The Largest Electronic Contract Manufacturers For PC Board Assembly In The Global Market?
The largest electronic contract manufacturers for pc board assembly usually operate at massive global scale, serving consumer electronics, automotive, telecom, industrial, and computing markets. They are important benchmarks, but they are not always the best fit for every OEM.
Large Global EMS Players Are Known For
- Very high production capacity
- Broad regional manufacturing footprint
- Mature supply chain influence
- System-level integration capability
- Strong process standardization
But Size Is Not The Only Buying Criterion
| Large Global EMS | Agile Mid-Sized Specialist |
|---|---|
| Best for huge volume | Best for responsive support |
| Strong purchasing power | Faster engineering feedback |
| More layered communication | More direct project contact |
| High process maturity | Better fit for NPI and mixed batch |
What Many OEMs Actually Need
- Faster response than a mega-EMS can offer
- Better support for prototypes and low-volume orders
- Stronger engineering discussion during DFM and BOM review
- Easier customization for mixed products
- A more practical expedited service path
For many PCB-centered projects, the ideal partner is not necessarily the biggest. It is the supplier with the right mix of engineering support, assembly control, sourcing agility, and communication speed.
Ultimately, contract manufacturing electronic assembly is a high-value manufacturing approach that helps OEMs transform PCB designs into reliable products through coordinated engineering review, sourcing control, assembly execution, testing, and scalable production support. This article covered the core workflow from DFM to final testing, thermal and current calculations, integration of PCB fabrication and sourcing, partner evaluation, prototype-to-volume transition, design support, electro-mechanical assembly, quality assurance, and the global EMS landscape.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) combines PCB fabrication, component sourcing, PCBA assembly, testing, and responsive engineering service to support expedited electronic manufacturing projects with stronger control and better communication. For RF boards, industrial controls, power electronics, medical devices, and other demanding applications, we help customers move faster with practical manufacturing support and dependable execution. If you have any electronics assembly contract manufacturing needs, pls feel free to contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com.
FAQs About Contract Manufacturing Electronic Assembly
What PCB Thickness Is Typically Used In Contract Manufacturing Electronic Assembly Projects?
Most PCB assemblies use board thickness between 1.0 mm and 1.6 mm, with 1.6 mm being the most common standard for industrial electronics. However, compact devices such as IoT modules may use 0.8 mm or thinner boards, while high-power or connector-heavy designs may require 2.0 mmâ3.2 mm thickness to improve mechanical rigidity and thermal performance. PCB thickness must also match connector specifications, enclosure tolerance, and impedance requirements.
What Copper Thickness Is Recommended For High-Current PCB Assemblies?
Copper thickness determines how much current a trace can safely carry. In most electronics assembly contract manufacturing projects, standard copper weight is 1 oz (35 ÎŒm). For power electronics or motor control boards, engineers may choose 2 oz (70 ÎŒm) or 3 oz (105 ÎŒm) copper. Heavy-copper PCBs above 4 oz are sometimes used in power converters, LED drivers, and industrial equipment where current paths exceed 10â20 A.
What Is The Typical Reflow Soldering Temperature Profile For SMT Assembly?
In electronic assembly contract manufacturing, the SMT reflow profile depends on the solder alloy used. For common lead-free SAC305 solder, the typical parameters are:
| Stage | Typical Temperature | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Preheat | 150â180°C | 60â120 s |
| Soak | 180â200°C | 60â90 s |
| Reflow Peak | 235â250°C | 20â40 s |
| Cooling | â3°C/sec typical | Controlled |
The peak temperature must remain below most component limits, which are usually 260°C maximum.
What Is The Typical Placement Accuracy In Modern SMT Assembly Lines?
Modern SMT production equipment used in electronics contract manufacturing assembly can achieve placement accuracy between ±30 Όm and ±50 Όm depending on machine class and component size. High-precision machines used for fine-pitch QFN, CSP, and 0201 components may achieve ±25 Όm accuracy. Accurate placement is critical for preventing solder bridging, improving yield, and ensuring consistent assembly quality in high-density PCB designs.