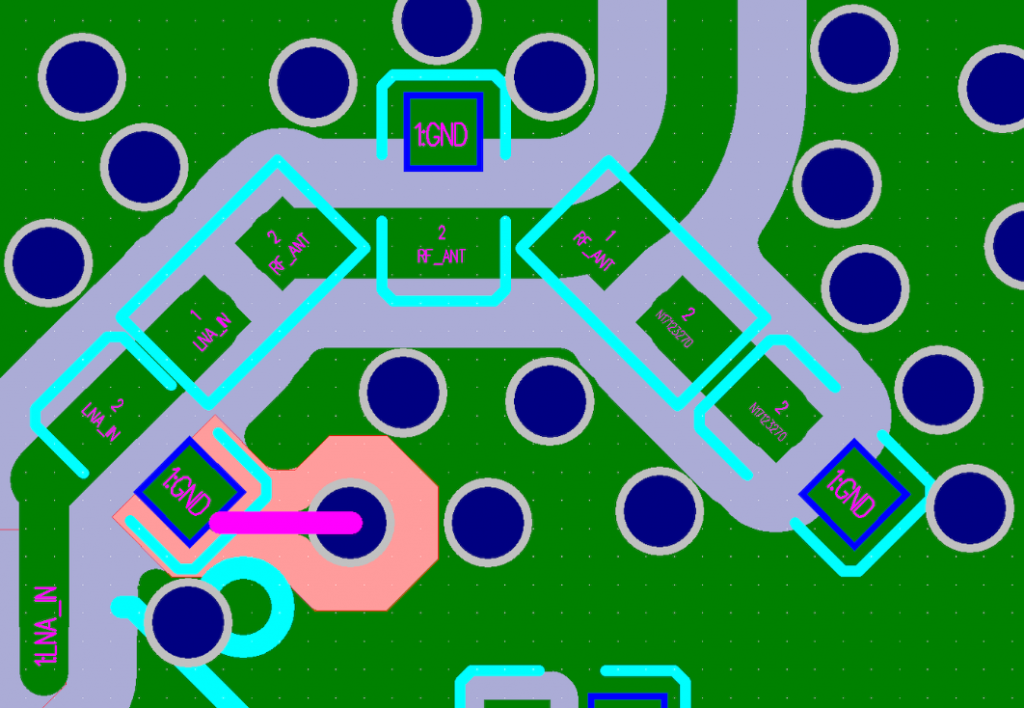
An RF board is a specialized printed circuit board designed to transmit and process radio-frequency signals ranging from 3 kHz to 300 MHz, and in many practical designs extending into the microwave range from 300 MHz up to 300 GHz, where signal integrity, low transmission loss, and precise impedance control are mandatory for reliable operation.
What are the most common obstacles in sourcing and deploying a reliable RF microwave PCB board?
- Material Missteps: Using standard FR-4 at GHz frequencies causes excessive dielectric loss and unstable thermal performance.
- DFM Gaps: RF circuit board designs pass simulation but fail in production due to unrealistic tolerances.
- Inconsistent Fabrication Quality: Poor process control leads to impedance variation, copper roughness, and delamination.
- Supply Chain Risks: Difficulty sourcing RF boards that consistently meet military or UL/CE compliance.
- Insufficient Testing: Basic inspections miss critical RF board test issues such as PIM or resonance.
The solution lies in collaborating with a specialist fabricator whose entire process is engineered for high-frequency success.
- Expert Material Selection: Choose proven RF laminates such as Rogers or Taconic, including metal-backed options when required.
- Early DFM Collaboration: Involve the fabricator during RF board layout to ensure manufacturable stack-ups and vias.
- Precision Manufacturing Processes: Apply LDI, plasma desmear, and controlled impedance etching for high-frequency accuracy.
- Certified Production Lines: Work with suppliers qualified for mil-spec and regulated RF board production.
- Advanced RF Testing: Verify performance using TDR, S-parameter analysis, and PIM testing for telecom applications.
