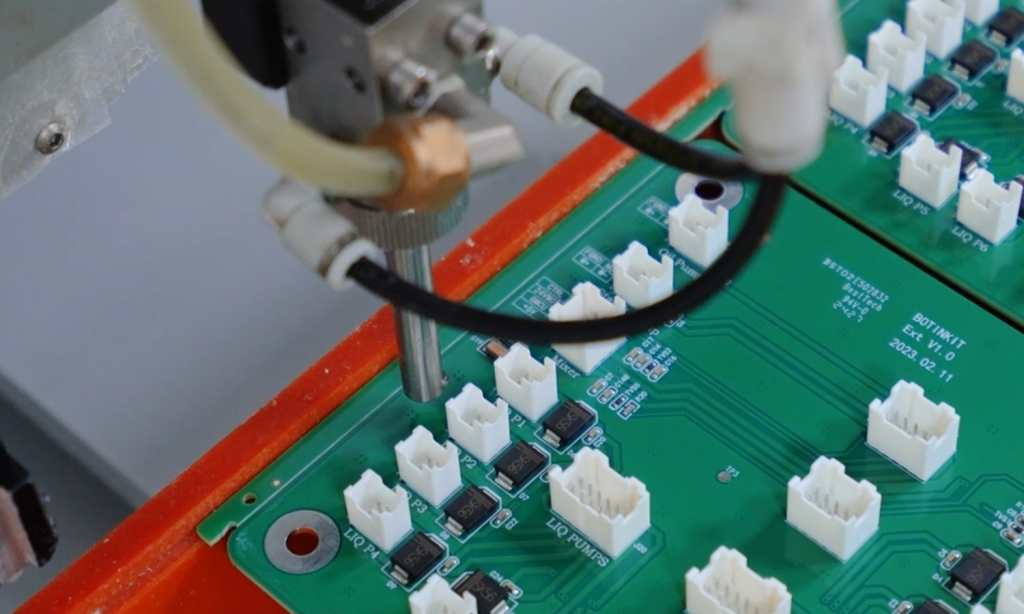
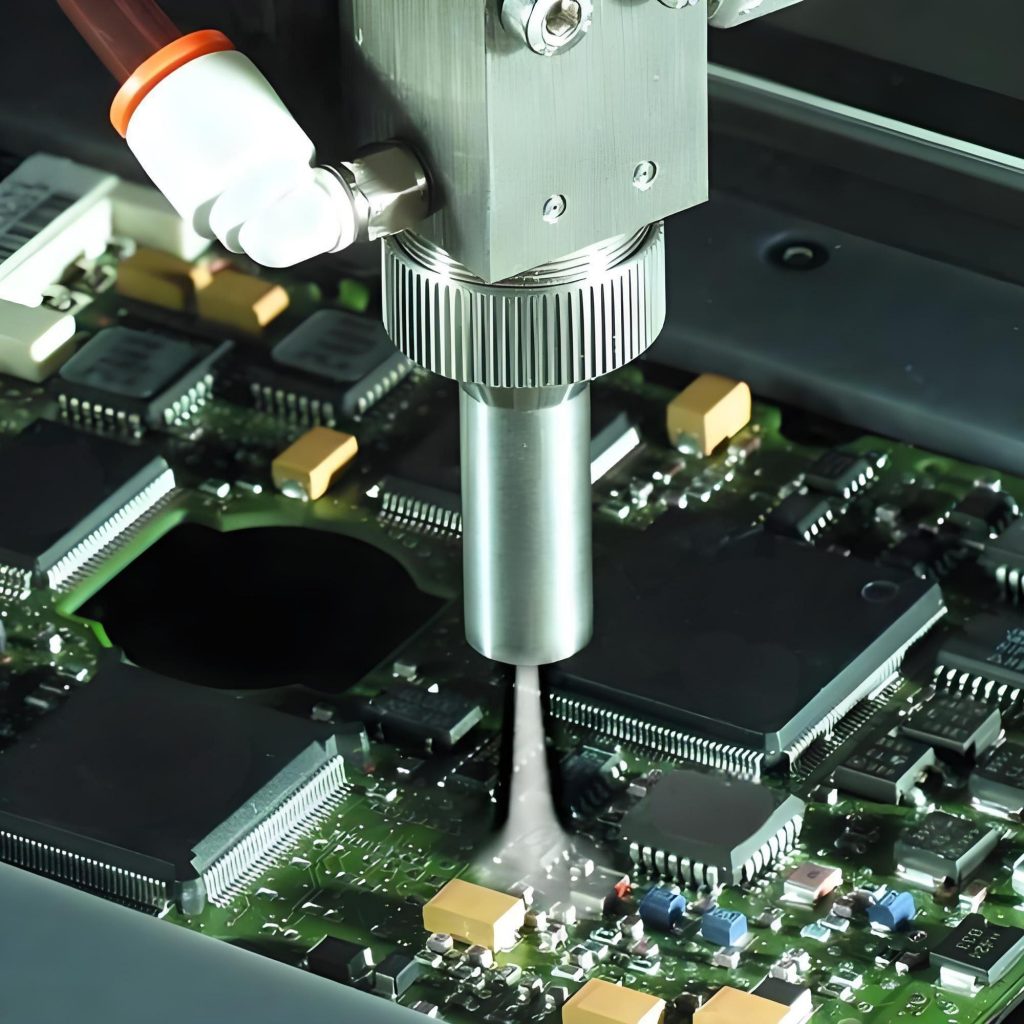
Why conformal coating is used in PCB? Let’s discover benefits, types, standards, process and removal solution for PCB conformal coating.
What Is Conformal Coating on PCB?
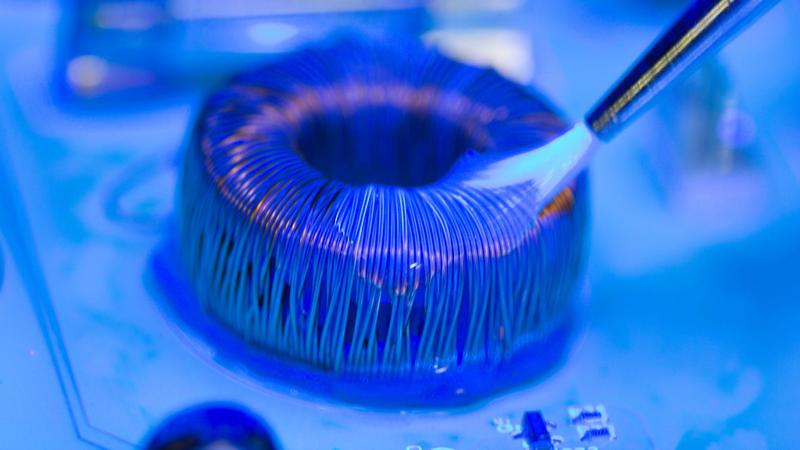
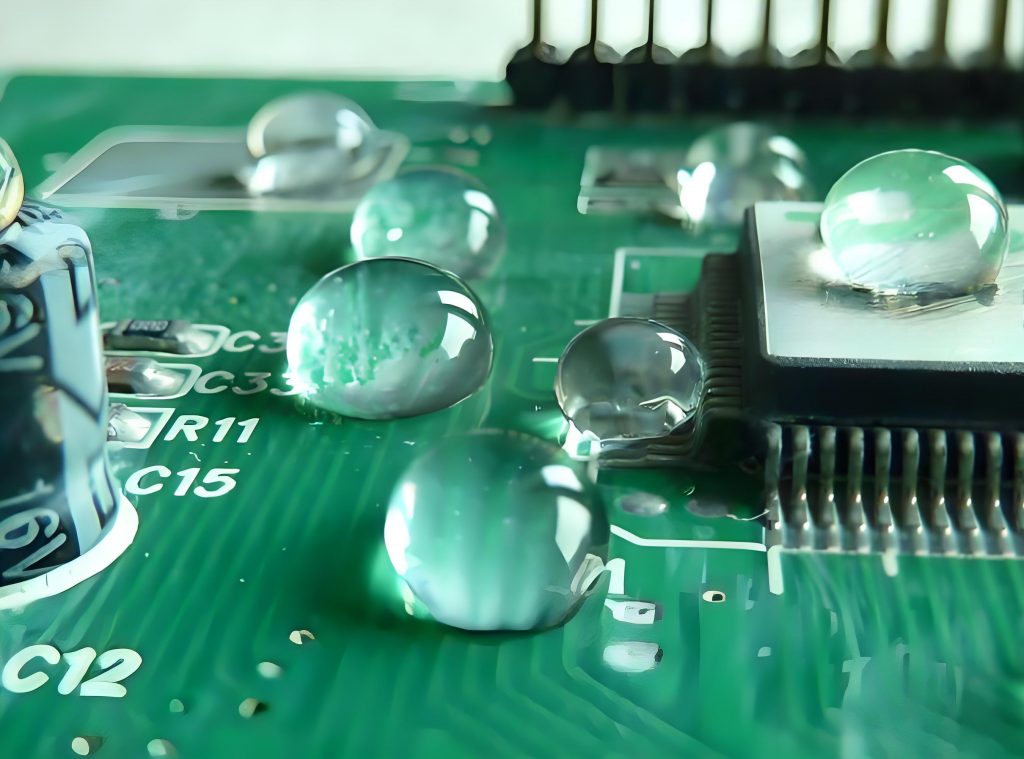
Conformal Coating is a specially formulated protective paint applied to PCB surfaces to form a 25-200μm transparent protective film. Its function is to provide protection against moisture, salt mist, and mold, effectively blocking water vapor, chemical corrosion, and biological erosion while offering comprehensive protective capabilities such as insulation, shock resistance, and resistance to high/low temperatures. This technology is widely used in automotive electronics, aerospace, medical devices, and other fields, effectively extending the service life of PCBs in complex environments and supporting miniaturized component designs.

Why Conformal Coating Is Used In PCB?
Benefits of PCB Conformal Coating:
- Enhanced Environmental Adaptability and Reduced Failure Risk: Moisture-proof, salt spray-proof, and mold-proof properties block moisture, chemical corrosion, and biological attack. For high-density