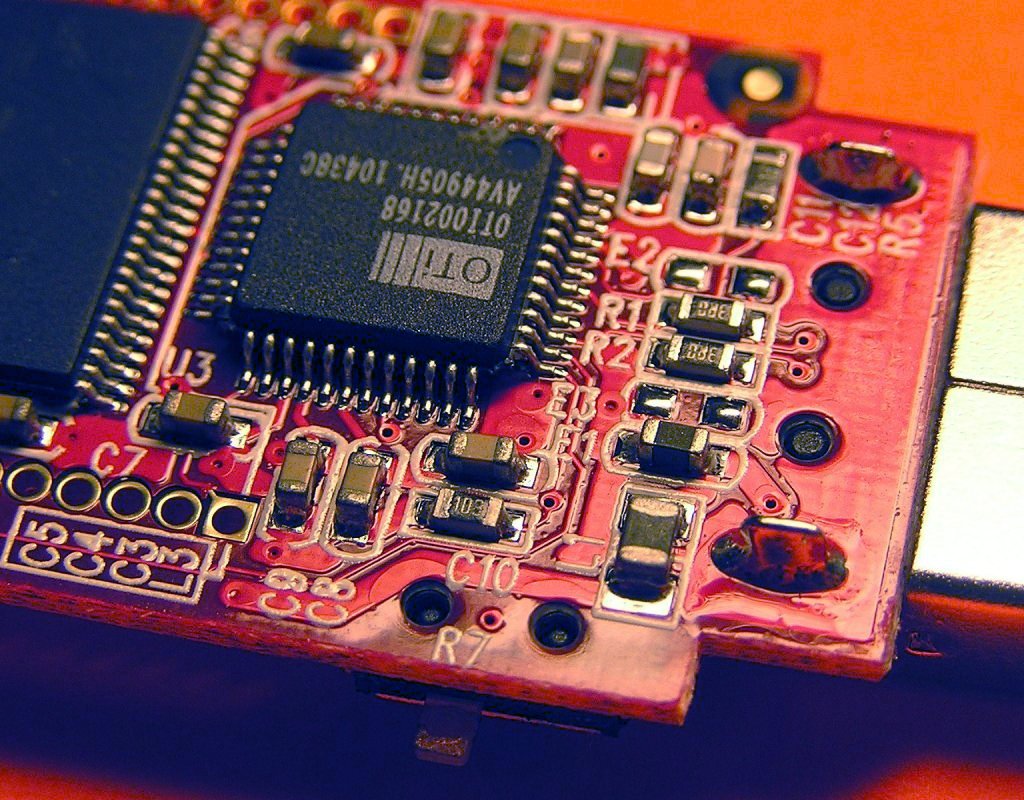
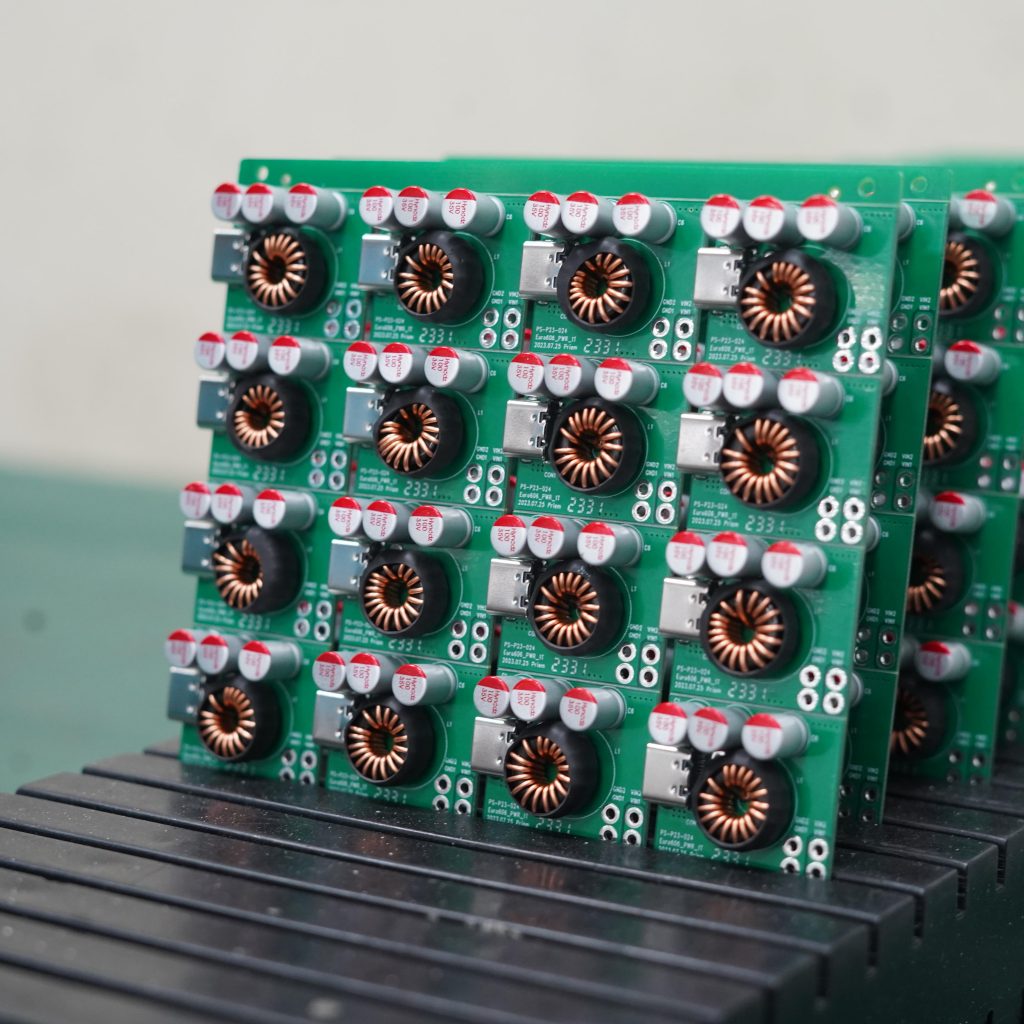
An SMT PCB board is a printed circuit board designed for surface mount technology, where electronic components are mounted directly onto copper pads on the board surface rather than inserted through drilled holes. This approach allows components to sit flat against the PCB, enabling compact layouts, shorter electrical paths, and efficient automated assembly through reflow soldering. As a result, SMT PCB boards support higher component density while maintaining consistent solder quality.
What Is an SMT PCB?
An SMT PCB is a printed circuit board designed specifically for surface mount technology, where electronic components are mounted directly onto copper pads on the surface of the board. Unlike traditional assembly methods, components do not use long wire leads inserted through drilled holes. Instead, they sit flat against the PCB and are soldered in place using controlled reflow processes.
This structural change enables much higher component density. Components can be placed on both sides of the board, and spacing between parts can be significantly reduced. As a result, SMT PCB boards are smaller, lighter, and more electrically efficient than older designs.
Another key benefit is manufacturing consistency. SMT placement is highly automated, allowing machines to position thousands of components per hour with exceptional accuracy. This repeatability improves yield and reduces defect rates, especially in high-volume production.
SMT PCB boards are now standard across consumer electronics, medical equipment, industrial controls, automotive electronics, and communication systems.
How Does SMT Impact PCB Design?
SMT influences PCB design from the earliest layout stage. Because surface-mounted components have short electrical paths, signal integrity improves, especially in high-speed and high-frequency circuits. This allows designers greater flexibility when routing traces and managing impedance.
Pad design becomes a critical factor in SMT layouts. Pad size, shape, and spacing directly affect solder joint quality and long-term reliability. Improper pad geometry can lead to solder bridging, tombstoning, or weak joints, all of which increase rework risk.
Layer stack-up also changes with SMT. Multilayer boards are common, as designers use internal planes for power distribution and noise control. Thermal management becomes more important as well, since compact components can generate localized heat that must be dissipated efficiently.
Finally, SMT PCB design must align with assembly equipment capability. Package size limits, placement tolerances, and inspection access all influence layout decisions.
Is SMT the Same as SMD?