This article explores the intricate world of RF and microwave PCB design, material science, and manufacturing, providing a roadmap for achieving reliability in the most demanding applications. BEST Technology is a specialized manufacturer of high-precision, high-frequency PCBs. We combine deep material science knowledge with state-of-the-art fabrication and testing facilities to transform complex microwave and RF designs‚Äč into reliable, production-ready hardware. From RF prototype boards‚Äč to high-volume runs, we ensure your board performs as simulated. Pls feel free to contact our experts at sales@bestpcbs.com‚Äč to start your project.
What Is the Definition of an RF Board?
An RF (Radio Frequency) board is a specialized printed circuit board engineered to transmit, route, and process electromagnetic signals in the radio frequency spectrum, generally covering 3 kHz to 300 MHz.
Within this range, signal behavior transitions from low-frequency electrical conduction to wave-dominated propagation, requiring controlled impedance, stable dielectric properties, and careful layout discipline.
When operating above 300 MHz, PCB designs enter the microwave domain, which typically spans 300 MHz to 300 GHz. At these frequencies, an RF board must function as a guided transmission structure rather than a simple interconnect, making dielectric constant (Dk), dissipation factor (Df), copper surface roughness, stack-up symmetry, and grounding strategy critical to performance.
Unlike standard digital PCBs, RF and microwave boards are designed around signal integrity, insertion loss, phase stability, and electromagnetic compatibility, ensuring predictable behavior across the intended frequency band and operating environment.
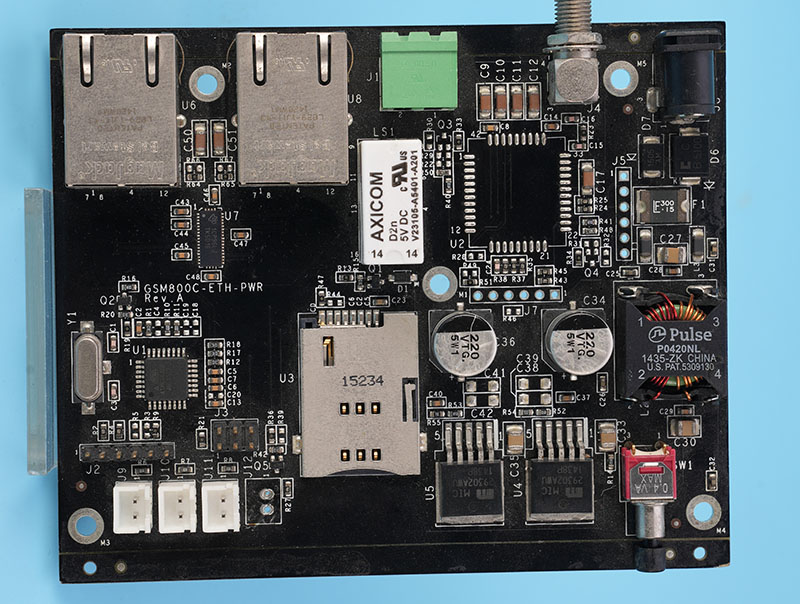
Why Microwave Systems Rely on Specialized Microwave PCBs Instead of Standard FR-4 Boards?
At microwave frequencies, the electrical properties of the PCB substrate become the dominant factor in performance. Standard FR-4 is unsuitable due to:
- High Dielectric Loss (Df):‚Äč Absorbs signal energy, converting it to heat and severely attenuating the signal.
- Inconsistent Dielectric Constant (Dk):‚Äč Varies with frequency and lot-to-lot, making stable impedance matching impossible.
- High Moisture Absorption:‚Äč Changes electrical properties and can lead to delamination.
- Poor Thermal Conductivity:‚Äč Inefficient for heat dissipation from active RF power amplifier‚Äč components.
Specialized microwave PCBs‚Äč use engineered laminates (e.g., PTFE-based ceramics, hydrocarbon ceramics) that offer low loss, stable Dk, low moisture absorption, and often better thermal performance, which is essential for reliable RF circuit board‚Äč operation.
What Materials and Stackups Are Best Suited for an RF Circuit Board Operating at GHz Frequencies?