PCBs or precision components, it prevents circuit oxidation, solder joint corrosion, or short circuits caused by environmental factors such as humidity and salt spray, significantly reducing rework rates and after-sales costs.
- Enhanced Mechanical Strength and Shock Resistance: After curing, it forms an elastic protective layer, reducing mechanical damage caused by vibration, impact, or thermal shock. Suitable for dynamic scenarios such as automotive and industrial equipment, effectively extending the PCB’s lifespan under harsh conditions.
- Optimized Design Space and Electrical Performance: Insulation supports smaller line spacing and higher power density, enabling miniaturized component design; leakage protection improves signal integrity and reduces electromagnetic interference (EMI) risks.
- Simplified Process and Cost Control: Utilizes automated coating (spraying/dipping) processes, which are highly efficient and mature. Material costs vary depending on the type, but overall costs are controllable during mass production, while reducing hidden losses caused by environmental failures.
- Meet Industry Standards and Certification Requirements: High-reliability fields (such as automotive electronics and medical devices) require conformal coating protection to ensure compliance with salt spray tests, flame retardant certifications, etc. Planning the coating process in advance can mitigate risks associated with later certification processes.
Common Types of PCB Conformal Coating
Acrylic resin conformal coating
- Features: Fast surface drying and curing time, excellent conformal properties, inexpensive, transparent, flexible texture, and easy to repair.
- Applications: Cost-sensitive consumer electronics products requiring rapid curing.
Polyurethane conformal coating
- Features: Long service life, strong chemical corrosion resistance, but relatively long curing time.
- Applications: Industrial equipment or automotive electronics requiring long-term stability.
Silicone resin conformal coating
- Features: Excellent high-temperature resistance, stable performance in extreme temperature environments, and good solvent resistance.
- Applications: Aerospace, military, and other fields requiring high temperature and extreme environmental resistance.
Rubber-based conformal coating
- Features: Good elasticity, providing good shock resistance and protection against mechanical damage.
- Applications: Electronic equipment subject to strong vibration or mechanical impact.
