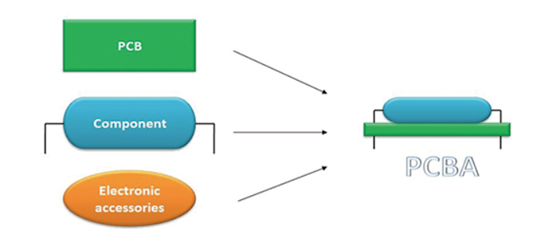
Circuit board PCBA means a finished Printed Circuit Board Assembly where components are sourced, placed, soldered, inspected, and tested to deliver a functional circuit board ready for integration into your product. This article explains how circuit board PCBA differs from bare PCB fabrication, what the PCBA process and testing include, how to avoid misbuild and rework, what drives pricing, and why short lead time depends on disciplined engineering inputs and production control.
When your schedule is tight, what usually blocks a âfastâ circuit board PCBA build from shipping on time?
- Quotes look fast, but lead time expands once parts are confirmed as long-lead or unavailable.
- Incomplete engineering data triggers back-and-forth that burns days before production even starts.
- The SMT line becomes the bottleneck when setup, stencil, or program readiness is late.
- Hidden rework loops appear after first build due to unclear polarity, footprint, or assembly notes.
- Testing is treated as an afterthought, so failures show up late and force retest or rebuild.
A circuit board PCBA manufacturer with short lead time removes these blockers by front-loading engineering clarity and locking a repeatable execution path.
- Validate BOM availability and alternates early to prevent material-driven delays.
- Standardize the engineering package so programs can be released without churn.
- Pre-stage SMT readiness (stencil, feeders, programs) to keep the PCBA SMT schedule predictable.
- Use risk-based inspections to catch defects before they become rework cycles.
- Define PCBA testing requirements up front and ship with measurable test evidence.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is a PCB and PCBA manufacturer built for speed without sacrificing control. We combine in-house PCB fabrication and PCBA assembly, disciplined DFM review, component sourcing through an established supply network, and digital traceability that helps teams track lots, progress, and build status with high responsiveness. If you need a fast, stable circuit board PCBA build, contact sales@bestpcbs.com.
How Does Printed Circuit Board Assembly PCBA Differ From Bare PCB Fabrication?
Bare PCB fabrication delivers the board structure; printed circuit board assembly PCBA delivers a working electronic assembly. For short lead time, the key difference is that PCBA adds supply chain and process dependencies that must be planned, not guessed.
What Changes When You Move From PCB To PCBA
- Input Files Expand: PCBA needs BOM, Pick-and-Place, assembly drawings, and test requirements, not just Gerber.
- Material Risk Appears: Availability, alternates, and minimum order quantities can control schedule.
- Process Windows Matter: Paste type, reflow profile, and handling rules affect yield.
- Inspection Becomes Mandatory: AOI/X-Ray strategy determines how early defects are caught.
- Testing Defines âDoneâ: Functional pass criteria must be agreed before shipping.
Quick Comparison Table
| Item | Bare PCB Fabrication | Printed Circuit Board Assembly PCBA |
|---|---|---|
| Deliverable | Board Structure | Working Assembly |
| Main Constraints | Stack-Up, Drilling, Finish | Parts, SMT Setup, Yield, Test |
| Typical Risks | Layer Registration, Impedance | Shortages, Misbuild, Rework |
| Lead Time Driver | Panel Schedule | Parts + SMT + Testing |
Short lead time is easier to achieve in PCBA when the assembly scope and acceptance criteria are defined as clearly as the PCB build notes.

What Does The PCBA Process Include From SMT To Final Testing?
The PCBA process is a chain of controlled steps. For a short lead time build, the fastest programs are those where each step has clear inputs, defined checkpoints, and minimal iteration.
Typical PCBA Process Stages
- Engineering Release: File validation, DFM, and build readiness checks.
- Material Preparation: Kitting, baking (as needed), and ESD/Moisture controls.
- SMT PCBA Setup: Stencil, program, feeders, and first article verification.
- Reflow And Inspection: Controlled profiling and AOI verification.
- THT Or Secondary Ops: Through-hole, selective soldering, or hand solder.
- Cleaning And Coating (If Required): Application-specific requirements.