Material selection is the first critical decision for a successful RF PCB.
| Material Type | Typical Brands | Key Properties | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE/ Ceramic‚Äč | Rogers RO4000¬ģ, Taconic RF-35 | Low loss, stable Dk, good performance | Multi-layer boards, digital analog integration‚Äč |
| Pure PTFE‚Äč | Rogers RT/duroid¬ģ | Ultra-low loss, excellent electrical stability | Critical RF amplifier board, aerospace |
| Hydrocarbon Ceramic‚Äč | Rogers RO3000¬ģ | Low loss, good thermal conductivity | Metal core boards‚Äč for high power |
| Thermoset Hydrocarbon‚Äč | Isola IS680-350 | Cost-effective, lower loss than FR-4 | Consumer RF module board‚Äč |
A optimal RF board‚Äč stackup for GHz frequencies should:
- Use a low-loss core material for RF layers.
- Implement a symmetrical stackup to prevent warpage.
- Minimize the distance between RF signal and reference planes to reduce radiation.
- Use multiple ground vias (stitching) around RF lines to suppress cavity resonances.
- Consider hybrid stackups (e.g., FR-4 for digital, Rogers for RF) for cost-sensitive, mixed-signal designs.
What Is RF Circuit Board Design?
RF circuit board design‚Äč is the discipline of laying out a PCB to effectively manage high-frequency electromagnetic waves. It transcends simple connectivity, focusing on controlling the behavior of signals as they travel along transmission lines. Core principles include:
- Controlled Impedance:‚Äč Ensuring signal traces have a consistent characteristic impedance (e.g., 50ő©) to prevent reflections.
- Transmission Line Theory:‚Äč Using microstrip or stripline geometries rather than simple “wires.”
- Minimizing Discontinuities:‚Äč Carefully managing bends, vias, and component pads to avoid parasitic inductance/capacitance.
- Isolation and Shielding:‚Äč Strategic use of grounding, board level EMI RF shields, and spacing to prevent crosstalk and radiation.
- Thermal Management:‚Äč Providing adequate heat sinking for active components, often integrated into the RF board layout.
What Is the Application of RF Circuit Board?
RF circuit boards‚Äč are the enabling technology for wireless connectivity and signal processing across industries.
- Telecommunications:‚Äč 5G/6G base stations, satellite comms equipment, and microwave backhaul links.
- Aerospace & Defense:‚Äč Radar systems, electronic warfare (EW), and avionics requiring suppliers for military specs.
- Automotive:‚Äč Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS), vehicle-to-everything (V2X), and GPS.
- Medical:‚Äč MRI machines, therapeutic and diagnostic equipment, and wireless monitoring devices.
- Consumer Electronics:‚Äč Smartphones, Wi-Fi routers, and gaming consoles (e.g., xbox one RF board‚Äč replacements).
Best HDI PCB Manufacturers for RF and Microwave Circuit Boards
Based on 2024‚Äď2025 industry data and global market research, the following companies stand out as the world‚Äôs leading HDI (High-Density Interconnect) PCB manufacturers for RF (Radio Frequency) and Microwave applications.
These manufacturers demonstrate proven capabilities in ultra-fine line processing, controlled impedance, high-layer HDI builds, and maintain robust certification systems tailored to high-frequency and high-reliability sectors.
🏆 Overall Market Leader
TTM Technologies | United States
Global HDI Market Leader for RF and Microwave Applications
- TTM Technologies is one of the world’s largest HDI PCB manufacturers, widely recognized for its advanced RF and microwave capabilities across aerospace, defense, telecommunications, and automotive electronics. Its long-term investment in signal integrity engineering and high-layer HDI platforms positions it as a benchmark supplier for mission-critical RF designs.
🇨🇳 China Market Leader
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) | China
Core Supplier for AI Servers and 5G Infrastructure
- EBest Circuit (Best Technology) plays a dominant role in AI computing infrastructure and advanced communication systems. It is a key PCB supplier for autonomous driving platforms and high-performance computing, with strong HDI and RF manufacturing depth supporting large-scale production.
