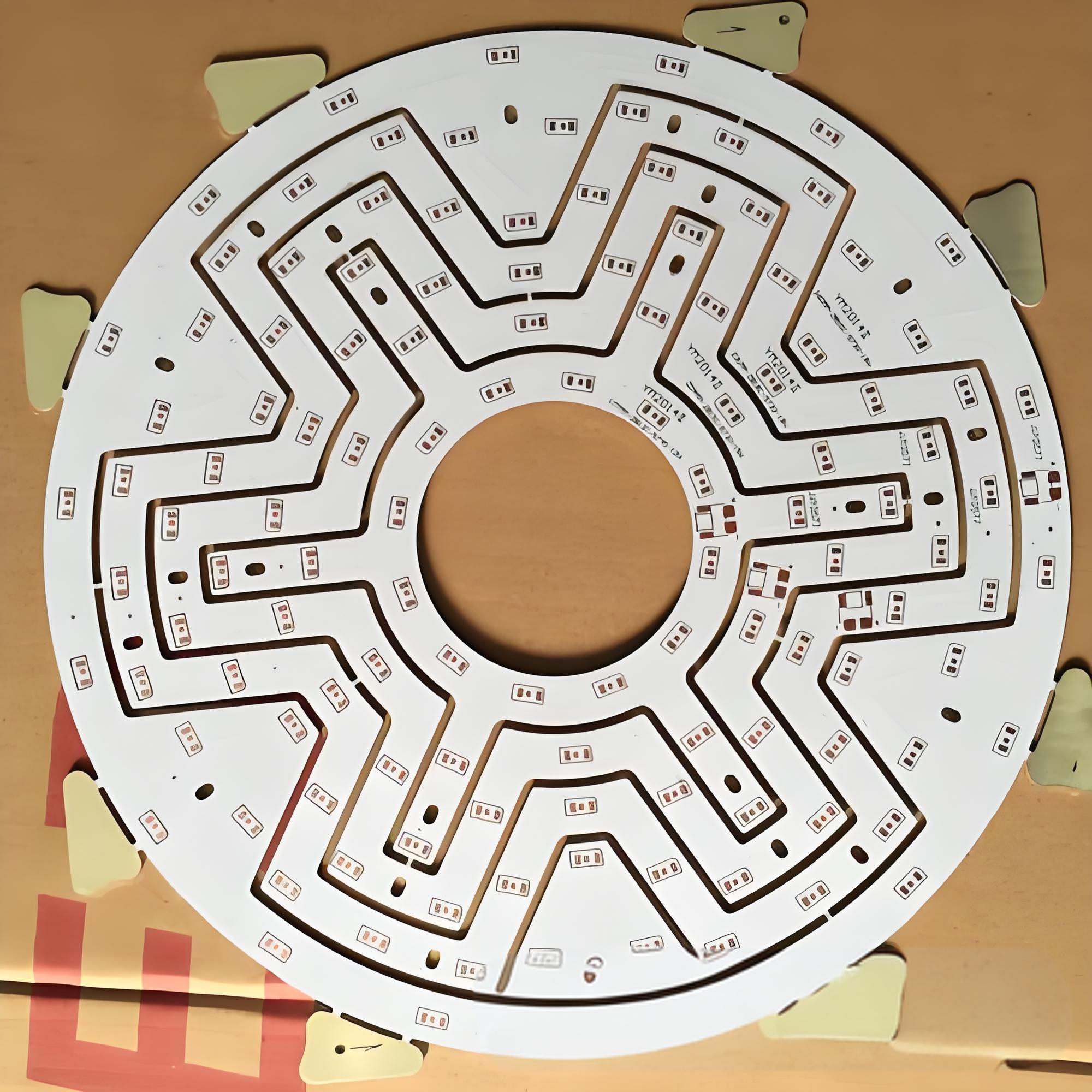
IMS PCB structure plays a vital role in modern LED applications, especially where thermal management is critical. LEDs generate heat during operation, and poor heat dissipation can shorten their lifespan. Thatâs where IMS PCBs come inâthey manage heat effectively while maintaining electrical performance. Letâs explore their structure, benefits, and how to choose the right solution for your needs.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) specializes in IMS PCB prototype, fabrication, assembly, and box build service. Our factory is equipped with automatic production lines, and the common lead time is shortened by 5 days. And we support 48 hours of prototyping. Moreover, we provide the ideal solutions from the DFM analysis to fabrication. Any doubts about the IMS PCB structure, just feel free to let us know at sales@bestpcbs.com.
