As a professional aluminum PCB manufacturer, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) delivers reliable, cost-effective solutions with a complete in-house aluminium PCB manufacturing processâfrom raw material sourcing to final assembly.
How is aluminium PCB made?
Unlike standard FR4 boards, aluminium boards require special materials, customized layering, and high-precision etching to perform reliably under high temperatures.
It begins with a base of aluminium, selected for its thermal conductivity and strength. This base acts as the backbone of the entire structure. Over this, a dielectric layer is addedâa thermally conductive yet electrically insulating material. This layer allows heat to pass through to the metal core without shorting the circuit.
Next comes the copper foil. This conductive layer is laminated onto the dielectric using heat and pressure. Once bonded, the copper is patterned using photolithography. Then, etching forms the conductive tracks that carry current across the board.
Finally, the surface is coated with a protective solder mask. The board is drilled, tested, and cut into its final shape, ready for assembly. Every step is controlled to ensure high precision and reliability.
What are the raw materials for aluminum manufacturing?
For aluminium PCBs. The base material is an aluminium alloy, often 5052 or 6061, known for corrosion resistance and good mechanical performance. These alloys are lightweight yet robust, ideal for handling mechanical stress and thermal loads.
Next is the dielectric layer. Typically made of epoxy resin or a ceramic-filled polymer, this layer must be thermally efficient. The goal is to transfer heat quickly without compromising electrical insulation.
The conductive layer is pure copper, usually between 1oz and 3oz thick. This copper sheet is what gets etched to form the traces. To finish, a solder mask is applied to protect the copper and prevent short circuits.
Each material plays a crucial role. Choosing the right combination impacts performance, durability, and cost. Thatâs why experienced manufacturers like EBest Circuit (Best Technology) take material quality and testing very seriously.
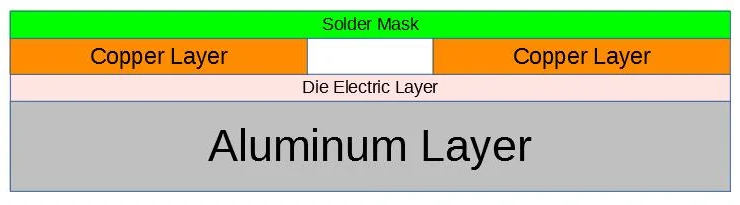
What are the layers of aluminum PCB?
Unlike traditional PCBs, these boards typically have three core layers:
- Copper Layer: Itâs where all the routing happens. The thickness varies based on current load, usually between 35μm and 105μm.
- Dielectric Layer: It insulates the circuit while transferring heat to the metal base. Its thickness affects thermal resistance.
- Aluminium Base Layer: This bottom layer supports the entire board. It also acts as a heat sink, dissipating excess energy and maintaining stable temperatures.
What are the manufacturing processes for Aluminium?
The aluminium PCB manufacturing process differs slightly from FR4, due to the metal base and heat-sensitive applications.
- Material Preparation: Aluminium base sheets are cleaned and coated with the dielectric layer.
- Copper Lamination: A copper foil is bonded using thermal pressure.
- Image Transfer: Photolithographic techniques are used to apply the circuit pattern.
- Etching: Unwanted copper is removed, leaving the circuit traces.
- Drilling: Holes are drilled for vias and mounting points.
- Plating: If needed, through-holes are plated for multi-layer connectivity.
- Solder Mask Application: A protective coating is applied to prevent oxidation.
- Silkscreen Printing: Labels, logos, and identifiers are printed.
- Surface Finish: ENIG, HASL, or OSP finishes are applied based on customer needs.
- Final Testing: Each board is electrically tested for continuity and shorts.
- Routing and Packaging: Boards are cut, inspected, and packed for delivery.
Every step must meet tight tolerances. Even minor defects can affect performance, especially in LED, automotive, and power systems.
What are the pros and cons of aluminum PCB?