Top HDI PCB Suppliers
| Company Name | Headquarters | Board Type Focus | Key Certifications |
|---|---|---|---|
| TTM Technologies | USA | RF / Microwave / Aerospace, ultra-fine lines, high-layer count | ISO 9001, AS9100, Nadcap, IPC-6012 Class 3 |
| AT&S | Austria | Automotive HDI / RF, sequential lamination, fine trace/space | IATF 16949, ISO 9001, ISO 14001, AS/EN 9100 |
| Unimicron | Taiwan | Mobile RF / IC Substrate, microvias, stacked vias | ISO 9001, UL, ISO 14001, IATF 16949 |
| Compeq | Taiwan | RF / High-Frequency, telecom infrastructure, mobile devices | ISO 9001, ISO 14001, UL, IATF 16949 |
| Meiko Electronics | Japan | Precision HDI / RF, high-reliability manufacturing | ISO 9001, ISO 14001, UL |
Note: Manufacturer selection is based on Prismark market data and a combined evaluation of RF/microwave process barriers, certification depth, and market share.
TTM Technologies (USA)
RF and Microwave Expertise
TTM demonstrates exceptional process maturity in millimeter-wave frequencies and high-frequency signal integrity control, making it a preferred supplier for aerospace and defense RF platforms.
Certification Strength
The company holds Nadcap accreditation, a critical aerospace qualification that many general PCB manufacturers cannot meet, reinforcing its position in high-reliability markets.
AT&S (Austria)
Automotive RF Leadership
AT&S excels in ADAS, automotive radar, and electric vehicle RF systems, where long-term reliability and thermal stability are mandatory.
Quality and Sustainability
Its operations emphasize renewable energy usage and strict compliance with IATF 16949, aligning with global automotive OEM requirements.
Unimicron (Taiwan)
Miniaturization Capability
With trace and space down to 2/2 őľm, Unimicron is well-suited for compact, highly integrated RF modules used in smartphones and wireless devices.
Advanced Interconnect Technology
Its strength in ALIVH (Any-Layer Interstitial Via Hole) technology supports complex RF stackups and dense interconnections.
Market Landscape and Industry Trends
Estimated Global HDI Market Share
- Compeq: 11%
- Unimicron: 11%
- TTM Technologies: 10%
- AT&S: 7.7%
- Other manufacturers: 60%
Data source: Prismark 2024 global HDI market report. The listed companies represent the core share holders in RF and microwave HDI manufacturing.
Practical Selection Recommendations
When selecting an HDI PCB manufacturer for RF and microwave applications, consider the following guidance:
- Aerospace or military-grade systems
Prioritize TTM Technologies or AT&S, as both maintain AS9100 and Nadcap certifications. - Automotive radar and ADAS platforms
AT&S offers the most comprehensive automotive-focused RF certification portfolio. - Consumer electronics and 5G infrastructure
Unimicron or Compeq provide high-precision RF manufacturing with competitive cost structures. - Ultra-thin or high-layer RF designs
Meiko Electronics delivers unique advantages in precision HDI and long-term manufacturing stability.
Top Companies for RF Microwave PCB and Metal Core Boards
Based on the latest industry data and search insights, the following five companies are widely recognized as global leaders in RF/Microwave and Metal Core PCB manufacturing.
Their market position is driven by strong capabilities in high-frequency material processing, precision fabrication, and strict certification systems, enabling them to serve demanding applications across aerospace, defense, telecom, automotive, and high-power electronics.
🌍 Global High-End Manufacturers
- Advanced Circuitry International (ACI)
United States | RF/Microwave Specialist
Core Strengths
ACI focuses exclusively on RF and microwave antenna PCB manufacturing, with more than 30 years of industry experience supporting high-reliability programs.
RF Capabilities
The company is well known for large-format PCB fabrication, blind and buried vias, and advanced Ohmegaply™ hybrid constructions, enabling excellent impedance stability and thermal control.
Material Support
Extensive experience with Rogers, Taconic, Arlon, and other premium RF laminates.
Certifications
ISO 9001, AS9100D, ITAR registered.
- Teledyne Labtech
UK / USA | Military and High-Reliability Applications
Core Strengths
Teledyne Labtech delivers solutions for military and harsh commercial environments, including advanced technologies such as embedded graphite layers for thermal management.
RF Capabilities
Full-size PCB manufacturing, antenna fabrication, and integrated thermal control solutions for RF and microwave systems.
