PCBA ISO13485‚Äč is the gold-standard quality management system specifically for the design, production, and servicing of printed circuit board assemblies destined for medical devices. This article provides a comprehensive guide to navigating ISO 13485 compliance for your medical electronics prototypes and production.
Medical device teams often discover that prototype PCBA sourcing becomes risky when speed, compliance, and future scalability are not aligned from the start.
- Unclear regulatory requirements at the prototype stage, leading to rework.
- Few suppliers capable of both rapid prototyping and ISO 13485 discipline.
- Cost and lead-time spikes when moving from non-compliant prototypes to production.
- Missing documentation and traceability that later block audits and transfer.
- Supply chain and quality risks that threaten safety and submissions.
These risks are mitigated by working with a PCBA manufacturer that applies ISO 13485 principles from the very first prototype build.
- Early DfM and regulatory alignment to keep prototypes on a compliant path.
- Fast-track prototype services executed within an ISO 13485 framework.
- Scalable processes supporting quick turn PCBA prototype ISO13485 builds through production.
- Complete DHR and end-to-end traceability for every prototype batch.
- Risk-based supplier management ensuring component quality and supply continuity.
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we are a specialized electronics PCBA supplier for medical equipment with ISO13485 approved. Our factory is dedicated to serving the demanding medical and high-reliability sectors. We combine ISO13485-certified processes with extensive engineering support to deliver custom ISO13485 medical PCBA‚Äč solutions that accelerate your development cycle while building a solid foundation for regulatory approval. For your prototype PCBA ISO13485‚Äč needs and beyond, contact our team at sales@bestpcbs.com.

What Is PCBA ISO13485 and Why Is It Critical for Medical Electronics?
PCBA ISO13485 refers to the application of the ISO13485:2016 standard‚ÄĒ‚ÄúMedical devices‚ÄĒQuality management systems‚ÄĒRequirements for regulatory purposes‚ÄĚ‚ÄĒspecifically to the Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) process. It is not just a certificate on the wall; it is an active, documented system that governs every aspect of a PCBA supplier‘s operations when serving the medical industry.
For medical electronics, this is critical because the PCBA‚Äč is often the ‚Äúbrain‚ÄĚ of the device. Its reliability, safety, and performance are non-negotiable. An ISO13485 PCBA‚Äč manufacturer provides assurance that the assembly process is consistently controlled, documented, and improved upon with a primary focus on meeting regulatory requirements and ensuring patient safety.
Key Reasons for its Critical Nature:
- Regulatory Gateway:‚Äč It is a fundamental requirement for CE Marking (under EU MDR/IVDR) and many other global regulatory submissions. Auditors review your supplier‚Äôs QMS.
- Risk Mitigation:‚Äč It enforces a proactive approach to identifying and controlling risks in design, manufacturing, and supply chain.
- Enhanced Traceability:‚Äč It mandates full traceability of components and processes, which is essential for recalls or field corrections.
- Supply Chain Confidence:‚Äč It ensures that the supplier manages its own supply chain to consistent quality standards.
In short, PCBA ISO13485‚Äč is the essential framework that transforms a generic electronic assembly into a reliable, medical-grade component.
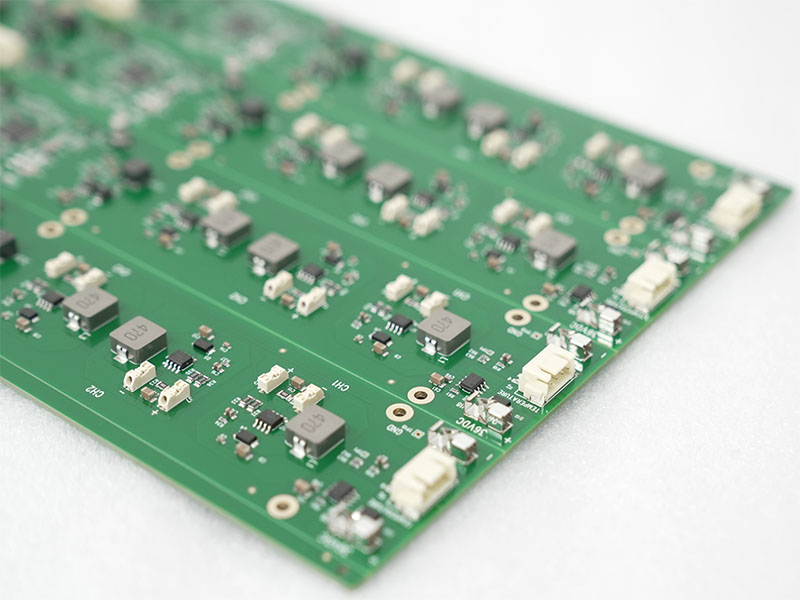
What Is the Purpose of ISO 13485 in Medical PCBA Manufacturing?