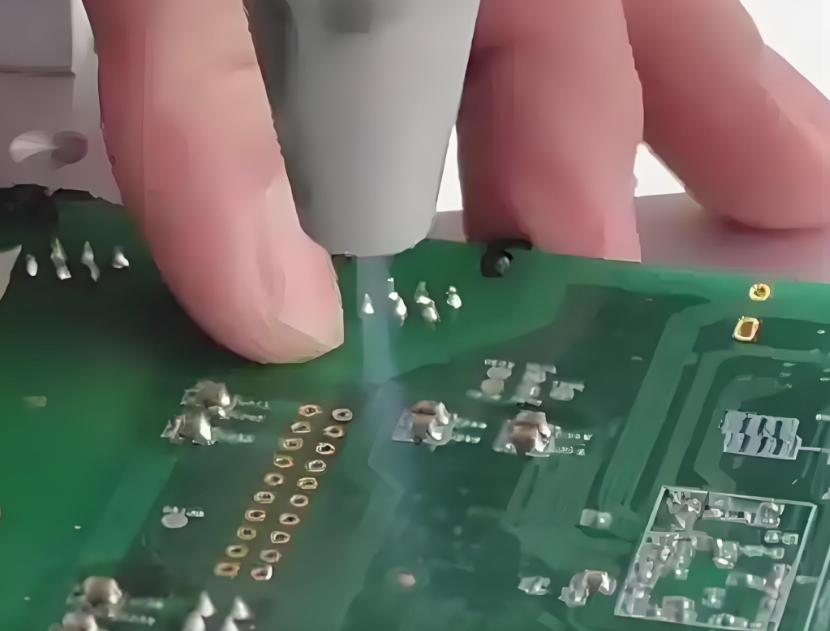
- PCBA Testing: Functional testing, programming, and final verification.
What Accelerates The Process In Real Builds
- Pre-approved alternates for common shortage items
- Clear polarity and reference designators in assembly drawings
- Defined test method and pass/fail rules before build starts
- Stable revision control to avoid last-minute ECO churn
A short lead time circuit board PCBA build is not ârushing.â It is eliminating rework loops by making the process deterministic.
Why Is Qi Wireless Charger PCBA Circuit Board Design Critical For Charging Performance?
Qi wireless charger PCBA circuit board performance depends on how the electronics, coil, and mechanical constraints interact. Even if you are outsourcing assembly, design choices determine yield and functional pass rate, which directly affects lead time.
Design Elements That Influence Performance And Build Success
- Coil Alignment Tolerance: Small alignment drift can reduce coupling efficiency.
- Thermal Management: Power stages need controlled heat paths to avoid throttling.
- EMI Layout Discipline: Switching noise can disrupt control loops and certification.
- Component Selection: Key ICs and power components often have supply constraints.
- Test Access: Pads and fixtures must support stable programming and validation.
Practical Note For Short Lead Time
If your Qi wireless charger PCBA circuit board coil supply is tight, lead time is often determined by coil procurement and incoming verification rather than by the SMT line speed.
For Qi builds, short lead time comes from aligning design-for-assembly, supply reality, and testability early, not from compressing the assembly window.
What Engineering Data Must Be Defined Before Starting A Circuit Board PCBA Build?
Fast builds start with complete, unambiguous engineering data. Missing or conflicting details usually create the longest delays because they pause the release process.
The Minimum Engineering Package For Speed
- Gerber And Fabrication Notes: Stack-up, finish, thickness, impedance needs.
- BOM With Manufacturer Part Numbers: Include alternates and do-not-substitute flags.
- Pick-and-Place File: Centroid, rotation, and side designation.
- Assembly Drawing: Polarity, special instructions, torque, and labeling needs.
- Programming And Test Requirements: Test points, firmware, and pass criteria.
- Revision Control: Clear version naming across all files.
A Simple Rule That Saves Days
If two files disagree, production stops. The fastest path is a single âsource of truthâ package.
A circuit board PCBA manufacturer with short lead time can only move as fast as the engineering package allows.
How Do Printed Circuit Board PCBA Services Reduce Rework And Misbuild Risk?
Good printed circuit board PCBA services reduce rework by preventing ambiguity and catching defects early. Rework is the silent lead time killer because it consumes capacity and forces retest.
What Reduces Misbuild Risk Most Effectively
- DFM And DFA Review: Identify footprint, spacing, and assembly hazards before build.
- BOM Risk Screening: Flag EOL, long-lead, and counterfeit-prone parts.
- First Article Control: Validate placement, polarity, and orientation before full run.
- Process Checkpoints: SPI (if used), AOI, and controlled reflow profiling.
- Clear Work Instructions: Special notes for connectors, shielding, or sensitive parts.
Compact âRework Costâ View
Rework Impact = (Rework Time à Line Rate) + Retest Time + Schedule Slip
Reducing rework is often the fastest and cheapest way to protect lead time.