Certifications
ISO 9001, ISO 14001, JOSCAR.
🇨🇳 Asia-Based Supply Chain Leaders
- EBest Circuit (Best Technology)
China | Comprehensive PCB and Assembly Services
Core Strengths
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) provides one-stop manufacturing services, covering both metal core PCB fabrication and complete PCBA assembly.
Metal Core Capability
Manufactures single-layer and multilayer aluminum- and copper-based metal core boards, suitable for power electronics and thermal-intensive designs.
Certifications
UL, IATF 16949, ISO 9001, ISO 13485, AS9100D CE, RoHS.
Key Capability Overview
| Company Name | Board Type | Key Certifications |
|---|---|---|
| Advanced Circuitry International | RF/Microwave, Antenna | ISO 9001, AS9100D, ITAR |
| Teledyne Labtech | RF/Microwave, Military | ISO 9001, ISO 14001, JOSCAR |
| EBest Circuit (Best Technology) | Metal Core, Flexible, Rigid PCB, RF/Microwave | ISO 9001, ISO 13485, IATF 16949, AS9100D, UL, REACH, and RoHS. |
How to Select the Right RF Microwave PCB Board Supplier for High-Reliability Industries
Choosing a RF microwave pcb board supplier‚Äč for medical, aerospace, or defense applications requires due diligence.
- Audit Quality Systems:‚Äč Review their AS9100 or ISO13485 certifications and audit reports.
- Evaluate Technical Support:‚Äč Assess their engineers’ ability to discuss RF board design guidelines‚Äč and material trade-offs.
- Inspect Testing Capabilities:‚Äč Ensure they have the required RF board test‚Äč equipment (e.g., TDR, network analyzer, flying probe).
- Review Documentation:‚Äč Request examples of travel coupons, test reports, and material certifications.
- Check Industry References:‚Äč Ask for case studies or contacts in your specific field (e.g., medical devices, telecom networks).
How Do You Streamline RF Board Installation for High-Reliability Designs?
Streamlining RF board installation‚Äč prevents field failures. Key practices include:
- Clear Mechanical Documentation:‚Äč Provide detailed drawings showing keep-out areas, shield placement, and torque specs for board to board RF connectors.
- Integrated Alignment Features:‚Äč Design in tooling holes, dowel pins, or guides for error-free assembly.
- Standardized Connectorization:‚Äč Use common, reliable RF board to board connector‚Äč types to simplify cabling.
- Comprehensive Assembly Instructions:‚Äč Create visual work instructions covering handling, ESD, soldering, and cleaning.
- On-Board Test Points:‚Äč Include accessible coaxial test points for validation during system integration.
What Testing and Validation Methods Are Required for Reliable RF Board Test Results?
A robust RF board test‚Äč protocol is essential for reliability.
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI):‚Äč Checks for surface defects and solder issues.
- Controlled Impedance Testing:‚Äč Uses a Time Domain Reflectometer (TDR) to verify trace impedance meets design specs (e.g., 50ő© ¬Ī10%).
- Network Analysis:‚Äč Measures S-parameters (S11, S21) to validate insertion loss, return loss, and isolation across the operational bandwidth.
- High-Potential (HiPot) Testing:‚Äč Ensures dielectric strength and electrical isolation.
- Specialized Tests:‚Äč May include passive intermodulation (PIM) testing for telecom, or thermal cycling for environmental robustness.
Where to Get RF Microwave PCB Boards Metal-Backed?
Metal-backed PCBs‚Äč (also called metal-clad or insulated metal substrates) are ideal for high-power RF applications. They are available from specialized fabricators who:
- Offer Various Metals:‚Äč Typically aluminum (for cost and weight) or copper (for best thermal performance).
- Handle Dielectric Bonding:‚Äč Expertly laminate a thin, thermally conductive but electrically insulating dielectric layer to the metal base.
- Manage CTE Mismatch:‚Äč Use processes that prevent warping or delamination during thermal cycling.
- Provide Secondary Operations:‚Äč Offer machining, tapping, and anodizing of the metal base as part of the service.
Why EBest Circuit (Best Technology) Is the Best Partner for RF Boards Fabrication?