The core purpose of ISO 13485 within medical PCBA manufacturing‚Äč is to provide a harmonized model for a Quality Management System (QMS) that consistently meets customer and applicable regulatory requirements. Its purpose extends far beyond basic quality control.
Unlike generic quality standards, ISO 13485 is laser-focused on the medical device lifecycle. In the context of a PCBA ISO13485‚Äč process, its purposes include:
- To ensure safe and effective medical devices:‚Äč By controlling the assembly of a critical component.
- To demonstrate regulatory compliance:‚Äč Providing objective evidence to Notified Bodies and regulatory agencies (e.g., FDA).
- To facilitate global market access:‚Äč Serving as a universally recognized benchmark for medical device quality.
- To enforce comprehensive documentation:‚Äč Creating a transparent, auditable record of all processes, from design change orders to test results.
- To drive continuous improvement in a regulated environment:‚Äč Mandating corrective and preventive actions (CAPA) based on data.
For a China custom-made ISO13485 multilayer medical electronics interface PCBA‚Äč supplier, adhering to this standard means their systems are designed to support the stringent documentation, validation, and traceability that a medical device OEM requires for successful regulatory submission and market launch.
What Are the Key Elements of ISO 13485 for PCBA Suppliers?
For a PCBA supplier, ISO 13485 is not an abstract quality standard‚ÄĒit must be translated into daily manufacturing discipline within electronics assembly. The key elements below define how ISO 13485 is operationalized in medical PCBA manufacturing.
Key ISO 13485 Elements Applied In PCBA Manufacturing
| Key Element | Application In PCBA Manufacturing |
|---|---|
| Management Responsibility | Leadership ownership of QMS and regulatory focus |
| Resource Management | Qualified staff, controlled ESD environment, maintained equipment |
| Product Realization | Controlled planning, sourcing, assembly, and testing |
| Risk Management | Risk-based control of materials, processes, and reliability |
| Measurement & Improvement | Inspection, testing, CAPA, and continuous monitoring |
How These Elements Work In Practice For Medical PCBA
- Management Responsibility ensures ISO 13485 is enforced at the system level, not delegated only to quality staff.
- Resource Management guarantees personnel competency, stable equipment performance, and controlled manufacturing conditions.
- Product Realization governs how medical PCBA moves from prototype to production under controlled, documented processes.
- Risk Management embeds preventive thinking across sourcing, assembly, and long-term reliability.
- Measurement, Analysis, and Improvement provides objective evidence through inspection data, customer feedback, and CAPA closure.
The consistent execution of these elements is what separates a general electronics PCBA supplier from a dedicated ISO 13485 medical PCBA manufacturer capable of supporting regulated medical device programs.
What Documentation Is Required for ISO13485 PCBA Medical Projects?
Documentation is the backbone of an ISO 13485 QMS. For a medical PCBA‚Äč project, the required documentation provides a verifiable audit trail. Key documents include:
- Quality Manual & Procedures:‚Äč The top-level documents describing the supplier’s QMS.
- Device Master Record (DMR) Equivalent:‚Äč For the PCBA, this includes all specifications: Gerber files, BOM, approved vendor list (AVL), assembly drawings, and test specifications.
- Device History Record (DHR) Equivalent:‚Äč The batch-specific record proving the PCBA‚Äč was built to DMR. It includes:
- Traceability Records:‚Äč Lot codes for all components (ICs, resistors, connectors).
- Process Records:‚Äč Reflow oven profiles, conformal coating logs, programmer logs.
- Inspection & Test Results:‚Äč AOI reports, ICT results, functional test data.
- Labeling & Serialization:‚Äč Unique identifier for the assembly batch.
- Validation & Qualification Reports:‚Äč Reports for solder process validation, test fixture qualifications, and software validations.
- Supplier Management Records:‚Äč Certificates of Conformity (CoC), material declarations, and audits of key component suppliers.
- CAPA Records:‚Äč Documentation of any non-conformities and the corrective actions taken.
A competent supply ISO13485 medical PCba purchasing‚Äč partner will provide this documentation pack as a standard deliverable, essential for your own technical file.
