Are you worried about these issues?
- Is copper busbar overheating in high-current applications, causing efficiency drops or even system shutdowns?
- Is corrosion or oxidation in humid or harsh environments leading to frequent maintenance?
- Do you need flexible copper busbar customization to fit different battery modules or inverter layouts?
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) provides tailored copper busbar solutions that balance cost, performance, and flexibility. We offer:
- Competitive pricing directly from manufacturer
- Customized sizes, coatings, and shapes
- High durability = long-term cost savings
- No minimum order quantity requirements, I pcs prototype order is available
If you are comparing copper busbar manufacturers or exploring advanced copper busbar PCB designs, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) can help. With certifications including ISO9001, ISO13485, IATF16949, and AS9100D, we maintain strict quality control from raw material to finished product. Our MES system keeps every component traceable, while competitive copper busbar price and flexible engineering support bring added value.
Whether you need standard copper busbar, custom busbar copper shapes, or integrated PCB busbar solutions, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) offers expertise and reliability in every project. If you are interested in copper busbar or copper busbar pcb, welcome to contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com.
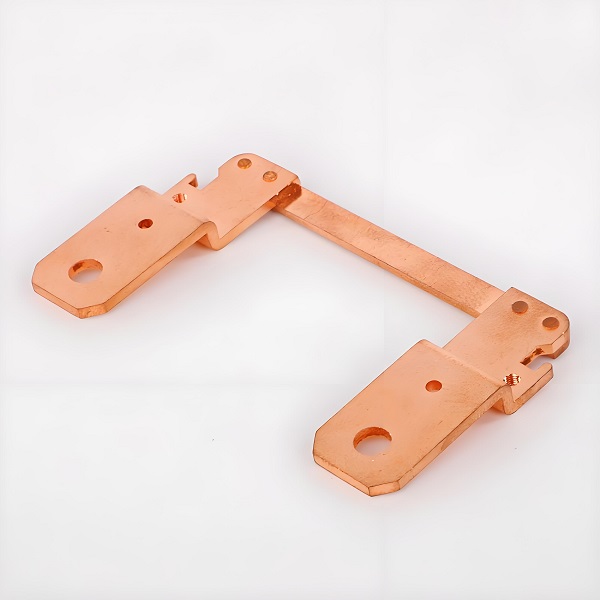
What is Copper Busbar?
A copper busbar is a flat strip, rod, or bar of copper designed to conduct electricity. Unlike flexible wires, itâs rigid, strong, and tailored to carry heavy current loads. Youâll often find it inside switchgear cabinets, power distribution panels, and large battery packs.
Why copper? Because copper has excellent conductivity and thermal performance. It carries more current per square millimeter than most other metals while staying stable over long service periods. For engineers, this means reduced energy losses and fewer overheating issues.
In short, copper busbar is the highway for electricity inside modern systems.

What is Copper Busbar?
Why is it Called a Busbar?
The word âbusâ in electrical engineering describes something that collects and distributes. Just as a city bus gathers passengers and delivers them to different stops, a busbar gathers current from various circuits and spreads it across the system.
The âbarâ part is literalâitâs a bar of conductive material. Together, the term âbusbarâ reflects its function and shape. Over decades, this word became standard, and now itâs used across industries worldwide.
How to Make a Copper Busbar?
The process of making busbar copper combines precision with material science. Hereâs how manufacturers typically approach it:
1. Copper Selection â Most copper busbar manufacturers choose high-conductivity grades such as ETP (Electrolytic Tough Pitch) or OFHC (Oxygen-Free High Conductivity). These ensure stable performance.
2. Cutting and Shaping â Large copper sheets are cut into required sizes. CNC punches and hydraulic presses shape the bar with consistent accuracy.
3. Drilling and Punching â Holes and slots are added for bolted connections. This step requires exact tolerances so that joints stay secure.
4. Bending â Depending on installation needs, busbars are bent into L, U, or Z shapes without compromising mechanical strength.
5. Surface Finishing â To prevent oxidation, surfaces may be tin-plated, silver-plated, or coated with nickel. This not only protects but also improves contact reliability.
6. Insulation (Optional) â In compact systems, epoxy coatings or heat-shrink sleeves are added to prevent accidental shorts.
Every step is controlled to deliver high current capacity while keeping mechanical stability intact.
How to Clean Copper Busbar?
Over time, copper busbar surfaces can tarnish. A thin oxide layer forms, which slightly increases resistance. Cleaning restores performance. Here are some practical methods:
- Mechanical cleaning â Sandpaper, wire brushes, or abrasive pads can remove the oxidation layer.
- Chemical cleaning â Mild acidic solutions like vinegar mixed with salt, or commercial copper cleaners, dissolve corrosion without damaging the base metal.
- Protective treatment â After cleaning, applying a thin coat of petroleum jelly or anti-oxidation grease helps slow down further tarnish.
Routine cleaning is important in high-current systems, as even small resistance increases can generate heat under load.
How to Calculate Copper Busbar Size?
Choosing the right copper busbar size means balancing current capacity with safety. Engineers often use a current density rule to determine cross-sectional area.
The common design range is 1.2 to 1.6 A per square millimeter of copper in open air.
