RS485 is one of the most enduring and widely adopted communication standards in industrial electronics. Despite the rise of Ethernet, wireless communication, and Industrial IoT protocols, RS485 continues to play a critical role in factories, building automation, energy systems, and embedded control applications.
Why has RS485 stood the test of time? The answer lies in its long-distance capability, high noise immunity, multi-device support, and cost-effectiveness. For engineers, system integrators, and OEMs, RS485 remains a dependable solution when reliability matters more than raw bandwidth.
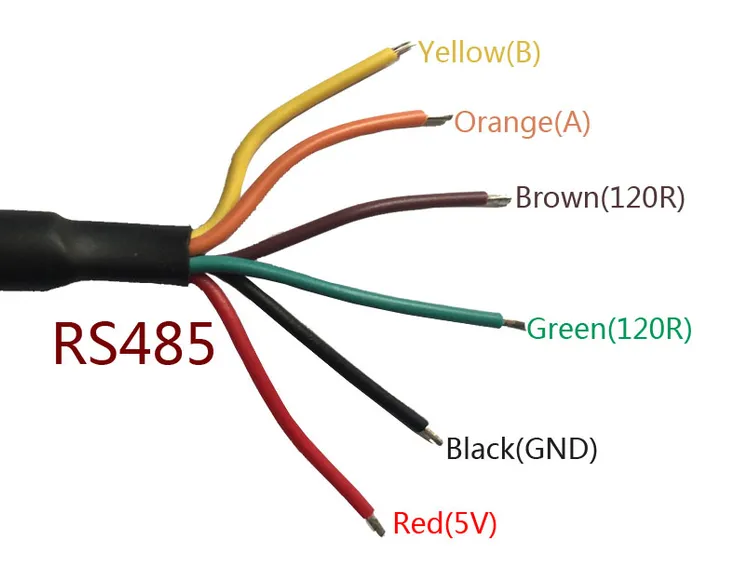
What is RS485 Cable?
An RS485 cable is a balanced, twisted-pair transmission medium that carries differential signals between devices. Instead of referencing voltage to ground, RS485 receivers interpret the voltage difference between two signal lines, which dramatically improves noise immunity.
In practical installations, RS485 cables usually consist of:
- One twisted pair for differential data (A/B or D+/Dâ)
- Optional signal ground conductor
- Optional foil or braided shield
The twisting ensures that external electromagnetic interference couples equally into both conductors, allowing the receiver to cancel common-mode noise.
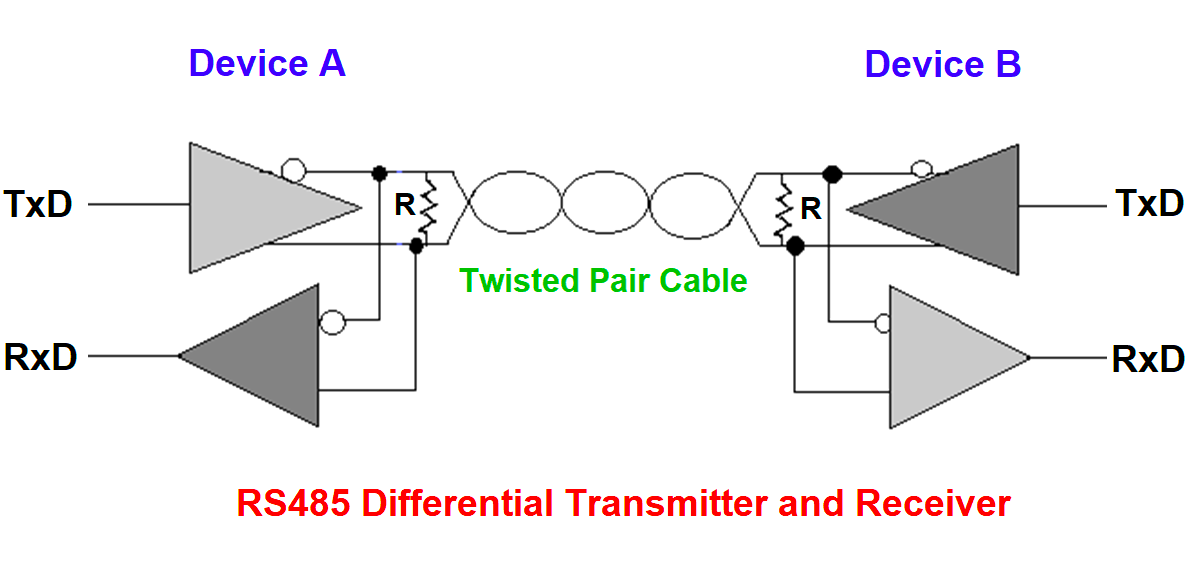
In industrial cabinets, shielded RS485 cable is preferred to suppress interference from VFDs, relays, and switching power supplies.
Is RS485 Still Used?
Yes. RS485 is still widely used, and in many industries, it is intentionally preferred.