How Is Traceability Implemented in ISO13485 PCBA Manufacturing?
Traceability in ISO13485 PCBA manufacturing‚Äč is implemented as a systematic chain of custody, from component to finished assembly. Its goal is to enable the tracking of all materials, processes, and inspection results related to a specific batch of PCBAs.
Implementation Steps:
- Component Level:‚Äč Every critical component on the BOM is purchased with and tracked by its unique manufacturer lot/date code. This is recorded in the AVL and DHR.
- Material Handling:‚Äč Warehousing systems (often barcode-driven) ensure FIFO (First-In, First-Out) and prevent the mixing of component lots.
- Process Binding:‚Äč During assembly, the unique PCBA‚Äč batch/serial number is logically linked to the specific:
- Solder paste lot used.
- Stencil and fixture IDs.
- Reflow oven profile run.
- Conformal coating batch.
- Data Collection:‚Äč At each test stage (AOI, ICT, FCT), results are automatically or manually logged against the PCBA‘s unique identifier.
- Output Record:‚Äč The final DHR‚Äč compiles all this linked data, creating a complete lineage. In the event of a field issue, this allows for precise identification of affected batches, dramatically limiting recall scope.
For a wholesale ISO13485 medical PCBA company, robust traceability is not optional; it is a fundamental requirement of the standard and a critical service to their medical device clients.
What Is the Difference Between ISO 13485 and EN ISO 13485 in PCBA?
The difference between ISO 13485 and EN ISO 13485 is primarily one of regional adoption and legal standing, not technical content.
- ISO 13485:‚Äč This is the international standard published by the International Organization for Standardization. It is the global benchmark.
- EN ISO 13485:‚Äč This is the European Norm (EN)‚Äč version of the standard. It is identical‚Äč to the ISO standard in its technical requirements but has been formally adopted by the European Committee for Standardization (CEN). This adoption gives it a special status in the European Union.
Key Implication for PCBA:
For a PCBA manufacturer‚Äč serving the European market, having a certification that explicitly states “EN ISO 13485:2016″‚Äč is crucial. It is the version referenced in the European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) and In Vitro Diagnostic Regulation (IVDR). A Notified Body auditing a device manufacturer will look for evidence that critical suppliers like PCBA‚Äč providers operate under a system compliant with EN ISO 13485. While an ISO 13485‚Äč certificate is excellent, the EN‚Äč prefix provides the clearest and most direct evidence of compliance with EU regulatory expectations.
How Does ISO13485 PCBA Control Risk in Medical Device Manufacturing?
ISO13485 PCBA‚Äč controls risk by mandating a culture of proactive risk-based thinking integrated into every stage of the manufacturing process. It applies the principles of ISO 14971 (Risk Management for Medical Devices) to the assembly operation.
Risk Control Mechanisms:
- Design & Development Controls:‚Äč For a custom ISO13485 medical PCBA, risk analysis during DfM reviews identifies potential assembly, test, or reliability issues early.
- Supplier Control:‚Äč Mitigates the risk of counterfeit, non-conforming, or unreliable components through stringent purchasing processes and supplier audits.
- Process Validation:‚Äč High-risk processes (e.g., soldering, cleaning) are validated to prove they consistently produce results meeting pre-determined specifications, controlling process variation risk.
- Inspection & Test:‚Äč Defined checkpoints (like AOI, ICT) are designed to detect failures that pose the highest risk to device function.
- Traceability:‚Äč Limits the impact of a discovered failure by enabling precise, bounded field actions, controlling financial and reputational risk.
- CAPA System:‚Äč Requires systematic investigation of non-conformities to address root cause, preventing recurrence and controlling systemic risk.
This embedded risk management is why partnering with an ISO 13485 PCB manufacturer‚Äč is a primary risk mitigation strategy for the device OEM itself.
How Does Prototype PCBA ISO13485 Support Early Medical Device Development?
Leveraging a prototype PCBA ISO13485‚Äč service from the outset provides strategic advantages that go beyond mere compliance, actively supporting and de-risking early development.
- Builds a Compliant Foundation:‚Äč Design choices made during prototyping (component selection, layout, test points) are made with production compliance in mind, avoiding costly redesigns later.
- Generates Regulatory-Grade Data:‚Äč Even early builds come with traceability and test data, which can be included in verification/validation reports for regulatory submissions.
- Facilitates a Seamless Design Transfer:‚Äč The processes, documentation, and even personnel involved in the prototype phase are the same as for production, making scale-up predictable and smooth.