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) distinguishes itself as a leader in the fabrication of complex Radio Frequency (RF) and Microwave printed circuit boards. Our expertise is demonstrated through hard process data, advanced engineering capabilities, and full control over the manufacturing value chain.
1. Mastery of High-Frequency Materials
We specialize in processing a wide range of advanced substrates critical for RF performance, ensuring optimal signal integrity and controlled dielectric properties.
- Material Portfolio:‚Äč Expertise in Rogers (e.g., 4350B, 4003), PTFE (Taconic, Arlon), and ceramic-filled materials (M-series).
- Layer Count:‚Äč Capable of manufacturing highly complex multilayer boards up to 50 layers‚Äč (standard), with advanced capabilities for up to 100 layers‚Äč (upon review).
2. Precision Engineering for Critical RF Parameters
Our processes are calibrated to meet the tight tolerances required for high-frequency applications.
- Fine Lines/Spacing:‚Äč Standard outer layer trace/space of 3.5/4 mil‚Äč for 1oz copper, with advanced capabilities down to 3/3 mil.
- Micro-Vias & Drilling:‚Äč Laser drilling for HDI designs down to 0.07mm. Exceptional mechanical drill hole position accuracy of ¬Ī0.05mm.
- Controlled Impedance:‚Äč Industry-leading impedance control with tolerances as tight as ¬Ī4ő© (for impedances <50ő©)‚Äč or ¬Ī6% (for impedances ‚Č•50ő©).
- RF-Suitable Surface Finishes:‚Äč Including ENIG‚Äč (Nickel: 3-8¬Ķm, Gold: 0.025-0.125¬Ķm), Immersion Silver, and OSP.
3. Uncompromising Quality and Reliability
We ensure board performance and reliability through stringent process controls.
- Layer-to-Layer Registration:‚Äč Advanced registration control of ‚ȧ0.13mm.
- Solder Mask Alignment:‚Äč Precision alignment tolerance of ¬Ī0.05mm.
- Board Flatness:‚Äč Superior warpage control, with a capability of 0.005.
To sum up, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) provides a proven foundation for your most demanding RF applications, backed by concrete data in high-frequency material processing (Rogers/PTFE), complex stack-ups (to 50L), fine features (3/3 mil), tight impedance control (¬Ī4ő©), and precision drilling (0.07mm laser vias).
All in all, RF Boards‚Äč are the precision-engineered backbone of modern wireless systems, where every micron and material property dictates performance. This guide has navigated the critical aspects of RF and microwave PCB design, manufacturing, and validation, emphasizing the partnership required to achieve reliability.
For projects where performance cannot be compromised, partnering with a specialist is paramount. BEST Technology provides that essential edge, combining deep technical expertise with manufacturing excellence to deliver robust, high-yield RF solutions. Reach out to start a conversation about your most challenging high-frequency designs via sales@bestpcbs.com.
FAQs
What is the function of an RF prototype board?
- An RF prototype board‚Äč serves to physically validate the RF circuit board design, material selection, and manufacturing processes before committing to full-scale production. It allows engineers to test real-world performance, debug issues, and refine the layout, ensuring the final product meets all electrical and mechanical specifications.
What are the common pitfalls in RF board installation?
- Common pitfalls in RF board installation‚Äč include:
1) Using excessive torque on connectors, damaging the PCB pads;
2) Improper grounding of board level EMI RF shields, creating unintended antennas;
3) Pinching or stressing coaxial cables, altering their impedance;
4) Applying incorrect soldering profiles, damaging heat-sensitive laminates; and
5) Failing to clean flux residues, which can become conductive at RF frequencies.
How do you optimize designs for double-sided RF board assemblies?
To optimize designs for double-sided RF board assemblies:
- 1) Dedicate one side primarily as a continuous, unbroken ground plane.
- 2) Route sensitive RF traces on one side only, using the other side for DC/power and low-speed signals.
- 3) Use abundant ground vias to stitch the top and bottom ground planes together, minimizing ground loop impedance.
- 4) Place components strategically to avoid interference, and
- 5) carefully model and place vias that must transition signals between layers to minimize their discontinuity.