What is the IMS PCB Structure?
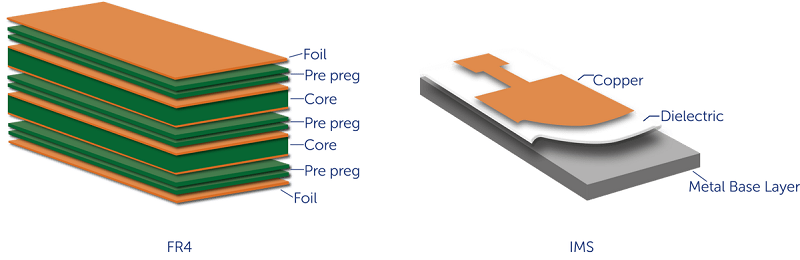
IMS stands for Insulated Metal Substrate, and its structure is designed to combine electrical performance with efficient heat dissipation. The IMS PCB structure is built from three key layers:
- Copper Foil Layer â This top layer forms the conductive circuit and carries electrical signals with high reliability.
- Dielectric Layer â Positioned between the copper and the metal base, this layer serves two vital roles: it provides electrical insulation and delivers high thermal conductivity, typically ranging from 1.5 to 8.0 W/m·K. This allows heat to pass quickly from the copper traces down to the metal base, protecting temperature-sensitive components like LEDs.
- Metal Base Layer â Usually made of aluminum or copper, this bottom layer acts as a solid foundation and an effective heat sink, spreading and releasing heat away from the board.
Together, these layers create a structure that conducts electricity efficiently while also managing heat effectively, which is especially critical in LED lighting and power electronics. Unlike FR4 boards, IMS PCBs are purpose-built for applications where thermal control is crucial to performance and reliability.
What is the Difference Between IMS Circuit Board Structure and FR4 PCB?
Letâs compare IMS circuit boards and FR4 PCBs in terms of material and performance. FR4 PCBs use fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin as the base, while IMS boards use a metal base. The insulation in IMS is thermally conductive but electrically resistant. Hereâs a comparison table for better clarity:
| Feature | IMS Circuit Board | FR4 PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Base Material | Aluminum or Copper | Fiberglass (FR4) |
| Thermal Conductivity | High | Low |
| Durability | Stronger for harsh use | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher initial, lower long-term | Lower initial |
Clearly, IMS PCB structure offers better thermal performance, which is key for LEDs that must run cool and stable.
How Durable Is IMS Circuit Board in Harsh Environments Compared to FR4 PCB?
Durability is a major concern for LED applications in outdoor or industrial settings. IMS PCBs handle extreme temperatures, moisture, and mechanical stress better than FR4 boards. The metal base provides strength and stability, while the insulation resists breakdown. As a result, IMS circuit boards last longer and require fewer replacements, reducing maintenance costs. Many customers have faced early LED failures due to poor PCB durabilityâIMS technology solves this problem efficiently.
How to Select the Right Insulated Metal Substrate for Your IMS PCB Structure?
Choosing the right metal substrate depends on your specific needs. For standard LEDs, aluminum is common. For higher thermal demands, copper might be better. Also, consider the thickness of the metal base and dielectric layer. Thicker metal can handle more heat but adds weight and cost. Here’s a quick guide:
- Aluminum:Â Affordable, good for most LED uses.
- Copper:Â Higher thermal performance, higher cost.
- Dielectric Layer:Â Choose based on thermal resistance (lower is better).
Working with an experienced IMS PCB manufacturer can help you make the right choice without wasting time or money.
What is the Manufacturing Process of IMS Board PCB?
