If youâre an engineer working on industrial systemsâfrom medical imaging to aerospace telemetryâyou know that best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applications isnât just a ânice-to-haveâ; itâs the backbone of reliable, high-performance equipment. The wrong fabrication choices lead to signal loss, frequency drift, and costly system failuresâproblems no industrial project can afford. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applications, from material selection to process control, real-world case studies, and how to avoid common pitfalls that plague even experienced teams.

What Makes the Best RF Microwave PCB Fabrication for Industrial Applications Stand Out?
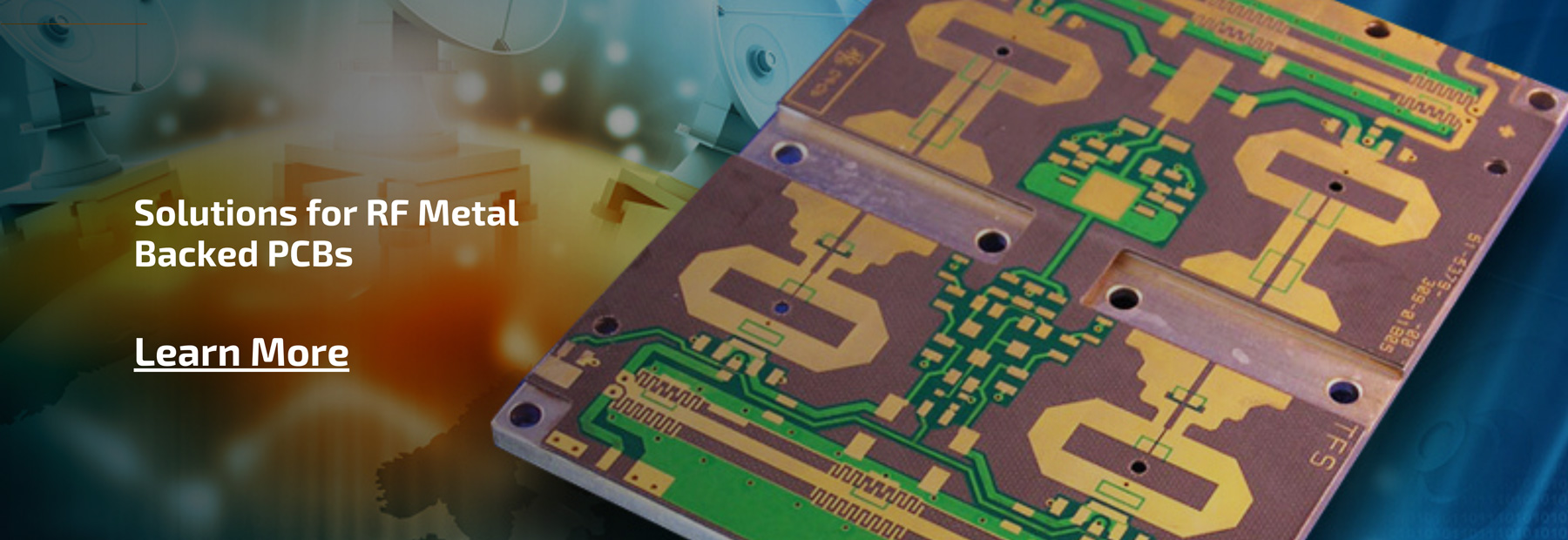
The best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applications differs from standard PCB manufacturing in three non-negotiable ways: strict impedance control, low-loss material consistency, and precision manufacturing tolerancesâall tailored to the harsh conditions of industrial use (extreme temperatures, vibration, humidity). Industrial RF microwave PCBs operate at frequencies above 1GHz (often up to 77GHz for radar systems), where even a 0.1mm etching deviation or 0.05 dielectric constant (Dk) fluctuation can render a board useless.
Key Differentiators of Industrial-Grade RF Microwave PCB Fabrication
- Impedance Tolerance ±5% or Tighter: Critical for signal integrity; industrial systems (like aerospace telemetry) require consistent impedance to avoid reflection and signal distortion.
