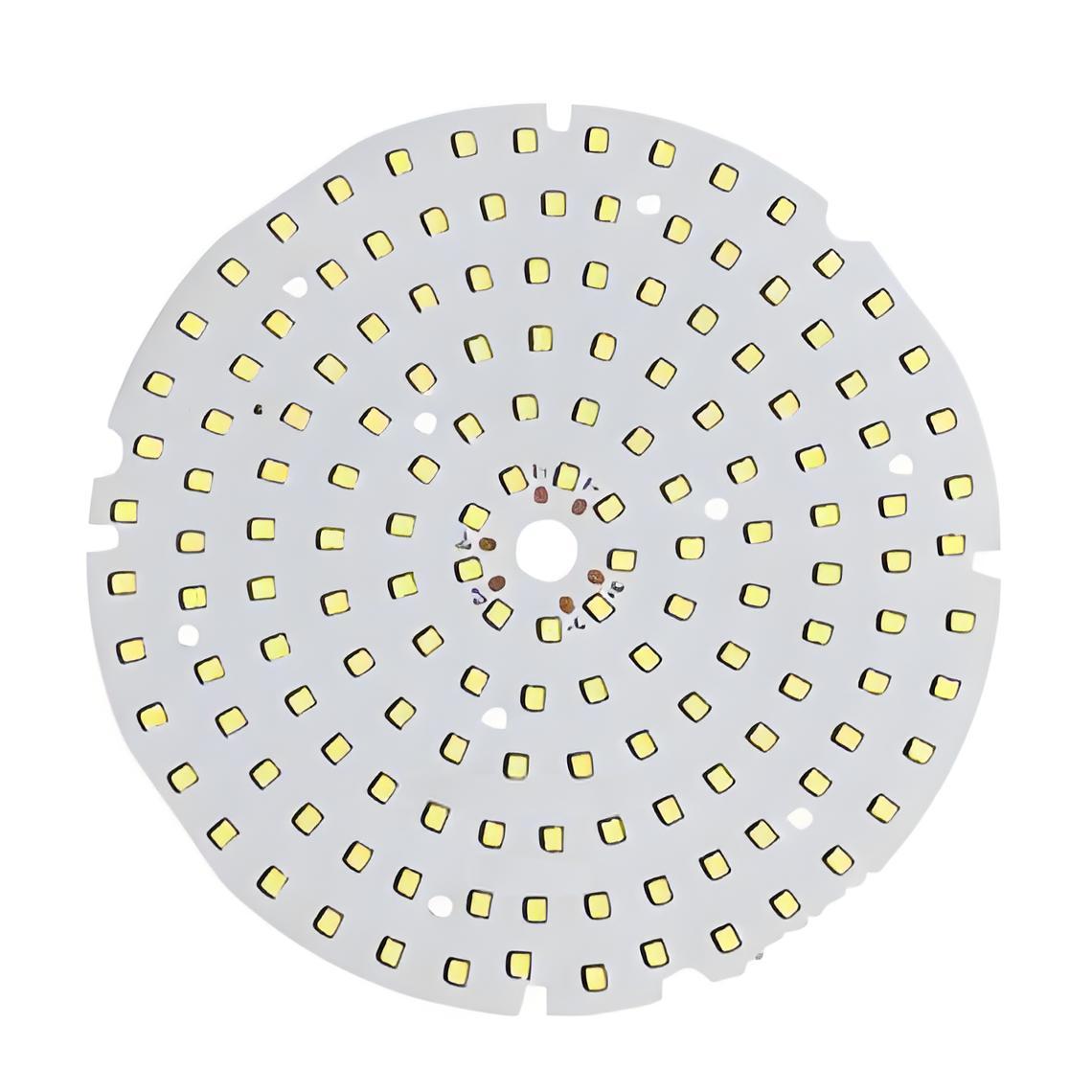
An aluminium LED PCB board is a circuit board with an aluminum base that quickly removes heat from LED components. This keeps the lights cooler, brighter, and longer-lasting. Known for its durability and efficiency, itâs widely used in LED lighting for homes, cars, and industrial devices.
What is an LED aluminium PCB?
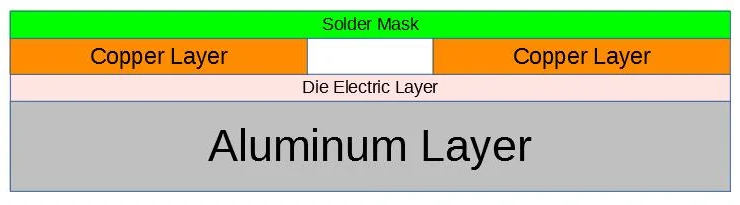
An aluminium LED PCB board is a printed circuit board that uses aluminium as the base material. This layer replaces the traditional fiberglass or epoxy base youâll find in standard PCBs. The board usually consists of three layers: a copper circuit layer, an insulating layer, and the aluminium base.
Why aluminium? Because it dissipates heat much better than other materials. LEDs generate a significant amount of heat, and if itâs not managed well, performance and lifespan suffer. This is where aluminium boards shine.