Aluminium PCBs have their strengthsâand a few limitations.
Pros:
- Superior Heat Dissipation: Aluminium spreads heat fast. This reduces hotspots and extends component life.
- High Mechanical Strength: These boards are robust, reducing the risk of cracks and warping.
- Lightweight Yet Durable: Aluminium provides rigidity without the weight of steel or ceramic.
- Cost-Effective: Compared to ceramic substrates, aluminium PCBs are more affordable for high-performance needs.
- Eco-Friendly: Aluminium is recyclable, making it a greener choice.
Cons:
- Limited Flexibility: Aluminium is rigid. It’s not suitable for flexible PCB applications.
- Single-Sided Complexity: Most aluminium PCBs are single-layered. Multi-layer designs are possible but more complex and costly.
- Processing Requirements: Special tools are needed for drilling and etching, raising initial setup costs.
Still, the benefits far outweigh the downsides in most high-power applications. Thatâs why aluminium boards dominate industries like LED, power electronics, and automotive lighting.
How thick is aluminum PCB?
Thickness matters. It affects strength, heat transfer, and overall reliability.
For aluminium PCBs, the metal base typically ranges from 0.8mm to 3.2mm. The most common thickness is 1.6mm, offering a good balance between strength and heat dissipation. Some high-power applications may use up to 5mm for extra thermal control.
Thickness also depends on the productâs end use. For compact devices like LED bulbs, thinner substrates are preferred. For industrial use, thicker bases ensure long-term performance under heavy loads.
What is the thermal resistance of aluminum PCB?
Thermal resistance is crucial. It determines the heat dissipation performance of the PCB board. The lower the thermal resistance, the better the heat transfer effect, which is one of the advantages of aluminum PCB boards.
A typical aluminium PCB has a thermal resistance between 0.3°C/W and 1.0°C/W. The exact value depends on the dielectric material and its thickness.
The dielectric is designed to transfer heat quickly from the copper layer to the metal base. This lowers component temperature, improves performance, and extends lifespan.
How thick is the dielectric layer of aluminum PCB?
The dielectric layer not only ensures the passage of heat, but also acts as an insulator. The thickness of the dielectric layer directly affects the insulation performance and thermal resistance.
Most dielectric layers are between 50μm and 150μm thick. Thinner layers offer better heat transfer but may reduce electrical insulation. Thicker layers improve isolation but limit thermal performance.
Choosing the right thickness is about balance. It depends on voltage requirements, power density, and end-use environment.
How do aluminium PCBs work?
Aluminium PCBs work by balancing three critical needs: electrical conduction, mechanical support, and heat dissipation. They combine a conductive copper layer with a heat-spreading aluminium base, connected by a special dielectric.
When current flows through the copper traces, it generates heat. The dielectric layer moves this heat down to the aluminium base, which then spreads it across the board and out to the environment. This keeps components cool, even under heavy load.
When to use aluminum PCB?
Aluminum PCBs are widely used in applications where heat is an issue. That includes:
- LED Lighting: Heat control improves brightness, lifespan, and efficiency.
- Power Supplies: High-current paths stay cool and stable.
- Automotive Electronics: High vibration resistance is perfect for engine bays and dashboards.
- Communication Equipment: Enhanced thermal management ensures signal reliability.
- Industrial Controllers: Strong mechanical support reduces failure under stress.
If your design involves high-power components or tight thermal tolerances, aluminium PCBs are the solution.
Conclusion:
Aluminum substrates have good thermal conductivity, mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness. Whether you’re building LED lights, industrial controls, or automotive systems, aluminium PCBs provide a solid foundation. Their superior heat management protects components, improves efficiency, and extends service life.
If youâre ready to upgrade your design with dependable aluminium PCBs, our experts at EBest Circuit (Best Technology) are here to help. With advanced equipment, experienced engineers, and quick turnaround, we deliver quality you can trust. Contact us now at sales@bestpcbs.com