- Low Dissipation Factor (Df †0.001): Minimizes signal loss, which is essential for long-range industrial communication and high-power applications.
- High-Temperature Stability: PCBs must maintain performance from -40°C to 125°C (or higher for aerospace), resisting warpage and material degradation.
- Precision Etching (±0.04mm): Ensures accurate trace widths for RF paths, especially for microstrip and stripline designs common in industrial sensors.
Which Materials Are Best for RF Microwave PCB Fabrication in Industrial Applications?
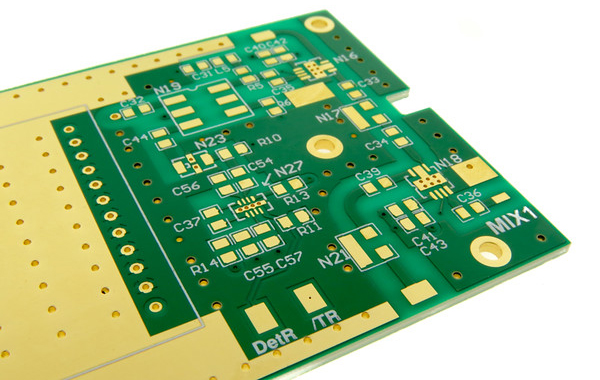
Best RF Microwave PCB
Material selection is the single most important factor in best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applicationsâyour choice directly impacts signal loss, temperature stability, and overall reliability. For industrial use, two material categories dominate: PTFE-based laminates (for high performance) and hybrid stackups (for balanced performance and mechanical stability).
Top Materials for Industrial RF Microwave PCBs
| Material Type | Key Properties | Best Industrial Applications | Example Brands |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE-Based (Rogers RO4350B) | Dk=3.48, Df=0.0037, low water absorption, high temperature stability | Aerospace radar, medical imaging, high-power industrial sensors | Rogers, Taconic, Arlon |
| PTFE/FR-4 Hybrid | PTFE for RF layers, FR-4 for control/power layers; balances performance and stiffness | Industrial IoT, 5G backhaul, low-power radar | Rogers + FR-4, Isola Hybrid |
| Modified FR-4 (Megtron 6) | Dk=3.6, Df=0.004, excellent mechanical strength, stable performance at mid-frequencies | Industrial control systems, low-frequency RF sensors | Panasonic, Isola |
How to Control Impedance in Best RF Microwave PCB Fabrication for Industrial Applications?
Impedance control is non-negotiable for best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applicationsâwithout it, signal reflection, attenuation, and crosstalk will destroy performance. Industrial RF microwave PCBs typically require 50Ω (for most sensors/radar) or 75Ω (for communication systems) impedance, with a tolerance of ±5% (±3% for aerospace/medical).
Step-by-Step Impedance Control Process
- Design Optimization: Use impedance calculation tools to define trace width, dielectric thickness, and copper weight. For microstrip lines, the formula Zâ = 87/â(dk + 1.41) Ă ln(5.98h/(0.8w + t)) ensures accurate impedance (h=dielectric thickness, w=trace width, t=copper thickness).
- Material Consistency: Source materials with tight Dk tolerance (±0.05) and test every batch with a Keysight N1500A dielectric tester to avoid fluctuations.
- Precision Etching: Use electroformed stencils (±0.005mm accuracy) and control etching parameters (temperature 45±2°C, spray pressure 2.5±0.2kg/cmÂČ) to maintain trace width consistency.
- Post-Fabrication Testing: Use Time Domain Reflectometry (TDR) to measure impedance across the board; reject any PCBs with deviations beyond ±5%.
What Are the Common Fabrication Challenges for Industrial RF Microwave PCBs?
Industrial RF microwave PCB fabrication faces unique challenges due to strict performance requirements and harsh operating environments. The most common issues are signal loss, warpage, and dielectric inconsistencyâbut all are avoidable with proper process control.
