Double sided PCBA refers to a printed circuit board assembly where components are mounted and soldered on both sides of the PCB, enabling higher circuit density and more functional integration within a compact footprint. This article explains how double sided PCBA production works, when it should be selected, what risks commonly occur during assembly, and how an experienced manufacturer controls quality, cost, and delivery across the full production lifecycle.
Why Do Double Sided PCBA Projects So Often Run Into Trouble?
- DFM issues are discovered after parts are ordered, forcing rework or redesign.
- Double reflow introduces alignment and solder joint reliability risks.
- BOM choices look acceptable on paper but fail under real supply constraints.
- Quality varies between batches due to inconsistent process control.
- Communication gaps slow down prototype-to-production transitions.
A double sided PCBA manufacturer with long-term production experience addresses these risks systematically rather than reactively.
- Perform DFM review and process validation before material commitment.
- Control double-sided reflow profiles and fixture strategy to stabilize yield.
- Optimize BOMs with lifecycle checks and approved alternates.
- Apply standardized inspection and quality checkpoints across all builds.
- Use clear engineering communication workflows to reduce iteration cycles.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is a professional PCB and PCBA manufacturer with over 20 years of double sided PCBA production experience, serving more than 1,800 customers and 10,000 engineers worldwide. With in-house PCB fabrication, PCBA assembly, certified quality systems, and a digitalized production workshop, we help OEM teams move from prototype to volume. For technical consultation or quotations, pls feel free to contact us via sales@bestpcbs.com.
What Does Double Sided PCBA Involve In A Production Assembly Program?
A production-level double sided PCBA program includes more than placing parts on both sides of a board. It is a coordinated manufacturing system.
Key Elements Involved
- Engineering Review â DFM, DFA, and process feasibility checks.
- PCB Fabrication Alignment â Stack-up, finish, and panelization matched to assembly needs.
- Component Preparation â Moisture control, polarity validation, and alternate sourcing.
- Double-Sided Assembly â Controlled first-side and second-side reflow sequencing.
- Inspection And Testing â AOI, X-Ray (when required), and functional validation.
A structured assembly program ensures that double sided PCBA remains stable and repeatable at production scale.
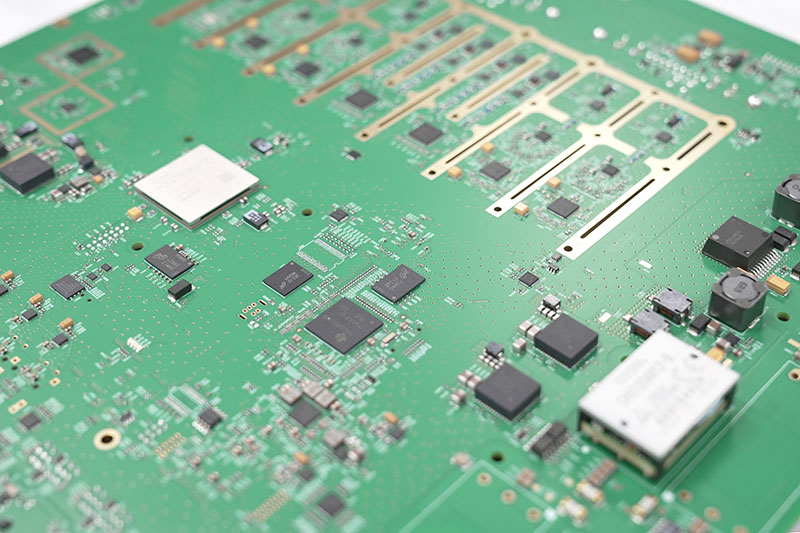
What Is The Typical Double Sided PCB Manufacturing Process From Design To Assembly?
The manufacturing process must account for thermal, mechanical, and inspection challenges unique to double sided boards.
Typical Process Flow
- PCB fabrication with defined copper balance and solder mask design.
- First-side SMT placement and reflow.
- Board flipping with fixture support.
- Second-side SMT placement and reflow.
- AOI and selective inspection.
- Through-hole assembly if required.
- Final test and shipment.
Process discipline is critical to prevent cumulative defects introduced during multiple thermal cycles.
When Should Engineers Choose Double Sided PCB Design Over Single-Sided PCB?
Double sided PCB design is selected when functional density and routing flexibility outweigh the simplicity of single-sided PCB layouts.
Typical Selection Criteria
- Circuit density exceeds single-sided routing capability.
- Signal integrity benefits from shorter interconnect paths.
- Board size constraints limit expansion.
- Cost pressure makes multilayer PCB unnecessary.
- Product requires moderate complexity with controlled assembly risk.
To wrap up, double sided PCB design often represents the best balance between functionality and manufacturing cost.
What Are Common Double-Sided PCB Applications In Modern Electronic Products?
Double-sided PCB applications span a wide range of industries where space efficiency and cost control are critical.
Common Applications
- Industrial control modules
- Power management boards
- Consumer electronics
- Automotive subassemblies
- Communication interface boards
To summarizeâ, double sided PCBA remains a workhorse solution for modern electronics across multiple sectors.
What Factors Affect Quality In China Double Sided PCBA Production?
China double sided PCBA quality depends more on process governance than on geography.
Key Quality Factors
- DFM depth and timing
- Component sourcing discipline
- Reflow profile stability
- Inspection coverage and standards
- Production traceability
To wrap things up, choosing a China-based manufacturer with mature controls is essential for consistent quality.
What Assembly Risks Are Common In Double Sided PCBA Production?
Double sided PCBA introduces specific risks that must be managed proactively.
Common Assembly Risks
- Component shift during second reflow
- Tombstoning on small passives
- Shadowing effects during AOI
- Thermal stress on sensitive devices
- Yield loss from inconsistent handling
To sum up, experienced manufacturers mitigate these risks through fixturing, profiling, and inspection strategy.
How Does Double Sided PCBA Compare With Multilayer PCBA In Cost Structure?
From a cost perspective, double sided PCBA often occupies a middle ground between simplicity and complexity.
Cost Structure Comparison
| Aspect | Double Sided PCBA | Multilayer PCBA |
|---|---|---|
| PCB Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Assembly Complexity | Moderate | High |
| Yield Sensitivity | Medium | High |
| Design Flexibility | Moderate | Very High |
In essence, double sided PCBA is often the most cost-effective solution when multilayer routing is not strictly required.
Overall, double sided PCBA enables compact, cost-efficient electronic manufacturing when supported by disciplined engineering and production control. This article reviewed the production scope, manufacturing process, application scenarios, quality factors, assembly risks, and cost structure considerations associated with double sided PCBA.
As a double sided PCBA manufacturer with 20 years of production experience, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) combines engineering depth, certified quality systems, digital traceability, and fast turnaround to help OEMs achieve stable, scalable results. For project evaluation or quotations, pls feel free to contact us via sales@bestpcbs.com.
FAQs
What is the difference between single sided and double sided PCB?
A single sided PCB places components on one side only, while a double sided PCB allows components on both sides, increasing circuit density and routing options.
How are double-sided PCBs assembled?
Double-sided PCBs are assembled through sequential placement and reflow, typically soldering one side first, then flipping the board and assembling the second side with controlled fixturing and thermal profiles.