Despite the rise of Ethernet and wireless communication, RS485 remains common because it solves problems that newer interfaces do not prioritize. These include:
- Reliable communication over hundreds or thousands of meters
- Operation in high-EMI environments
- Simple wiring without switches or hubs
- Deterministic behavior for control systems
In factories, substations, and infrastructure projects, predictability and noise tolerance matter more than raw bandwidth. RS485 continues to meet these requirements effectively.
RS485 Cable Specification
A stable RS485 network depends heavily on cable characteristics. Typical RS485 cable specifications include:
| Parameter | RS485 Specification |
| Standard | TIA-485-A (RS-485) |
| Signaling Type | Differential (Balanced) |
| Number of Wires | 2-wire (half-duplex) or 4-wire (full-duplex) |
| Conductor Type | Twisted pair |
| Characteristic Impedance | 120 Ω (typical) |
| Maximum Cable Length | 1200 m (4000 ft) |
| Maximum Data Rate | Up to 10 Mbps |
| Differential Voltage | ℠±1.5 V |
| Receiver Sensitivity | ±200 mV |
| Common-Mode Voltage Range | â7 V to +12 V |
| Maximum Nodes | 32 (standard) |
| Topology | Linear bus (daisy chain) |
| Termination Resistor | 120 Ω at both ends |
| Cable Shielding | Optional (Recommended in industrial use) |
| Ground Reference | Optional but recommended |
| Connector Types | Screw terminal, DB9, RJ45 |
| Supported Protocols | Modbus RTU, BACnet MS/TP, DMX512 |
| Noise Immunity | High |
| Typical Cable Type | STP twisted pair, Cat5/Cat6 |
Is RS485 2-wire or 4 wire?
RS485 supports both 2-wire and 4-wire configurations.
2-wire RS485 (half-duplex)
- One twisted pair for transmit and receive
- Most common in multi-drop networks
- Requires direction control
4-wire RS485 (full-duplex)
- Separate pairs for transmit and receive
- Allows simultaneous communication
- Typically used in point-to-point links
Most industrial RS485 networks use 2-wire topology due to simpler cabling and easier expansion.
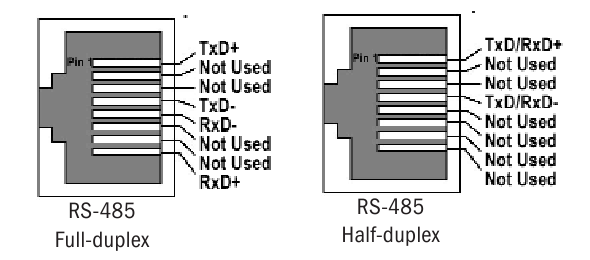
RS485 Pinout
There is no universal RS485 pinout, as RS485 defines electrical signalingânot connectors.
However, common conventions include:
| Signal | Description |
| A (D+) | Non-inverting line |
| B (D-) | Inverting line |
| GND | Signal reference (optional but recommended) |
Typical pin assignments may be found on:
- Terminal blocks
- DB9 connectors
- RJ45 connectors (vendor-specific)
A frequent source of commissioning failure is A/B polarity reversal, especially when vendors label signals inconsistently. Always verify with a scope or by swapping lines during testing.
⚠️ Important: Some manufacturers label A and B oppositely. Always verify the device datasheet before wiring.
Is RS485 the Same as Ethernet?
No. RS485 is not the same as Ethernet, although RJ45 connectors are sometimes used for RS485.
| Feature | RS485 | Ethernet |
| Communication type | Serial | Packet-based |
| Topology | Bus | Star |
| Distance | Up to 1200 m | 100 m (copper) |
| Speed | Up to 10 Mbps | 100 Mbps â 10 Gbps |
| Protocol stack | Simple | Complex (TCP/IP) |
RS485 focuses on reliability and simplicity, while Ethernet focuses on speed and networking flexibility.
What Type of Cable to Use for RS485?
Recommended RS485 cable characteristics:
- Twisted pair (mandatory)
- 120 Ω impedance
- Shielded (STP) for noisy environments
- Low capacitance for longer distances
Common choices:
- Belden 9841 / 9842
- CAT5e (short runs, low noise only)
- Industrial RS485-rated cables
What is RS485 Used For?
RS485 is commonly used in applications that require:
- Long cable runs
- Multiple devices on one bus
- Reliable communication under electrical noise
Typical use cases include:
- PLC and industrial controllers
- Modbus RTU networks
- Energy meters and power systems
- Building automation and HVAC
- Access control and alarm systems
These systems value stability and predictability over raw data speed.
How Do I Connect My RS-485 to My Computer?
Most computers do not have native RS485 ports. Common connection methods include:
- USB to RS485 converter (most popular)
- PCI/PCIe RS485 expansion card
- RS232 to RS485 converter
After connecting, configure:
- Baud rate
- Data bits
- Parity
- Stop bits
to match the RS485 device settings.