Top Challenges and Engineering Solutions
- Signal Loss from Poor Surface Finish: Solution: Use immersion gold (0.1ÎŒm minimum thickness) instead of HASLâgold has lower resistivity (2.4ΌΩ·cm) and minimizes insertion loss at high frequencies.
- Warpage in Hybrid Stackups: Solution: Maintain symmetrical stackups (equal copper weight on both sides) and control lamination parameters (175±5°C, 35±2kg/cmÂČ pressure) to avoid resin unevenness.
- Dielectric Degradation from Moisture: Solution: Store materials in dry environments (RHâ€40%) and pre-bake PCBs at 120°C for 40 minutes before fabrication to remove moisture.
- Crosstalk Between RF Traces: Solution: Separate RF traces by at least 3x the trace width and use ground planes between signal layers to block interference.
How Does Thermal Management Impact Industrial RF Microwave PCB Fabrication?
Thermal management is critical for best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applicationsâhigh-power industrial systems (like microwave heaters or radar transmitters) generate significant heat, which degrades dielectric performance and causes component failure. Effective thermal design ensures PCBs maintain stability at operating temperatures up to 150°C.
Proven Thermal Management Techniques
- Thick Copper Layers: Use 2â6oz copper for power and ground planes to improve heat dissipationâthicker copper has lower resistance and spreads heat faster.
- Thermal Vias: Place high-density thermal via arrays (0.2mm diameter, 0.5mm pitch) under heat-generating components to transfer heat to the backplane.
- Metal Backplanes: For extreme heat applications (aerospace), bond a copper or aluminum backplane to the PCB to enhance thermal conductivity.
- Low-Thermal-Expansion Materials: Use Rogers RO3003 (CTE=6.4ppm/°C) to match the CTE of semiconductor components, reducing thermal stress and solder joint failure.
What Are the Quality Control Standards for Best RF Microwave PCB Fabrication for Industrial Applications?
Industrial RF microwave PCBs require rigorous quality control (QC) to meet performance and reliability standardsâespecially for medical and aerospace applications, where failure is catastrophic. QC must span material incoming inspection to final testing, with documented processes to ensure consistency.
Critical QC Checks for Industrial RF Microwave PCBs
- Incoming Material Inspection: Test Dk, Df, and copper thickness for every material batch; reject batches with Dk fluctuation >±0.05 or copper weight deviation >±10%.
- Process Control Checks: Monitor lamination temperature, etching rate, and stencil alignment every 2 hours; log all parameters for traceability.
- Electrical Testing: Perform TDR (impedance), insertion loss (IL), and return loss (RL) testingâindustrial PCBs require IL â€0.1dB/inch at 10GHz and RL â€-15dB.
- Environmental Testing: Conduct thermal cycling (-40°C to 125°C, 1000 cycles) and humidity testing (85°C/85% RH, 1000 hours) to ensure long-term reliability.
- Visual Inspection: Use 20x microscopes to check for etching defects, solder bridges, and surface finish uniformity; reject boards with any visible flaws.
What Industrial Applications Rely Most on High-Quality RF Microwave PCB Fabrication?
Numerous industrial sectors depend on best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applications, as their systems require high-frequency signal integrity, reliability, and durability. Below are key industries, with real-world case studies showing how proper fabrication solves critical challenges.
Key Industries + Real-World Case Studies
1. Aerospace & Defense
Aerospace radar systems (24GHz/77GHz) require PCBs with ultra-low loss and temperature stability. A major aerospace contractor approached us for PCB fabrication for a satellite telemetry systemâtheir previous supplierâs boards suffered from frequency drift (-0.5GHz) at extreme temperatures. We used Rogers RO4003C (Df=0.001) with a hybrid stackup, precision etching (±0.03mm), and thermal via arrays. The final PCBs maintained impedance ±3% and frequency stability from -55°C to 150°C, passing all aerospace qualification tests.