Conformal Coating for PCB Standards
| Industry | Standard | Thickness Requirement | Performance Indicators | Test/Verification Criteria |
| General Electronics | IPC-A-610 | 15~17μm (protection level dependent) | Moisture/salt/dust proof; Insulation ≥100V/μm | IPC-A-600 appearance grading (level 1-3) |
| Automotive Electronics | IPC-6012 | ≥25μm | Dielectric strength ≥500V/mil; Temperature resistance -40℃~150℃ | Thermal cycling 1000 cycles; Salt spray test 48H |
| Aerospace | MIL-I-46058C | 30~130μm | Extreme environment adaptability (-55℃~200℃); Chemical corrosion resistance; High frequency signal stability | MIL-STD-810H environmental reliability test |
| High Reliability Industrial | DIN EN 61086 | 50~200μm | Sulfurization resistance; Aging resistance (UV stability); Flame retardancy (UL94 V-0) | DIN 50021 salt spray test |
PCB Conformal Coating Process
Below Is A Detailed Guide to PCB Conformal Coating Process:
1. Surface Preparation and Cleaning
- Core Requirement: Thoroughly remove PCB surface contaminants (such as flux residues, grease, dust) to ensure coating adhesion.
- Operational Standards: Use ultrasonic cleaning, solvent wiping (e.g., isopropyl alcohol), or plasma cleaning technology. Verify that the surface contact angle after cleaning is ≤30° to meet the IPC-A-610 standard.
- Special Treatment: For high-reliability scenarios, additional micro-etching or chemical cleaning steps are required to enhance the bonding strength between the coating and the substrate.
2. Shielding Area Planning
- Precise Shielding: Use solvent-resistant masking tape or custom coating masks to protect connectors, test points, heat sinks, key switches, and other areas that require maintaining electrical contact or mechanical function.
- Automation Support: Adopt laser-cut masking templates or robotic spraying systems to achieve high-precision selective coating, preventing coating intrusion into sensitive areas.
3. Coating Material Selection & Matching
- Nanocomposite coating: Incorporating nano-silica or boron nitride particles to improve coating abrasion resistance and thermal conductivity (e.g., thermal conductivity > 1.2 W/m·K at 200℃), suitable for 5G base station PCBs.
- Environmentally friendly formulation: Water-based acrylic coating with VOC emissions < 50 g/L, complying with EU REACH regulations and California Proposition 65.
- Thickness gradient design: A 200 μm thick coating is used in critical solder joint areas, gradually decreasing to 25 μm at the edges, balancing protection and heat dissipation requirements.
4. Coating Application Techniques
- Spray: Suitable for large-area uniform coating. Requires control of nozzle pressure and atomization effect to ensure coating thickness of 20-100μm.
- Dip: Suitable for batch production. Requires control of immersion speed and withdrawal angle to avoid air bubble entrapment.
- Selective Coating: Uses robotic or needle systems to precisely control the coating area, reducing material waste.
- Brush: Suitable for small-batch or repair scenarios. Requires professional operation to avoid uneven coating.
- Automation Integration: For high-throughput scenarios, online spraying robots combined with vision inspection systems are used to adjust the coating path in real time.
5. Curing and Post-Processing
- Curing Process: Depending on material properties, choose thermal curing (80-120℃), UV curing (requires photoinitiator), or room temperature curing. Curing time must strictly follow the material data sheet (TDS).
- Post-Curing Verification: After curing, perform coating hardness test (pencil method), adhesion test (cross-cut tape test), and weathering test (double 85 test: 85℃/85% RH).
6. Quality Control and Inspection
- Process Monitoring: Use wet film thickness gauges to measure coating thickness in real time. UV detection systems identify coating defects such as pinholes and bubbles.
- Destructive Testing: Cross-sectional analysis verifies the interface bonding between the coating and the substrate. Thermal shock testing (-40℃~125℃ cycling) verifies the coating’s temperature change resistance.
- Non-Destructive Testing: Automated optical inspection (AOI) systems scan the coating surface to identify defects such as cracks and delamination.
7. Environmental and Safety Compliance
- Environmental Compliance of Materials: Comply with RoHS and REACH regulations. Prioritize the use of low-VOC (volatile organic compounds) or water-based coating materials.
- Operational Safety: Equip with ventilation systems and personal protective equipment (PPE). Curing exhaust must be treated by environmental protection equipment to meet emission standards.