Does RS-485 Need to Be Grounded?
RS485 does not strictly require grounding, but grounding is strongly recommended for stability and protection.
Best practices:
- Connect signal ground between devices
- Use shielded cable
- Ground the shield at one end only
- Avoid ground loops
Proper grounding improves noise immunity and prevents communication errors.
How to Quickly Prove Whether RS485 is Working?
When troubleshooting RS485, follow a structured process:
- Confirm correct A/B polarity
- Check termination resistors at both ends of the bus
- Verify biasing resistors are present
- Inspect grounding and shield connections
- Reduce baud rate to increase noise margin
- Observe waveforms with an oscilloscope if available
Most RS485 issues originate at the physical layer, not the protocol level.
RS485 vs RJ45: What are Differences?
RS485 and RJ45 are frequently confused, especially in industrial projects where RS485 signals are often routed through RJ45 connectors.
However, they represent two completely different layers of a communication system, and understanding this distinction is critical to avoid wiring errors, equipment damage, or unstable communication.
1. Standard definition
RS485 is an electrical signaling standard (TIA-485). It defines:
- Differential voltage levels
- Driver and receiver characteristics
- Noise immunity behavior
- Multi-drop bus capability
RS485 says nothing about connectors, pin counts, or cable jackets.
RJ45 is a connector specification. It defines:
- 8 physical pins
- Mechanical dimensions
- Contact layout
RJ45 does not define voltage levels, signaling methods, or communication protocols.
This is the root cause of confusion: RJ45 can carry RS485, Ethernet, CAN, or proprietary signals, depending entirely on how the pins are wired.
2. Signal transmission method
This is the most important technical difference.
| Aspect | RS485 | RJ45 |
| Role | Electrical communication standard | Physical connector |
| Signal type | Differential (A/B) | None defined |
| Noise immunity | Very high | Depends on protocol |
| Defines voltage levels | Yes | No |
| Defines data format | No | No |
RS485 uses differential signaling, which allows it to tolerate high EMI, long cable runs, and ground noise. RJ45 itself provides no electrical noise protection; it simply holds contacts in place.
3. Cable usage and common misconceptions
A major source of misunderstanding is the use of Ethernet cable with RS485.
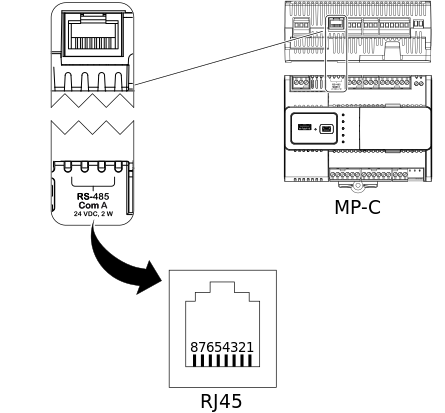
Many systems run RS485 over:
- Cat5 / Cat5e / Cat6 cable
- RJ45 connectors
This does not make the system Ethernet.
Why it works:
- Ethernet cable contains twisted pairs
- Twisted pairs suit RS485 differential signaling well
- 100 Ω Ethernet cable impedance is close to RS485âs typical 120 Ω requirement
Why problems still occur:
- Pinouts are not standardized
- Shielding and grounding may differ
- Termination and biasing are often ignored
Using an RJ45 connector does not change the fact that the system is still RS485 electrically.
4. Topology differences
RS485 topology
- Bus (daisy-chain)
- Termination at both physical ends
- Limited stub lengths
- Multi-drop without switches
RJ45-based Ethernet topology
- Star topology
- Uses switches and routers
- Each device has a dedicated link
This difference matters because star wiring works for Ethernet but often breaks RS485. Engineers accustomed to Ethernet wiring sometimes unknowingly apply the same topology to RS485, leading to reflections and unstable communication.
5. Distance and speed comparison
| Parameter | RS485 | RJ45 (Ethernet typical) |
| Typical distance | Up to ~1200 m (speed-dependent) | 100 m per segment |
| Typical speed | kbps to low Mbps | 100 Mbps â 10 Gbps |
| Noise tolerance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Infrastructure | Simple | Requires switches |
Confusing the two leads to incorrect assumptions about topology, grounding, termination, and compatibility. Once the distinction is clear, RS485 systems become far easier to design, troubleshoot, and maintain.
FAQs
1. Is RS485 the same as RS232?
No. RS485 supports longer distance, better noise immunity, and multi-drop networks, unlike RS232.
2. Can RS485 run over Ethernet cable?
Yes, twisted pairs in Ethernet cable can be used, but impedance and shielding must be considered carefully.
3. What happens if RS485 is not terminated?
Signal reflections may occur, causing data corruptionâespecially at higher speeds.
4. Is RS485 polarity important?
Yes. Reversing A and B lines typically prevents communication.
5. Can RS485 support multiple masters?
Electrically yes, but protocol design must manage bus access carefully.


