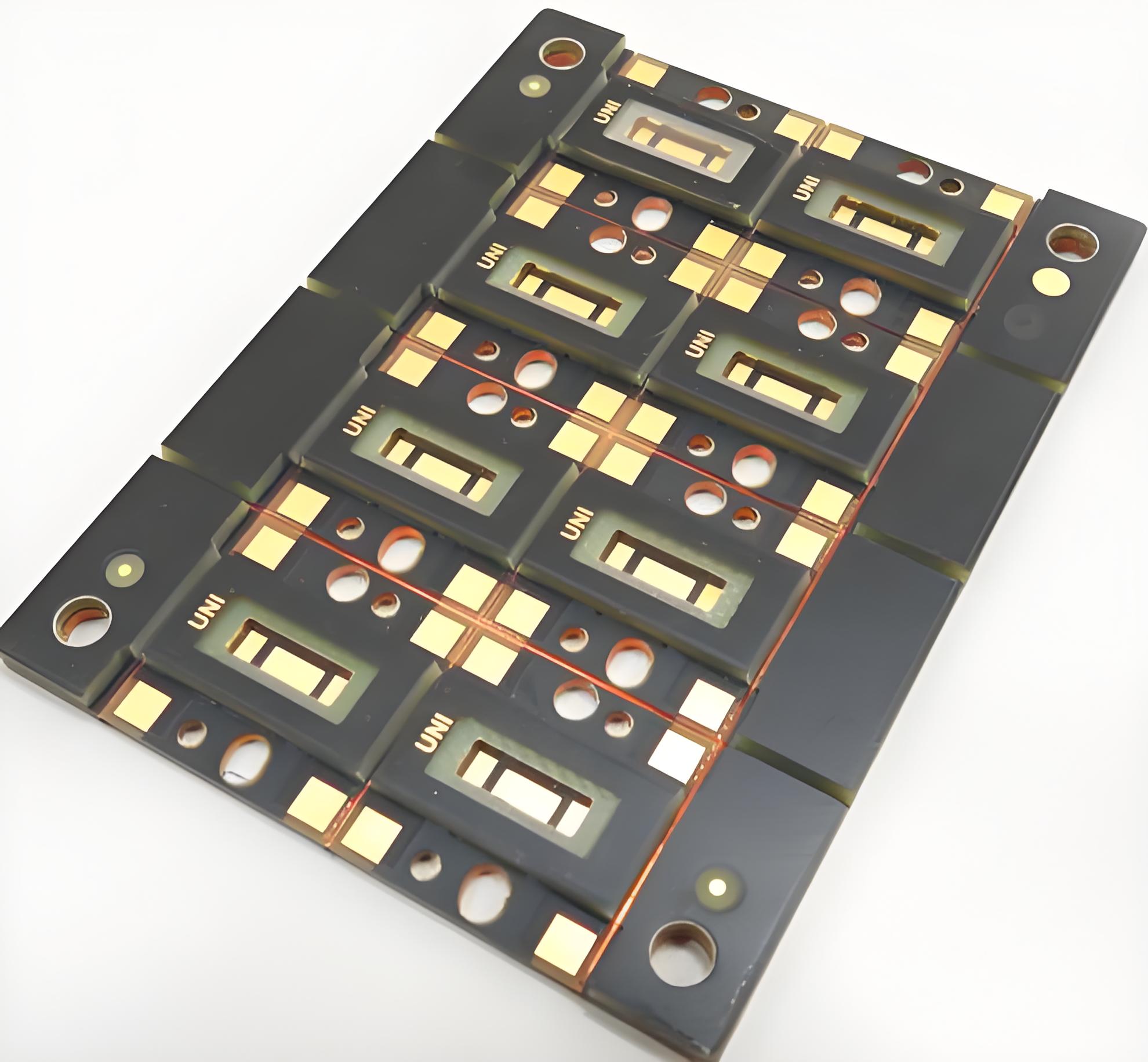
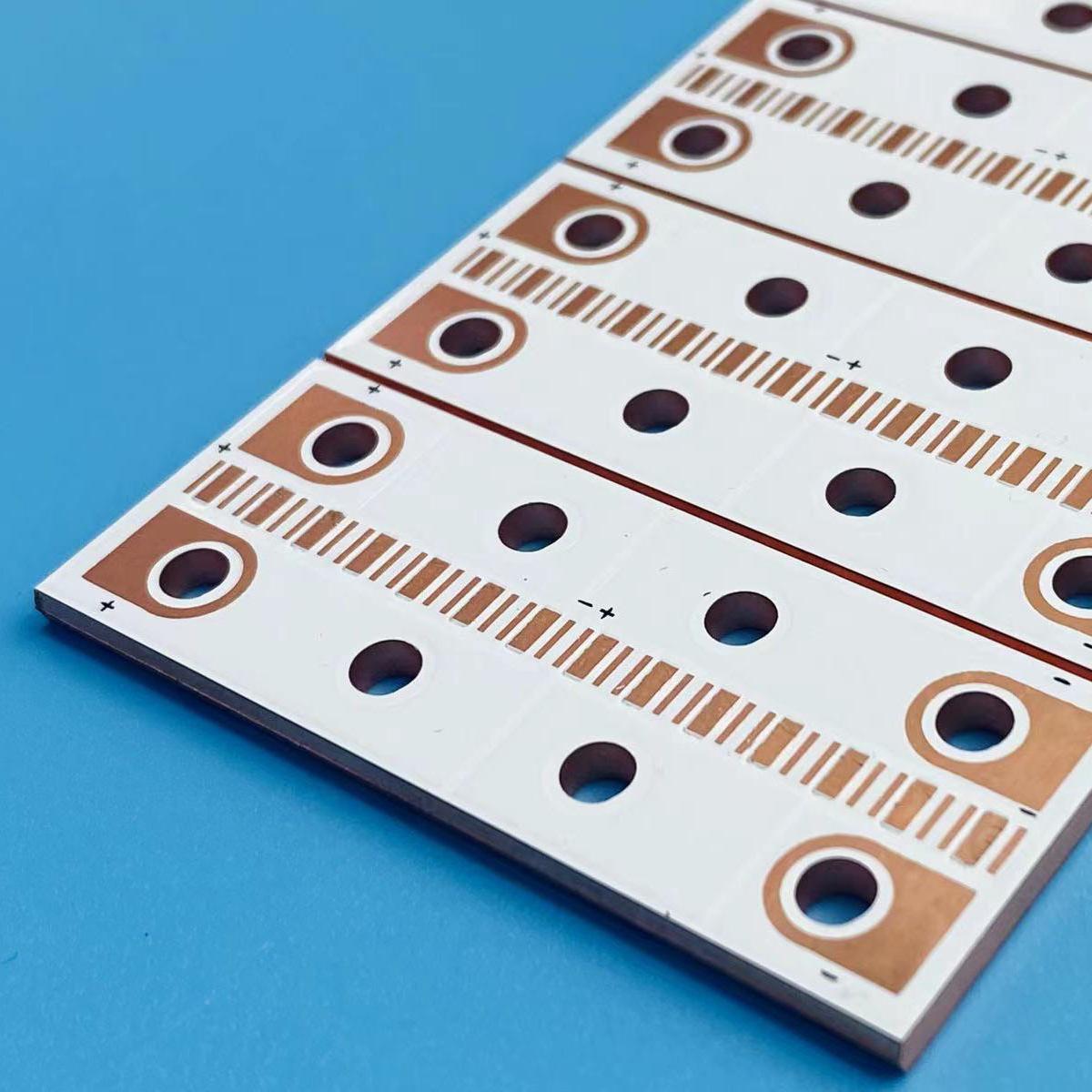
What is an IMS PCB?
Unlike traditional PCBs that rely on FR4 or other resin-based materials, IMS PCBs use a metal baseâtypically aluminum or copper. This base is paired with a dielectric layer and a copper circuit layer on top.
Itâs not just a circuit board. Itâs a thermal solution that keeps devices cool and running longer.
IMS PCB full form and meaning?
The full form of IMS PCB is Insulated Metal Substrate Printed Circuit Board. It’s a PCB built to move heat away from components. That means better reliability, higher efficiency, and longer lifespan for your electronic products.
In this type of PCB, the metal substrate acts as a heat spreader. The insulation layer isolates the copper circuit from the metal base, while still allowing heat to pass through. Itâs a smart design that balances performance with thermal control.
What is IMS material?
The core of every IMS PCB lies in its materials. These layers provide the best thermal and electrical performance. Hereâs what youâll find in a standard IMS stack:
- Metal Base Layer: Usually aluminum for cost-efficiency and light weight. Copper is also used when more heat dissipation is required.
- Dielectric Layer: A thermally conductive but electrically insulating material. It transfers heat from the circuit layer to the metal base.
- Copper Circuit Layer: This is where the actual electrical routing happens. It’s similar to traditional PCB copper layers but optimized for thermal contact.
These three layers form the structure of IMS. The combination is compact, efficient, and powerfulâespecially in LED lighting, automotive electronics, and power converters.