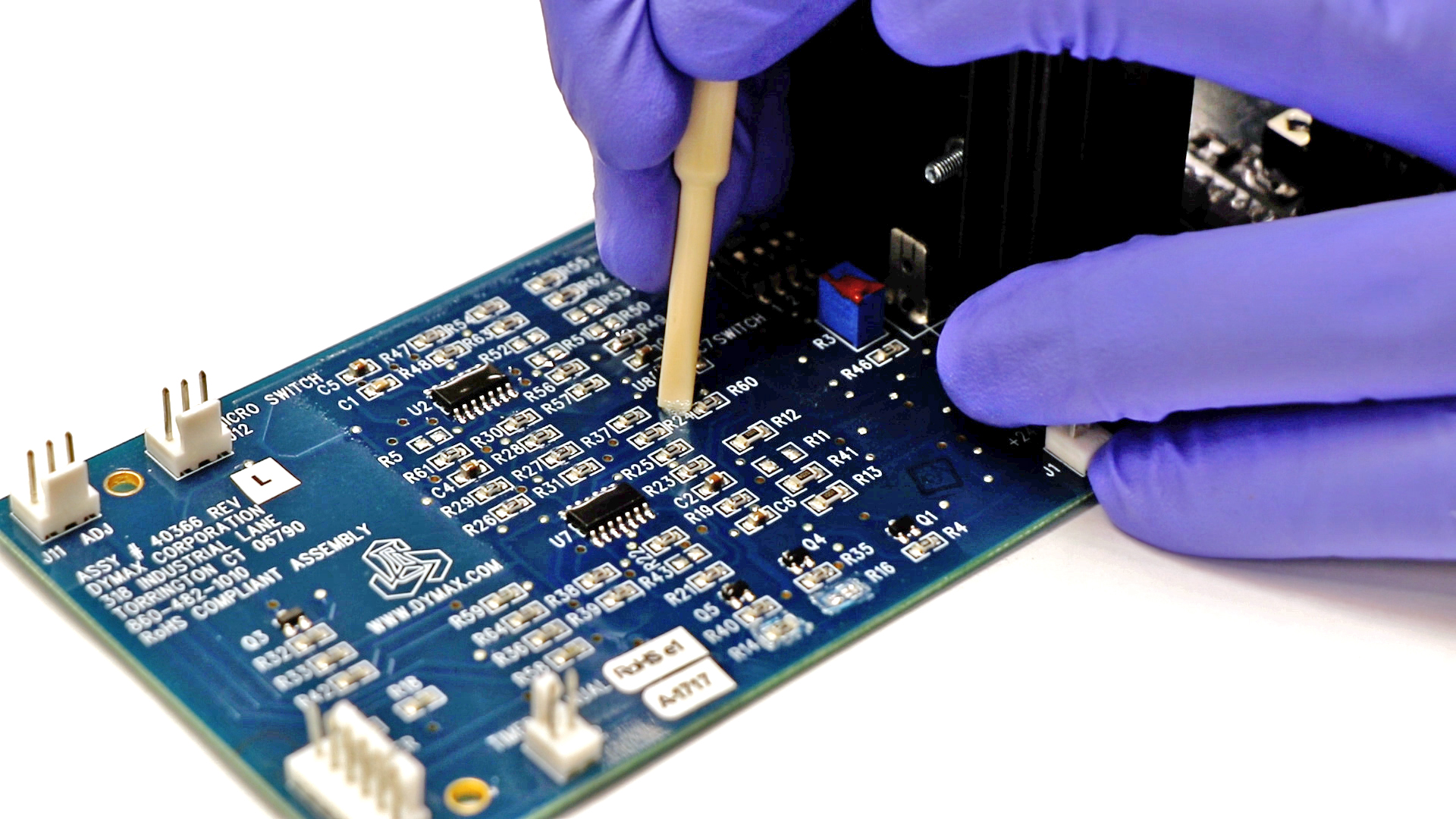
How to Remove Conformal Coating From PCB?
Below Is A PCB Conformal Coating Removal Solution:
1. Accurate Identification and Characteristics of Coating Types
- Acrylic (AR): General-purpose coating, soluble in acetone/isopropanol. Case: Humiseal 1B31 requires high-Kb flux cleaners; immersion requires lid to prevent evaporation (ref: “Classification of Conformal Coatings”).
