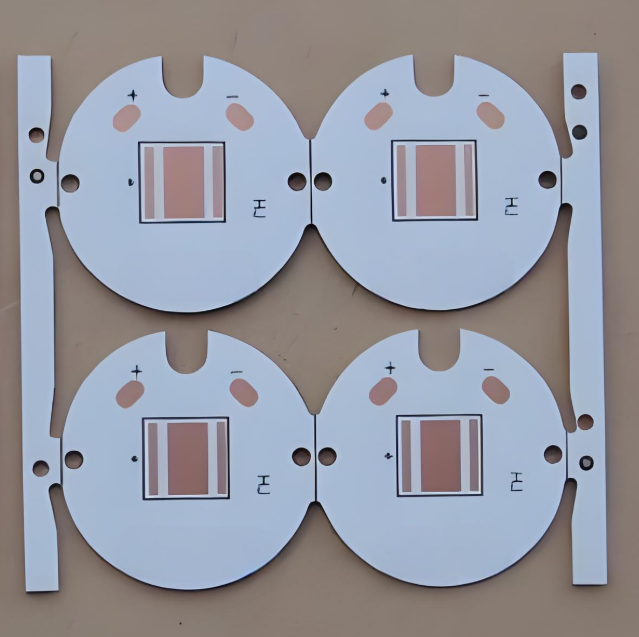
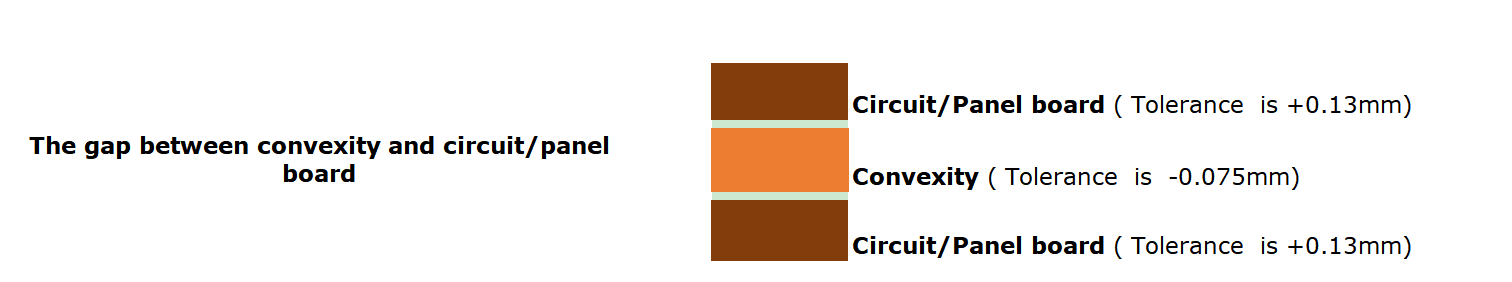
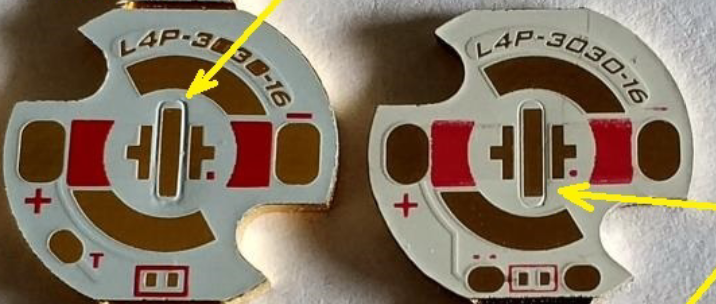
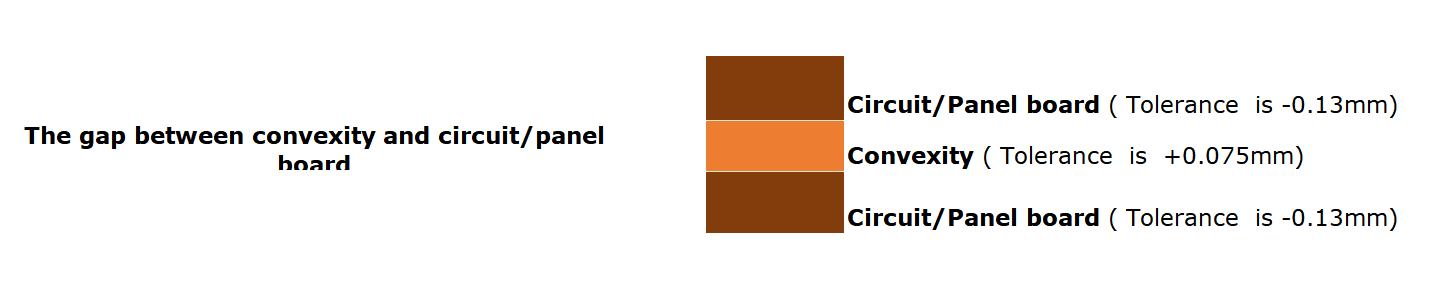
High-power LED applications come with a serious challenge: heat. When LEDs generate too much heat and itâs not properly managed, it can shorten the life of the light, affect its brightness, or even cause total failure. Thatâs where SinkPAD PCBs come in. Unlike regular MCPCBs, a SinkPAD PCB offers a direct thermal path that transfers heat away from the LED quickly and effectively. If youâre working with powerful LEDs, custom SinkPAD PCBs can make a big difference. At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we specialize in custom SinkPAD solutions designed for maximum heat dissipation and long-term reliability.