You might also hear terms like aluminum pcb board, led aluminum plate pcb board, or aluminium led pcb circuit board. They all refer to the same thing.
Why use aluminium PCB board for LED?
LEDs are efficient but sensitive to heat. A high temperature not only dims the brightness but also reduces the LEDâs lifespan. Thatâs why aluminium is the material of choice for LED PCBs.
Here are the reasons why the market chooses aluminum LED PCB boards:
- Superior heat dissipation: Keeps the LED cool.
- Stable performance: Even after long hours of operation.
- Longer lifespan: Your LEDs will last much longer.
- Lightweight: Ideal for slim lighting devices.
- Cost-effective: Fewer cooling components are needed.
What are the advantages of aluminium LED PCB?
- 1. Thermal conductivityThe main benefit is exceptional heat transfer. It quickly pulls heat away from LEDs, helping them work efficiently and safely.
- 2. DurabilityAluminium is tough. It can handle mechanical stress better than fiberglass boards.
- 3. Lightweight structureDespite being metal, aluminium is light.
- 4. Lower energy consumptionCooler operation means LEDs run at optimal performance, using less energy.
- 5. Eco-friendlyAluminium is recyclable. That makes LED aluminium PCBs a better choice for sustainable manufacturing.
- 6. High reliabilityThe performance remains stable, even in harsh conditions.
How to design a aluminium pcb circuit board?
Designing an aluminum pcb design takes careful planning. Here are the essential steps:
- 1. Choose the right stack-upA basic aluminium PCB has a metal base, a dielectric layer, and a copper circuit.
- 2. Heat analysisKnow where heat will concentrate. Plan the board so thermal paths lead to the aluminium base efficiently.
- 3. Layout for efficiencyPlace high-heat components away from each other. Spread them out to prevent hotspots.
- 4. Use thermal viasThey help transfer heat from the top layer to the aluminium base.
- 5. Pick the correct thicknessA thicker aluminium base offers better heat dissipation but adds weight.
- 6. Surface finish mattersGo for a finish that resists corrosion and ensures strong soldering.
Aluminium LED PCB vs standard PCB: What’s better?
Letâs compare a standard FR4 PCB with an aluminium led pcb board:
| Feature | Standard PCB | Aluminium LED PCB |
| Heat Dissipation | Poor | Excellent |
| Lifespan | Shorter | Longer |
| Durability | Moderate | High |
| Weight | Light | Light |
| Cost | Lower upfront | Saves on cooling costs |
| Reliability | Lower | Very high |
For high-power applications like LED lighting, the aluminium PCB is clearly the better choice.
What affects aluminium board price for LEDs?
You may be wondering what impacts the aluminium board price or aluminum board price? Several factors determine the cost:
- Board thickness: Thicker boards cost more.
- Copper layer weight: Heavier copper increases durabilityâand cost.
- Dielectric material: High-grade insulation adds to the price.
- Board size and shape: Custom shapes are more expensive.
- Order quantity: Bulk orders typically get better pricing.
- Surface finish: Extra coatings like ENIG or OSP raise the cost.
- Lead time: Faster delivery can add urgency charges.
Applications of aluminium LED PCB
These boards are found in a wide range of lighting applications. Hereâs where aluminium pcb board for LED really shines:
- Home lighting: LED bulbs, ceiling lights, and decorative strips.
- Street lights: Long hours and extreme temperatures demand aluminium PCBs.
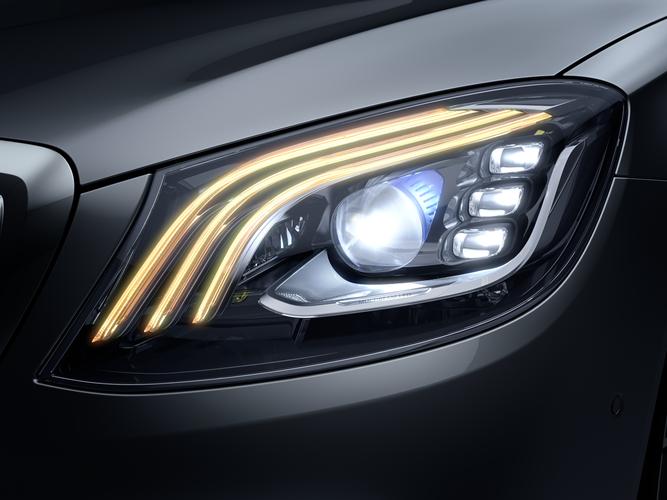
- Automotive lighting: Headlights and interior LED systems.
- Backlighting: TVs, monitors, and advertising displays.
- Medical lighting: Surgical and diagnostic tools need precision and reliability.
- Industrial lighting: High-bay and warehouse lights.
- Consumer electronics: Flashlights, phone lights, and wearable devices.
Conclusion:
The aluminium LED PCB board is ability to handle heat, maintain performance, and last longer gives it a huge edge over traditional PCBs. With rising demands for energy-saving and durable solutions, switching to aluminium pcb board for LED is the smart choice.
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we specialize in premium-quality aluminium LED PCB boards tailored to your needs. From design to full production, we offer dependable, cost-effective solutions with a quick turnaround.
Get in touch today: sales@bestpcbs.com