The insulation layer, in particular, must handle high thermal loads while resisting electrical breakdown. Advanced IMS designs often use proprietary dielectric materials to increase thermal conductivity and reduce overall thickness.
How thick is a IMS PCB?
The thickness of an IMS PCB depends on the application. But typically, hereâs what you can expect:
- Metal base layer: 0.5mm to 3.2mm
- Dielectric layer: 0.03mm to 0.2mm
- Copper layer: 0.035mm to 0.2mm
The total thickness usually ranges from 0.8mm to 3.5mm. For LED lighting and compact modules, thinner IMS boards (like 1mm) are common. But in power-heavy designs, thicker boards provide the support and thermal capacity needed.
Some custom builds even exceed 3.5mm if the heat demands are extreme. A thicker aluminum layer enhances mechanical strength and heat dissipation, but it also increases weight and cost. So choosing the right thickness is a balance of thermal needs and design efficiency.
What is the difference between FR4 and IMS PCB?
FR4 PCBs use glass-reinforced epoxy as their core. They are great for general electronics. But FR4 struggles with thermal stress. When high-power components run hot, FR4 doesn’t cool them fast enough. That leads to overheating and failure.
IMS PCBs, on the other hand, are built for thermal performance. The metal base acts like a built-in heat sink. It draws heat away from critical components and spreads it out. That protects the electronics and improves reliability.
| Feature | FR4 PCB | IMS PCB |
| Core Material | Epoxy-based fiberglass | Metal (usually aluminum) |
| Thermal Conductivity | ~0.25 W/mK | 1.0â9.0 W/mK or more |
| Heat Dissipation | Limited | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Slightly higher, but worth it |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | Stronger due to metal core |
For everyday consumer electronics, FR4 is fine. But for power-hungry devices, IMS PCBs offer unmatched reliability.
2 layer IMS PCB vs Multilayer IMS PCB
While single-layer IMS boards are most common, especially in LED lighting, 2-layer and multilayer IMS PCBs are gaining ground in complex applications.
2-layer IMS PCB means there are copper circuits on both sides of the dielectric layer, with one metal core layer. These offer more routing options while still allowing good heat dissipation.
Multilayer IMS PCBs, on the other hand, can include several copper layers, separated by insulation, and only one side is connected to the metal base for heat transfer. This allows for complex routing and high component density while keeping thermal control.
Benefits of 2-layer IMS PCB:
- Better circuit flexibility
- Moderate thermal management
- More design freedom
Benefits of Multilayer IMS PCB:
- High circuit complexity
- Suitable for dense power modules
- Thermal performance still superior to FR4
If you’re building a simple LED module, a single or 2-layer IMS may be enough. But if you’re designing a power controller, communication device, or automotive ECU, multilayer IMS is often necessary.
IMS PCB stackup: What to know?
Stackup design is more than just layers, it defines how your board handles heat, power, and performance. A typical IMS PCB stackup looks like this:
- Copper circuit layer
- Dielectric insulation layer
- Metal substrate (usually aluminum)
But thereâs room for customization. Hereâs what matters:
- Copper thickness: Choose 1oz, 2oz, or more depending on current flow.
- Dielectric performance: The higher the thermal conductivity (measured in W/mK), the better the heat transfer.
- Metal base: Aluminum is the go-to for most. But copper or stainless steel can be used for extreme performance or rigidity.
- Surface finish: Choose between HASL, ENIG, OSP, or others based on your assembly process.
Stackup choices directly affect reliability. A poor choice here means components will overheat, solder joints will crack, or performance will drop.
What are the applications of IMS PCB?
IMS PCB is widely used in high power industry.
- LED lighting: Keeps high-brightness LEDs cool, extending their life.
- Automotive electronics: Used in headlights, sensors, battery modules.
- Power converters: Manages heat in inverters and converters.
- Industrial control systems: Ensures smooth performance under high power loads.
- Communication base stations: Maintains signal integrity and prevents thermal breakdown.
Why choose the right IMS PCB Manufacturer?
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we understand the critical role IMS PCBs play. Weâve spent years perfecting the production process, materials, and stackup customization. Every board we deliver is tested for:
- Thermal conductivity
- Mechanical strength
- Electrical reliability
Whether you need standard single-layer boards or complex multilayer IMS PCBs, we can build it to your exact needs.
Conclusion:
IMS PCB is very important in high power electronics. From simple LED lights to advanced power modules, IMS boards keep your devices cool, stable, and efficient.
Looking for an IMS PCB manufacturer you can rely on? Contact us today at sales@bestpcbs.com