What is a SinkPAD PCB and How Does it Work?
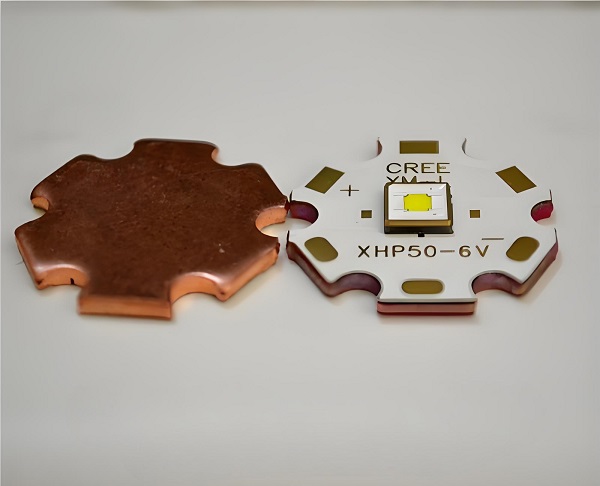
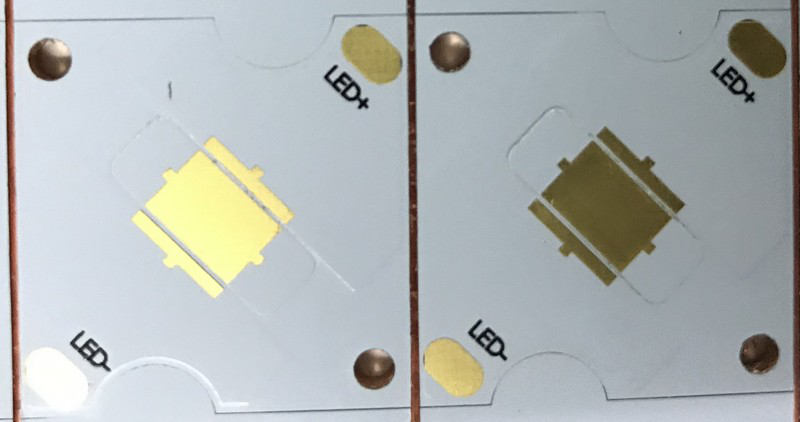
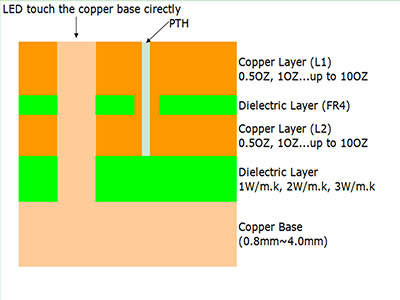
A SinkPAD PCB is a type of metal core PCB designed specifically for high-thermal performance. The term “SinkPAD” refers to a patented technology where the thermal pad of the LED is directly connected to the metal base of the PCB, creating an uninterrupted thermal path. In traditional MCPCBs, a dielectric layer sits between the copper circuit layer and the metal base, reducing thermal conductivity. But in a SinkPAD design, that barrier is removed or minimized in the area under the LED, allowing heat to flow directly to the metal core and then to the heatsink.