2. Medical Devices
Medical imaging systems (e.g., MRI RF coils) need PCBs with low signal loss and biocompatibility. A medical device manufacturer needed PCBs for a portable ultrasound machineâtheir existing boards had insertion loss >0.3dB/inch, degrading image quality. We used immersion gold surface finish, PTFE-based laminates, and optimized trace design to reduce IL to â€0.08dB/inch. The PCBs met ISO 13485 standards and improved image clarity by 30%.
3. Industrial Equipment
Industrial IoT sensors (5G-enabled) require PCBs that resist vibration and humidity. A factory automation client needed PCBs for a wireless temperature sensorâtheir previous boards failed due to moisture-induced dielectric degradation. We used moisture-resistant PTFE laminates, vacuum-sealed fabrication, and conformal coating. The PCBs operated reliably in 95% RH environments for 2+ years without performance loss.
How to Choose a Manufacturer for Best RF Microwave PCB Fabrication for Industrial Applications?
Choosing the right manufacturer is as critical as design and material selection for best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applications. Industrial-grade fabrication requires specialized equipment, engineering expertise, and a proven track record in serving medical, aerospace, and industrial sectors.
Key Criteria for Selecting a Manufacturer
- Specialized Capabilities: Ensure they offer PTFE/hybrid stackups, impedance control ±3â5%, and precision etching (±0.04mm or tighter).
- Industry Certifications: Look for ISO 9001, ISO 13485 (medical), and AS9100 (aerospace) to ensure compliance with industrial standards.
- Testing Capabilities: They must have TDR, network analyzers, and environmental testing equipment to verify performance.
- Case Study Experience: Ask for references in your industryâexperience with similar applications reduces risk of failure.
- Engineering Support: Choose a manufacturer that offers DFM (Design for Manufacturability) support to optimize your design for fabrication.
Whatâs the Difference Between Industrial and Commercial RF Microwave PCB Fabrication?
Many engineers confuse industrial and commercial RF microwave PCB fabricationâbut the two differ drastically in performance requirements, materials, and QC standards. Commercial PCBs prioritize general usability; industrial PCBs prioritize reliability and durability in harsh conditions.
| Criteria | Industrial RF Microwave PCB Fabrication | Commercial RF Microwave PCB Fabrication |
|---|---|---|
| Impedance Tolerance | ±3â5% | ±10% |
| Material Quality | PTFE/hybrid laminates (Df â€0.0037) | Standard FR-4 (Df â„0.01) |
| Temperature Range | -40°C to 150°C (or higher) | 0°C to 70°C |
| QC Standards | 100% electrical/environmental testing | Sampling testing only |
| Reliability Focus | Long-term (10+ years) performance | Short-term (2â5 years) use |
How to Optimize RF Microwave PCB Design for Industrial Fabrication?
Design optimization is key to achieving best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applicationsâeven the best manufacturer canât fix a poorly designed board. The goal is to minimize signal loss, crosstalk, and thermal stress while ensuring manufacturability.
Essential Design Tips for Industrial RF Microwave PCBs
- Minimize Trace Length: Keep RF traces as short and straight as possible to reduce insertion loss and phase shift.
- Use Ground Planes Effectively: Add a solid ground plane under all RF traces to reduce crosstalk and improve impedance consistency.
- Avoid Right-Angle Bends: Use 45° bends or curves for RF tracesâright-angle bends cause signal reflection and impedance mismatch.
- Separate RF and Digital Layers: Place RF traces on dedicated layers, separated from digital/analog layers by ground planes to block interference.
- Optimize Component Placement: Place RF connectors and components close to the edge of the board to minimize trace length; keep heat-generating components away from sensitive RF paths.
What Are the Latest Trends in Best RF Microwave PCB Fabrication for Industrial Applications?