PCBA services create speed by minimizing preventable mistakes, not by compressing inspection.
What Cost Drivers Actually Determine Printed Circuit Board PCBA Pricing?
Printed circuit board PCBA pricing is mainly determined by material strategy, assembly complexity, and testing scope. Fast builds can be cost-effective, but only if the program avoids last-minute changes and rework.
Primary Pricing Drivers
- BOM Cost And Availability: Supply volatility and alternates affect price stability.
- Placement Count And Mix: More placements and diverse packages increase cycle time.
- Setup And NRE: Stencils, programming, and fixture preparation.
- Double-Sided Or Fine-Pitch Requirements: Adds process and inspection time.
- Testing Depth: Functional testing, programming, burn-in, or coverage requirements.
- Yield Expectations: Tight yield targets require stricter process control.
Short Table For Quick Buyer Decisions
| Driver | How It Moves Cost | How It Moves Lead Time |
|---|---|---|
| BOM Risk | Higher when scarce | Higher when parts slip |
| Testing Scope | Higher with fixtures | Longer when undefined |
| Complexity | Higher with fine pitch | Longer with rework |
Accurate pricing comes from defined scope. âFastâ quotes become expensive when assumptions are left unstated.
When Does SMT PCBA Become A Bottleneck In Volume Circuit Board Production?
In volume builds, SMT PCBA becomes the bottleneck when capacity is not the limiting factorâreadiness is. The line can run quickly, but only if programs, materials, and change control are stable.
Common Bottleneck Triggers
- Late Material Kitting: Missing a few critical parts stalls the entire line.
- Program Instability: Frequent ECOs force revalidation and reset schedules.
- Feeder And Setup Complexity: High-mix builds increase changeover time.
- Stencil And Tooling Delays: Stencils and fixtures not ready on time.
- Quality Hold Cycles: Unclear defect ownership slows release.
Practical Volume Tip
If you want short lead time at volume, lock a stable BOM and revision cadence. Change control discipline is often worth more than extra SMT capacity.
SMT PCBA bottlenecks are usually planning and release bottlenecks in disguise.
What Testing Methods Are Commonly Used In PCBA Printed Circuit Board Assembly?
PCBA testing should be chosen based on risk, volume, and failure impact. The wrong approach either adds cost with little value or misses defects until late, which breaks short lead time goals.
Common PCBA Testing Methods
- Visual Inspection And AOI: Fast detection of solder and placement defects.
- X-Ray Inspection (When Needed): For hidden joints like BGA.
- In-Circuit Test (ICT): Strong for electrical opens/shorts in volume builds.
- Flying Probe Test: Useful for lower volume without fixture investment.
- Functional Test (FCT): Validates real-world operation and interfaces.
- Programming And Calibration: Firmware loading and parameter checks.
Quick Test Selection Table
| Build Type | Typical Best Fit |
|---|---|
| Prototype / Low Volume | Flying Probe + Functional Test |
| Medium Volume | AOI + Functional Test |
| High Volume | ICT + Functional Test |
Testing supports short lead time when it is defined early and matched to program risk, not added at the end as a rescue step.
To conclude, circuit board PCBA is the completed assembly that turns a bare PCB into a functional product-ready module, and its lead time is primarily controlled by engineering readiness, parts availability, SMT execution, and test definition.
This article explained how printed circuit board assembly PCBA differs from PCB fabrication, what the PCBA process includes, why Qi wireless charger PCBA circuit board design affects outcomes, how to reduce rework risk, what drives pricing, how SMT capacity becomes a bottleneck, and which PCBA testing methods fit different build scenarios.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) supports short lead time builds through disciplined engineering review, in-house PCB and PCBA capability, and production control that keeps schedules predictable. For quotations or engineering review, pls feel free to contact us via sales@bestpcbs.com.
FAQs
What is the difference between a circuit board and a PCBA?
A circuit board usually refers to a bare PCB, while a PCBA is the assembled version with components mounted and soldered, ready to function in a product.
What are common PCBA defects?
Common PCBA defects include solder bridges, insufficient solder, tombstoning, misalignment, wrong polarity, lifted leads, and intermittent connections caused by process variation.
How many types of PCBA are there?
PCBA is often categorized by assembly technology and complexity, such as SMT PCBA, through-hole PCBA, mixed-technology PCBA, single-sided, double-sided, and multilayer assemblies.
How Do Component Selection And Part Categories Affect Circuit Board PCBA Quote Accuracy?
Part categories influence whether components are readily available, require special sourcing, or create added handling and setup steps; these factors can change both cost and lead time if not defined in the quote assumptions.