- Enables Realistic Testing:‚Äč Prototypes are built using near-production-grade materials and processes, providing more reliable performance data for clinical trials or bench testing.
- De-risks the Supply Chain:‚Äč The supplier validates and qualifies components and sub-assemblies early, identifying sourcing or quality issues long before production ramp.
For startups and established companies alike, using a fast track PCBA ISO13485‚Äč service for prototypes turns the compliance requirement into a competitive accelerator.
How Can You Verify ISO13485 PCBA Compliance Before Supplier Selection?
Verifying a potential supplier’s ISO13485 PCBA‚Äč compliance requires due diligence beyond checking for a certificate. Here is a practical checklist:
- Request the Certificate:‚Äč Ensure it is valid, lists the correct company name/location, and explicitly includes “PCBA”‚Äč or electronic assembly in its scope. Look for EN ISO 13485‚Äč if targeting the EU.
- Audit Report (Optional but Powerful):‚Äč Ask for a summary or certificate from their latest notified body or certification body audit, noting any major non-conformities.
- Review QMS Documentation:‚Äč Ask for their quality manual outline or specific procedures related to design control, purchasing, and traceability.
- Request a Sample DHR:‚Äč Ask to see a redacted sample Device History Record packet for a previous medical project. This reveals their practical documentation and traceability depth.
- Conduct an On-site or Virtual Audit:‚Äč Focus on areas like incoming inspection, ESD controls, traceability systems on the production floor, and the calibration status of test equipment.
- Interview Technical Staff:‚Äč Discuss their experience with medical equipment‚Äč projects, risk management practices, and their CAPA process. Gauge their understanding of the regulatory landscape.
Choosing a China electronics PCBA supplier for medical equipment with ISO13485‚Äč requires this level of verification to ensure they are a true partner in quality, not just a vendor with a certificate.

To conclude, PCBA ISO13485‚Äč is the indispensable framework that ensures the electronic heart of a medical device is manufactured with the consistency, traceability, and quality rigor demanded by global regulators and, ultimately, patient safety. This guide has detailed how it applies from the first prototype through to volume production.
When seeking a partner for your medical PCBA customized‚Äč needs, from fast track‚Äč prototypes to full-scale wholesale supply, choosing one with deep expertise in the standard is critical. EBest Circuit (Best Technology)‚Äč operates as a dedicated ISO 13485 PCB manufacturer‚Äč for the medical sector. We provide the engineering support, custom-made‚Äč solutions, and audit-ready documentation to seamlessly advance your medical device from concept to compliant reality. Pls feel free to contact us anytime to discuss your project requirements at sales@bestpcbs.com.
FAQs
What Is the Difference Between ISO PCB and ANSI PCB?
This terminology is often confused. ISO‚Äč here refers to a Quality Management System standard (ISO 13485) for the manufacturing processof the PCB/PCBA. ANSI‚Äč (American National Standards Institute) often refers to the design file formatstandards (like Gerber RS-274X) or layer naming conventions for the PCB design itself. One governs how you build, the other governs how you design.
Is ISO 13485 Certification Required for a PCBA Manufacturer or Only for Medical Device OEMs?
It is not legally required for the PCBA manufacturer‚Äč in the same way it is for the final device OEM who places the device on the market. However, it is a practical necessity. Most medical device OEMs are required by regulation (FDA QSR, EU MDR) to only use suppliers whose QMS ensures product quality. An ISO 13485 certificate is the most efficient and universally accepted way for a PCBA supplier‚Äč to demonstrate this. Therefore, while not mandated directly on them, it is de facto required to serve the medical industry.
Can You Use a Non-ISO13485 PCBA Supplier for Early Medical Prototypes?
Technically, yes, for very early proof-of-concept work. However, it carries significant risk. Any data generated may not be usable for regulatory submissions, and the transition to a compliant supplier will likely require a complete redesign and re-validation to meet traceability and process control standards, ultimately costing more time and money. Starting with an ISO13485‚Äč partner for prototypes‚Äč is the prudent strategy.
Does ISO13485 PCBA Manufacturing Significantly Increase Cost and Lead Time?
For the initial project setup, yes, there is an incremental cost and time investment related to enhanced documentation, validation activities, and controlled component sourcing. However, for production and overall project lifecycle, it reduces‚Äč total cost and risk. It prevents costly rework, failed audits, delayed submissions, and field failures. The lead time for a quick turn PCBA prototype ISO13485‚Äč service from an experienced supplier is often competitive, as their processes are streamlined for regulated agility.