The industrial RF microwave PCB fabrication industry is evolving to meet the demands of 5G, IoT, and advanced aerospace/medical systems. The latest trends focus on higher frequency support, miniaturization, and more sustainable manufacturingâall while maintaining industrial-grade reliability.
Top 2026 Trends for Industrial RF Microwave PCBs
- Millimeter-Wave Fabrication: As industrial radar and 5G systems move to 60â77GHz, manufacturers are adopting advanced techniques (like laser drilling and thin-film deposition) to support these frequencies.
- Miniaturization: Industrial IoT sensors require smaller PCBsâtrends include finer line widths (0.05mm), smaller vias (0.1mm), and integrated passives to reduce board size.
- Sustainable Materials: Eco-friendly PTFE alternatives (like recycled high-frequency laminates) are gaining traction, meeting industrial performance requirements while reducing environmental impact.
- Automated Fabrication: AI-driven process control (for etching, lamination, and testing) improves consistency and reduces human errorâcritical for industrial QC.
FAQ: Common Questions About Best RF Microwave PCB Fabrication for Industrial Applications
Q1: Do industrial RF microwave PCBs always need PTFE-based materials?
NoâPTFE is ideal for high-frequency (above 5GHz) or high-reliability applications (aerospace/medical), but modified FR-4 (like Megtron 6) works for lower-frequency industrial systems (1â5GHz). The key is matching the materialâs Dk/Df to your operating frequency.
Q2: What impedance tolerance do I need for industrial RF microwave PCBs?
Most industrial applications require ±5% impedance tolerance. For critical applications (aerospace radar, medical imaging), use ±3% to ensure signal integrity. Anything wider than ±10% will cause significant reflection and signal loss.
Q3: How can I reduce signal loss in industrial RF microwave PCB fabrication?
Reduce signal loss by using low-Df materials (Df â€0.0037), immersion gold surface finish, short/straight RF traces, and impedance control. Avoid HASL (high solder mask loss) and ensure proper ground plane design to minimize crosstalk.
Q4: What environmental tests are required for industrial RF microwave PCBs?
Industrial PCBs typically require thermal cycling (-40°C to 125°C, 1000 cycles), humidity testing (85°C/85% RH, 1000 hours), and vibration testing (10â2000Hz) to ensure durability. Medical/aerospace may require additional tests (e.g., radiation hardness for satellites).
Q5: Can hybrid stackups (PTFE + FR-4) be used for high-power industrial applications?
Yesâhybrid stackups are ideal for high-power industrial applications. Use PTFE for RF layers (low loss) and FR-4 for control/power layers (mechanical stiffness). Ensure symmetrical stackups and proper lamination to avoid warpage.
Q6: How long does industrial RF microwave PCB fabrication take?
Lead times vary by complexity: simple 2-layer boards take 5â7 days, while complex 8-layer hybrid boards (with impedance control and testing) take 10â14 days. For aerospace/medical, add 3â5 days for additional QC and certification.
Q7: Whatâs the most common mistake in industrial RF microwave PCB fabrication?
The most common mistake is neglecting material consistencyâusing low-quality laminates with wide Dk fluctuations leads to frequency drift and signal loss. Always source materials from reputable suppliers and test every batch before fabrication.
Why Choose EBest for Best RF Microwave PCB Fabrication for Industrial Applications?
At EBest, we specialize in best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applications, with decades of experience serving aerospace, medical, and industrial equipment manufacturers. Our capabilities include PTFE/hybrid stackups, impedance control ±3â5%, precision etching, and rigorous QC testing to meet ISO 9001, ISO 13485, and AS9100 standards. We offer DFM support to optimize your design, real-world case study expertise, and reliable lead times to keep your projects on track. Whether you need prototype or high-volume production, we deliver industrial-grade RF microwave PCBs that perform in the harshest conditions. We provide best RF microwave PCB fabrication for industrial applicationsâif you need high-quality, reliable RF microwave PCBs for your industrial project, contact us today to place your order at sales@bestpcbs.com.