- Silicone (SR): Extreme temperature resistance (-65°C to 200°C). Requires siloxane-specific solvents or micro-sandblasting (80μm glass beads). Example: Aerospace PCBs use 200°C hot air to soften coating before plastic scraper removal, avoiding copper trace damage.
- Polyurethane (UR): Chemical corrosion resistance. Requires strong solvents (dichloromethane) or 200–300°C hot air. Note: Uncured coatings use dedicated removers; cured coatings need extended solvent immersion.
- Epoxy (ER): High hardness. Requires mechanical grinding (400–600 grit) or 150–200°C hot air stripping. Example: Automotive PCBs limit sandblasting pressure to ≤0.3 MPa to prevent trace fractures.
- Parylene (XY): Vapor-deposited coating. Only removable via plasma etching (industrial equipment required). Compliance: RoHS 3.0, heavy metal ions ≤0.5 mg/L.
2. Chemical Solvent Method – Detailed Operational Standards
Solvent Selection & Compatibility: Acrylic → acetone/IPA; silicone → siloxane solvents; polyurethane → dichloromethane. Test solvents on scrap boards to avoid ABS/plastic/connector corrosion.
Procedures:
- Localized Repair: Apply solvent with cotton swab, wait 1–2 min, gently scrape with plastic spatula.
- Full Board Stripping: Immerse in SUS304 solvent tank for ≥1 hr, brush with soft bristles.
Safety & Environmental Compliance: Operate in ventilated areas; wear nitrile gloves + goggles. Hazardous waste disposal required; UV blacklight checks for ionic residues (fluorescence indicates contamination).
3. Mechanical & Thermal Methods – Technical Details & Case Studies
- Micro-Sandblasting: Precision pen with 80μm glass beads, 3-sec scan at 10cm. Ideal for BGA corners. Example: High-frequency PCBs use this to maintain 2GHz signal integrity.
- Hot Air Gun: 150–200°C for 10–20 sec, followed by plastic scraper removal. Caution: Temperatures >180°C risk burning silkscreen; use thermal tape to protect sensitive zones.
- Mechanical Grinding: 400–600 grit sandpaper or rotary tools (500–1000 RPM), paired with compressed air to clear debris. Critical: Minimize pressure to avoid trace/solder mask damage.
4. Advanced Techniques – Laser & Plasma Etching
- Laser Ablation: UV laser (355nm) for selective removal of parylene. Parameters: Energy density ≤10 J/cm² to prevent substrate carbonization.
- Plasma Etching: Ionized gas stripping via equipment (e.g., Schuler HFA). Case: High-value aerospace PCBs use this for substrate-safe removal.
5. Safety & Environmental Compliance
- PPE: Respirators + goggles + solvent-resistant gloves; avoid direct skin contact.
- Environmental Management: Waste solvents require licensed disposal; effluent COD ≤500 mg/L, heavy metals ≤0.5 mg/L (GB/T 26572).
- Recoating Procedures: Post-cleaning wipe with 90%+ IPA, match original coating type (e.g., silicone-to-silicone). Apply thin layers (25–50μm), cure per manufacturer specs (e.g., UV acrylic: 8-sec cure). Inspect via 10x magnification for bubbles/pinholes.
PCB Conformal Coating Services Offered by EBest Circuit (Best Technology)
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) offers professional conformal coating services for PCBs, including four types of PCB conformal coating services:
- Acrylic resin conformal coating
- Polyurethane conformal coating
- Silicone resin conformal coating
- Rubber-based conformal coating
Our Quality Assurance
- Coating Process: Spraying, dip coating, and brush coating are used, with film thickness controlled between 25-75μm.
- Curing Control: Supports UV curing (3-5 seconds surface dry) and heat curing (stepped temperature increase).
- Quality Requirements: The paint film is smooth and defect-free, and adhesion passes the cross-cut adhesion test to ensure protective effect.
Why Choose us?
- Environmental Protection and Customization: Provides water-based products and customized solutions, compliant with RoHS and other standards.
- High-Precision Equipment: Uses selective coating machines to achieve film thickness control accuracy of ±2μm.
- Rapid Response: Supports small-batch trial production and mass production, flexibly meeting customer needs.
Welcome to contact us if you have any request for PCB conformal coating service: sales@bestpcbs.com.