Why is Thermal Management So Critical in High-Power LED Applications?
LEDs are efficient, but theyâre not immune to heat. In fact, around 70%â85% of the electrical energy in an LED is converted into heat. If that heat isnât quickly removed, it can cause several issues:
- Decreased light output (lumen depreciation)
- Color shifting over time
- Shorter lifespan
- Component failure in extreme cases
Good thermal management maintains LED brightness, performance, and stability. For high-power LEDs, such as those used in automotive headlights or industrial lighting, standard cooling methods often fall short. Thatâs why advanced thermal solutions like custom SinkPAD PCBs are essential â they offer superior heat dissipation to keep your LEDs working reliably.
What are the Advantages of Custom SinkPAD PCBs for LED Projects?
Choosing a custom SinkPAD PCB means tailoring the thermal design to fit your exact LED setup. Here are the key benefits:
- Better heat dissipation: The direct thermal path lowers the junction temperature, which helps maintain brightness and prevent overheating.
- Compact design: You can eliminate bulky heatsinks, which saves space in your lighting product.
- Improved reliability: Lower operating temperatures lead to fewer failures and longer LED lifespan.
- Higher power density: You can run brighter or more LEDs in a small area without worrying about thermal overload.
- Consistent performance: No hotspots or uneven heat spread â just stable and predictable operation.
A custom SinkPAD solution allows you to match the board layout, materials, and thickness exactly to your LED requirements, which is especially helpful for complex or high-end lighting systems.
What Materials are used in SinkPAD LED PCBs?
The choice of materials is crucial for any high-performance PCB, especially one handling thermal management. In SinkPAD PCBs, the most common materials include:
- Aluminum base: Widely used due to its cost-effectiveness and good thermal conductivity. Suitable for medium-power LED applications.
- Copper base: Offers superior heat conductivity compared to aluminum and is typically used in ultra-high-power or demanding environments.
- High-thermal conductivity dielectric (if used): In areas not using the exposed metal pad, a thin dielectric layer may still be present. The goal is to keep thermal resistance as low as possible.
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we work with both aluminum and copper bases and can advise on the best choice depending on your heat requirements and budget.
How is a SinkPAD PCB Manufactured?
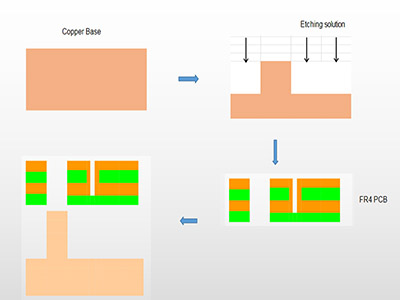
The SinkPAD PCB manufacturing process requires high precision and special techniques to expose the thermal pad directly to the metal base. Hereâs how it typically works:
- Material preparation: Selection of copper or aluminum core with appropriate thickness.
- Drilling and routing: Laser or mechanical drilling is used to create openings that allow the thermal pad to contact the base metal directly.
- Etching and circuit formation: Copper traces are etched for the electrical circuit.
- Thermal pad exposure: Dielectric material is selectively removed from under the LED thermal pad area.
- Plating and finishing: Surface finishes like ENIG or OSP are applied to the copper pads.
- Testing and inspection: Thermal and electrical tests ensure the board performs as intended.
This process allows the heat from the LED to travel through the exposed pad directly into the metal base, rather than relying on thermal via stacking or thick dielectric layers.