Producing an IMS board PCB involves several precise steps to ensure thermal and electrical performance. Hereâs how the process typically works:
- Material Selection
The process begins by choosing the right metal baseâusually aluminum or copperâbased on thermal and mechanical needs. - Metal Base Preparation
The metal base is cleaned thoroughly to remove any contaminants. This ensures strong adhesion and consistent quality in the next layers. - Dielectric Layer Application
A high thermal conductivity dielectric layer is laminated onto the metal base. This layer provides insulation and helps transfer heat efficiently. - Copper Foil Lamination
Copper foil is then bonded to the top of the dielectric layer. This copper layer will form the conductive circuit paths. - Circuit Patterning
Using photoresist and chemical etching, the desired circuit design is created on the copper surface. This step must be precise to avoid defects. - Drilling
Holes for component placement or vias are drilled using automated equipment for accuracy and consistency. - Surface Finishing
A surface finish such as ENIG, OSP, or HASL is applied to protect the copper and improve solderability. - Testing and Quality Control
Each board undergoes electrical testing and thermal performance checks. Any defective board is removed to maintain high standards.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) controls every stage with care. As a professional IMS PCB manufacturer, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) gains specialized knowledge in the MCPCB industry, and we have a stable, cutting-edge manufacturing process and strict quality control. Any inquiry about the material selection, IMS PCB structure, or any help with the IMS PCB project, pls let us know at sales@bestpcbs.com.
What is the Value of the IMS PCB Structure for LED?
The IMS PCB structure provides significant value in LED applications, especially where heat dissipation and reliability are critical. Many customers experience LED failure due to poor thermal design, leading to reduced brightness, shorter product life, and costly replacements. IMS PCBs address these issues effectively. Hereâs how:
- Superior Heat Dissipation
The most important value of IMS PCB structure is its ability to conduct heat away from the LED junction efficiently. The metal base combined with a high thermal conductivity dielectric (1.5â8.0 W/m·K) ensures heat is spread and released quickly. This prevents thermal buildup and keeps LEDs operating within safe temperatures. - Longer LED Lifespan
Overheating is a major cause of LED failure. By keeping temperatures low, IMS boards help extend the operating life of LEDs. This reduces maintenance needs and replacement frequency, especially in outdoor or industrial environments. - Stable Light Output
Temperature affects LED brightness and color stability. IMS PCB structure helps maintain consistent light output over time, which is essential for lighting applications in retail, automotive, or architectural sectors. - Compact and Lightweight Design
Because IMS boards handle heat so well, designers can reduce the size of heat sinks or eliminate them entirely. This allows for slimmer, lighter LED products without compromising performance. - Cost Efficiency Over Time
While IMS PCBs may have a higher initial cost than FR4, they offer long-term savings by reducing failure rates and minimizing heat-related damage. For high-power LED systems, IMS is a cost-effective solution. - Greater Reliability in Harsh Conditions
LEDs used in outdoor lighting, automotive, or factory settings must withstand vibration, moisture, and temperature changes. IMS PCBs provide mechanical strength and thermal stability, making them highly reliable in tough environments. - Fewer Failures, Higher Customer Satisfaction
Poor thermal design often leads to customer complaints and product returns. IMS technology helps companies deliver durable, high-performance LED products, increasing customer trust and reducing warranty claims.
In short, IMS PCB structure adds value by improving heat control, product durability, and design flexibility. For any LED application where efficiency and reliability matter, IMS is a smart and future-ready choice.

Why Choose EBest Circuit (Best Technology) as Your Chinese IMS PCB Manufacturer?
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) understands your concernsâslow delivery, poor quality, and unclear communication. We solve these headaches through the following strengths:
| Customer Pain Point | EBest Circuit (Best Technology) Solution |
|---|---|
| Delayed Delivery | Fast prototyping and strict lead-time management |
| Low Quality | Certified by ISO 9001, ISO 13485, IATF 16949, AS9100D, UL, RoHS; full quality checks |
| Unstable Supply Chain | Traceability with MES system and reliable sourcing |
| Technical Support Gaps | Professional engineers ready for design advice |
With 19 years of experience, rigorous quality control, and responsive service, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is the right partner for your IMS PCB needs. From LED lighting to industrial controls, we deliver quality you can count on. For IMS PCB inquiry from prototype to assembly, pls let us know at sales@bestpcbs.com.