Formula:
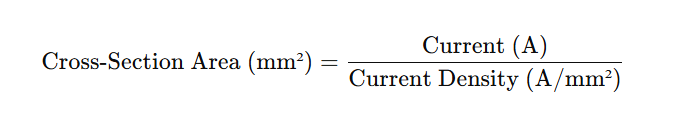
For example, a busbar that needs to carry 800A at 1.5 A/mmÂČ should have at least:
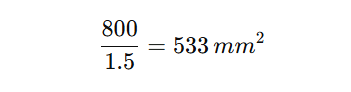
If designed as 40 mm wide and 14 mm thick, this cross-section provides adequate capacity. Designers then check thermal rise and cooling conditions to finalize the dimension.
Copper Busbar vs Copper Busbar PCB
Although both serve as conductors, there are differences between traditional copper busbar and copper busbar PCB:
- Copper Busbar â A standalone strip or bar. Common in switchgear, transformers, and large distribution panels.
- Copper Busbar PCB â A printed circuit board reinforced with very thick copper layers or embedded copper strips. Used in compact high-power electronics such as EV inverters.
The advantage of copper busbar PCB is space efficiency. Instead of bulky bars and cables, the PCB integrates power and signal layers together, simplifying assembly.
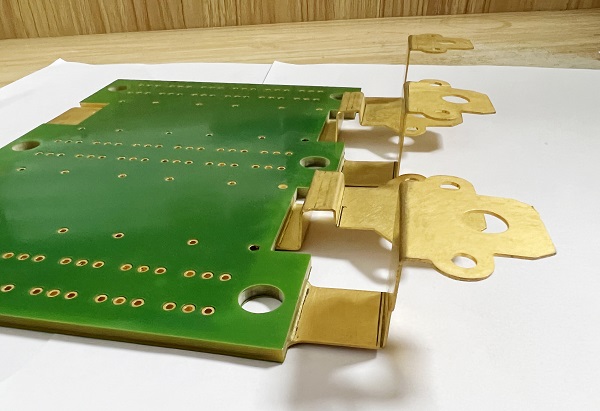
Busbar Copper PCB
Why Choose Copper Busbar PCB?
Copper busbar PCB, sometimes called embedded busbar PCB or busbar-integrated PCB, is a smart evolution of traditional busbars. In some industries, it is also referred to as reinforced thick copper PCB, since the board integrates additional copper bars or strips inside or on the surface to handle heavy current.
The reason many designers choose copper busbar PCB over standalone busbars lies in its unique advantages:
- Compact design â Instead of bulky copper bars and multiple cables, busbar copper is embedded in the PCB, reducing space requirements.
- Improved thermal balance â Heat spreads evenly across the board, preventing local hotspots in high-power circuits.
- Simplified assembly â Fewer mechanical joints mean lower installation time and reduced risk of loose connections.
- Cost efficiency â By combining signal and power layers in one PCB, manufacturers save both material and labor cost.
- Reliability â With laminated structure and less mechanical stress, copper busbar PCB performs well even in vibration-heavy environments such as automotive or industrial drives.
Copper Busbar Size and Current Rating Table
Hereâs a general table showing copper busbar size with approximate current ratings (open air, 35°C rise). Values vary depending on installation and cooling.
| Thickness (mm) | Width (mm) | Max Current (A) | Typical Applications |
| 1 | 10 | 50 | Small electronics |
| 2 | 20 | 150 | Industrial control |
| 3 | 25 | 250 | Switchboards |
| 5 | 50 | 500 | EV battery modules |
| 10 | 100 | 1200 | Power distribution systems |
These values are approximate. Always confirm with copper busbar manufacturers for precise specifications based on your operating environment.
How Much Does a Copper Busbar of Length 40 cm Carry?
The capacity depends mainly on cross-section, not just length.
- A 20 Ă 5 mm busbar of 40 cm can carry about 160â200A.
- A 40 Ă 10 mm busbar of the same length can handle up to 700A.
Length matters for voltage drop, but current capacity is almost entirely governed by cross-section and cooling.
Why Copper Busbar is Suitable for Electric Vehicles?
Electric vehicles place extreme demands on conductors. High current during acceleration, fast charging, and compact layouts require components that can cope with stress. Copper busbar delivers in several ways:
- Efficient conduction â Copper reduces resistive loss, extending driving range.
- Thermal control â With high conductivity, copper disperses heat effectively during charging cycles.
- Space saving â Laminated copper busbars replace bundles of cables, reducing weight and assembly time.
- Durability â Resistant to vibration and mechanical wear, critical for vehicles exposed to constant motion.
Thatâs why most EV battery packs and controllers today rely heavily on laminated busbar copper.
What is a Copper Busbar PCB Used For?
- Power electronics â Converters, inverters, and rectifiers.
- Automotive â EV drive systems, on-board chargers, and battery management units.
- Renewable energy â Solar string inverters and wind turbine controllers.
- Industrial systems â Robotics, automation drives, and motor controllers.
FAQs
Q1: What makes copper busbar better than aluminum busbar?
Copper has higher conductivity and better mechanical durability, leading to improved performance and longer service life.
Q2: Can copper busbar be customized?
Yes. Width, thickness, plating, and hole punching can all be tailored to specific installations.
Q3: What is the Copper Busbar HS Code?
Most copper busbars fall under HS Code 7407, covering copper bars and profiles.
Q4: What drives copper busbar price?
Mainly copper market fluctuations, plus cost of processing and plating.
Q5: Is copper busbar PCB the same as heavy copper PCB?
It is a type of heavy copper PCB, but they have several differences. Heavy copper PCB only increases copper layer thickness, while copper busbar PCB embeds solid busbars for even higher current handling.
This is the end of this blog, if you have any other questions about copper busbar pcb, you are welcome to contact our team, our sales are always online!