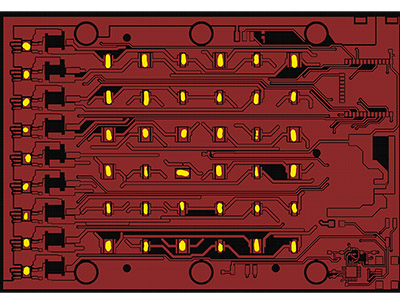
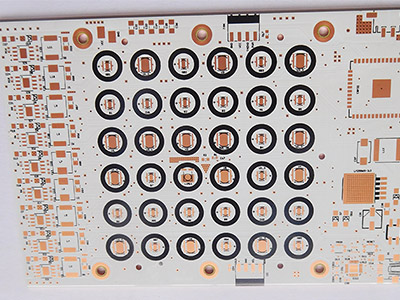
Where are SinkPAD PCBs Used in Real Applications?
SinkPAD PCBs are used in any application where high power and reliable thermal control are required. Here are some real-world examples:
- Automotive headlights and fog lamps: Require compact designs and powerful light with efficient heat dissipation.
- Industrial floodlights: Often run for long hours and need stable performance under high thermal stress.
- Medical lighting: Such as surgical lights that demand high brightness and zero failure during operation.
- UV curing systems: Used in printing and adhesives, which generate intense heat.
- Stage or studio lighting: Where color consistency and brightness are key, and high-powered LEDs are standard.
These applications benefit from the direct thermal pathway offered by SinkPAD PCBs, ensuring the LEDs can operate at full brightness for long periods without failure.
Design Considerations of SinkPAD PCB in LED Lighting Devices
When designing a SinkPAD PCB for LED lighting, itâs not just about efficient heat dissipation â itâs about optimizing performance, reliability, and manufacturability. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. LED Thermal Pad Alignment
Ensure the thermal pad of the LED package aligns precisely with the exposed metal area of the SinkPAD. Any misalignment can increase thermal resistance and reduce heat transfer efficiency.
2. Base Metal Selection
Aluminum is cost-effective and sufficient for many applications, but copper is preferable for ultra-high-power LEDs due to its superior thermal conductivity. Choose the base metal based on your LED’s power output and operating environment.
3. Board Thickness
The thickness of the metal core affects both heat spreading and mechanical strength. Thicker cores (e.g., 2.0mm copper or aluminum) can handle more heat but may increase the overall weight and cost.
4. Dielectric Isolation (If Applicable)
In areas that donât require direct heat transfer, a thin dielectric layer may still be used. Select materials with high thermal conductivity (>1.0 W/m·K) and low thermal resistance to maintain performance.
5. Surface Finish
For high-reliability soldering and corrosion resistance, finishes like ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) or OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative) are commonly used. Choose a finish compatible with your LED’s soldering profile.
6. Component Layout and Spacing
Leave enough space between LEDs and other heat-sensitive components. This helps prevent local hotspots and ensures even heat distribution across the board.
How Does EBest Circuit (Best Technology) Serve You for Custom SinkPAD PCBs?
Choosing the right SinkPAD PCB partner is as important as the design itself. Hereâs how EBest Circuit (Best Technology) supports you at every step:
- Advanced thermal engineering support
- Material flexibility including copper and aluminum
- Custom layout design
- Certified quality system
- Full traceability
- Fast quoting and prototyping
With over a decade of experience in custom thermal PCB design, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is your reliable partner for SinkPAD LED solutions.
FAQs
1. Whatâs the difference between SinkPAD and standard MCPCBs?
Standard MCPCBs use a dielectric layer between the LED and the metal core, while SinkPAD removes that layer under the thermal pad for direct heat transfer.
2. Can SinkPAD PCBs handle very high-wattage LEDs like 10W or 50W?
Yes. SinkPAD PCBs are specifically designed for high-wattage LEDs where rapid and efficient heat dissipation is critical.
3. Is copper better than aluminum for SinkPAD PCBs?
Copper offers better thermal conductivity than aluminum, but itâs also more expensive. The choice depends on your application and thermal budget.
4. Are SinkPAD PCBs only used for LED lighting?
While theyâre most commonly used in LED applications, they can be used in any high-power electronics needing excellent thermal control.
5. How can I get a quote for a custom SinkPAD PCB?
Simply send us your Gerber files and project details. Our engineering and sales team will respond with a tailored solution and quotation within 24 hours.