SMT and SMD are closely related terms, but they are not interchangeable. SMT stands for surface mount technology and refers to the manufacturing process used to assemble components onto a PCB. SMD stands for surface mount device and refers to the component itself.
In simple terms, SMT is the method, while SMD is the part. Factories use SMT processes to place SMD components onto SMT PCB boards.
What Is the Difference Between SMD and SMT PCB?
An SMT PCB describes both the board design and the assembly method, while an SMD describes only the component package. SMT PCBs are designed with specific land patterns that support surface-mounted components and reflow soldering processes.
SMD components include chip resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, and discrete semiconductors packaged for surface mounting. Without an SMT-compatible PCB, SMD components cannot be properly assembled or soldered.
In practice, SMT PCBs and SMD components always work together, but their roles are distinct.
How Does PCB Board SMT Differ From Through-Hole Assembly?
The difference between SMT and through-hole assembly is structural and operational. Through-hole assembly uses drilled holes where component leads pass through the board and are soldered on the opposite side. SMT places components directly onto surface pads without penetrating the board.
SMT enables much higher component density and allows assembly on both sides of the PCB. This supports smaller board sizes and more complex functionality. Through-hole assembly, while mechanically robust, occupies more space and limits layout flexibility.
SMT also supports full automation, while through-hole assembly often requires manual or semi-automated steps. This difference has a significant impact on cost and scalability. However, some products use both methods together, such as board assembly SMT DIP PCB or board assembly SMT THT PCB designs, where connectors or power components still benefit from through-hole strength.
What Is the Major Advantage of Using SMT?
The primary advantage of SMT PCB assembly is efficiency at scale. Automated placement machines operate at high speed with consistent accuracy, enabling reliable mass production. This efficiency directly reduces assembly time and labor costs.
SMT also supports miniaturization. More functionality fits into less space, enabling thinner, lighter, and more portable devices. Electrical performance improves as well, since shorter lead lengths reduce parasitic effects and signal noise.
Reliability benefits from controlled soldering processes. Reflow soldering produces uniform joints, reducing variation and long-term failure risk.
What Components Are Used in SMT?
SMT supports a wide range of electronic components. Common passive parts include chip resistors and capacitors in standardized package sizes. Integrated circuits appear in formats such as SOIC, QFP, QFN, and BGA, supporting everything from simple logic to advanced processors.
Discrete components like diodes, transistors, and MOSFETs are widely used in SMT designs. Many connectors and RF modules are also available in surface-mount packages, allowing compact system integration.
Each component type requires proper footprint design, accurate stencil thickness, and precise placement to ensure reliable solder joints. Successful SMT PCB assembly depends on matching component selection with process capability.
What Quality Checks Are Used in SMT PCB Assembly?
Quality control is central to SMT PCB assembly. Inspection begins with solder paste application, where volume and alignment are monitored to prevent downstream defects. Automated optical inspection then verifies component placement and visible solder joints.
For components with hidden connections, such as BGAs, X-ray inspection is used to evaluate internal solder quality. Reflow temperature profiles are carefully controlled to avoid thermal damage or weak joints.
Electrical testing confirms circuit continuity and functionality, while final inspection ensures cleanliness and cosmetic quality. These layered quality checks protect product reliability and customer confidence.
Where Do We Use SMT?
SMT is used across nearly every electronics sector. Consumer electronics rely on it for compact form factors and high functionality. Industrial and medical devices depend on SMT for precision, consistency, and long-term reliability.
Automotive electronics use SMT for control units and sensor systems that must withstand harsh conditions. Telecommunications and networking equipment rely on SMT to support high-speed signal performance and dense layouts.
As electronics continue to evolve, SMT PCB assembly remains a foundational technology enabling innovation at scale.
Conclusion:
An SMT PCB board is a circuit board built for surface mount technology, where components are placed on surface pads and soldered by reflow for fast, repeatable production. Compared with through-hole assembly, SMT PCB assembly supports higher density, smaller products, and strong electrical performance, which is why it dominates modern electronics.
To learn more about how Best Technology supports these SMT PCB assembly technologies, please contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com