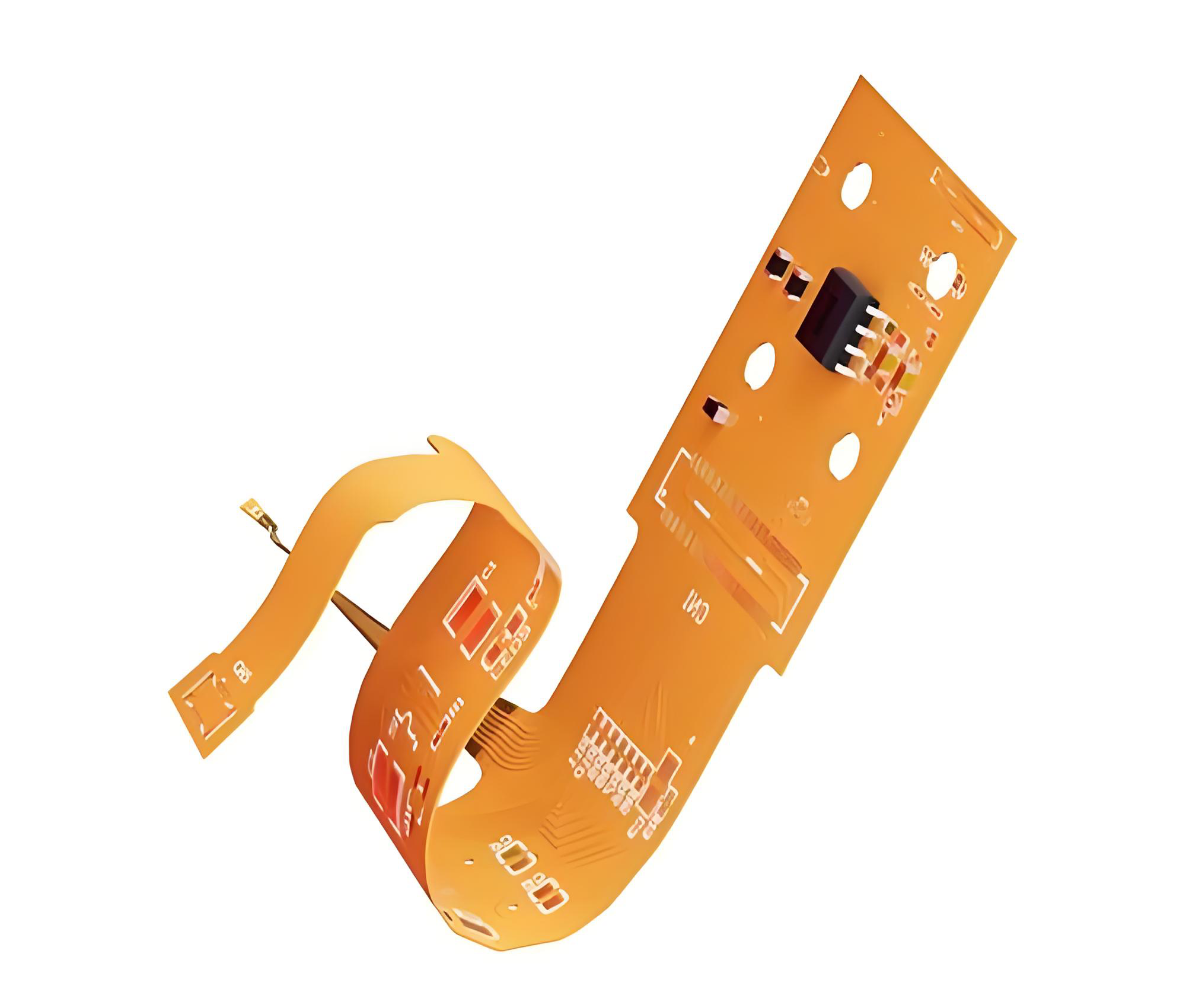
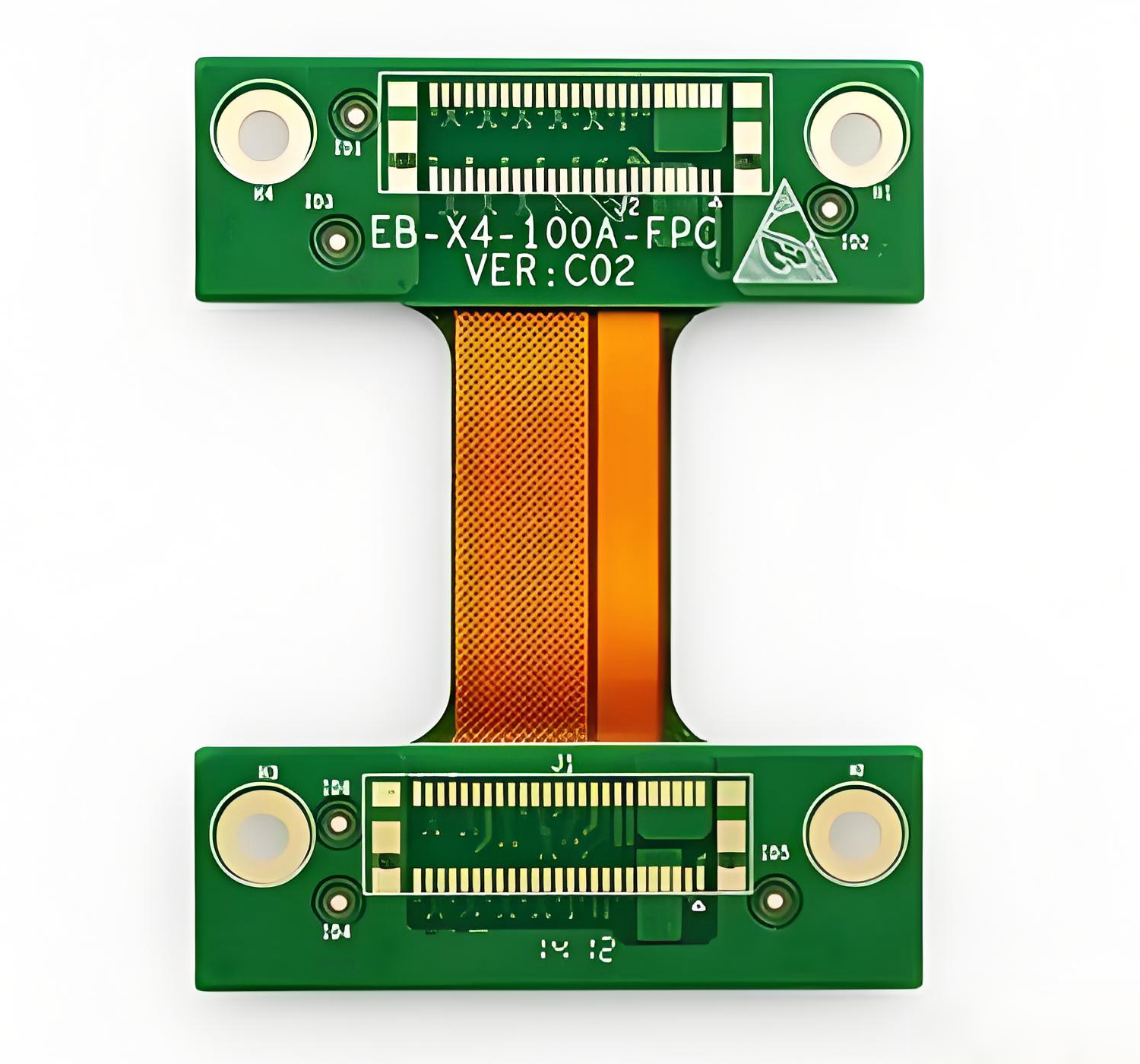
An FPC circuit board (Flexible Printed Circuit board) is a thin, bendable electronic board made from copper and polyimide film. Unlike rigid PCBs, it can fold and twist, saving space and weight. FPC PCBs are widely used in compact devices like smartphones, cameras, and wearables for their flexibility, reliability, and easy integration in tight spaces.
As a custom flexible PCB manufacturer, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) has dedicated years of innovation to produce durable, high-quality FPCs that meet the evolving demands of electronics manufacturing.
Do you have any of the following problems?
- Frequent bending leads to easily damaged circuits and frequent signal transmission issues?
- Complex customized specifications make it difficult for suppliers to accurately match dimensions and process requirements?
- Frequent small-batch, urgent orders result in delayed delivery times and concerns about inconsistent quality?
Our services and solutions:
- One-on-one rapid integration ensures precise adaptation to even the most unique customized needs.
- Targeted optimization of circuitry and materials enhances bending durability, ensuring stable signal transmission.
- Priority is given to urgent orders, and even small batches can be delivered quickly, with consistently reliable quality.
What are FPC Printed Boards?
An FPC printed circuit board (Flexible Printed Circuit) is a type of electronic interconnection technology that replaces traditional rigid boards with a thin, flexible substrate ā usually made of polyimide (PI) or polyester (PET). These materials allow the circuit to bend or fold without breaking the conductive traces.
Unlike rigid PCBs that have fiberglass (FR4) as their core, FPCs use flexible films. Copper foil is laminated on these films, and circuits are etched to form signal paths. The structure can be single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer depending on the design requirements.
The main advantage lies in its ability to fit into tight or irregular spaces. When installed, an FPC acts like a ribbon connecting multiple components, saving space and improving electrical performance.
Many electronic devices ā such as smartphones, wearables, and medical tools ā rely heavily on FPC flexible circuit boards because of their light weight, compactness, and flexibility.
What are the Components of FPC PCB Materials?
An FPC PCB might look simple at first glance, but itās a combination of several layers, each serving a critical role.
- 1. Base Film (Substrate):
The most common materials are polyimide (PI) and polyester (PET). PI provides outstanding thermal resistance, making it suitable for soldering and high-temperature environments. PET is more affordable but suited for lower-temperature applications.
- 2. Adhesive Layer:
This layer bonds the copper foil to the base film. Common adhesives include epoxy, acrylic, or modified resins. An adhesive-less process is sometimes used for better heat resistance and signal performance.
- 3. Copper Foil:
Copper acts as the conductor for electrical signals. It can be rolled annealed (RA) copper for superior flexibility or electro-deposited (ED) copper for standard applications.
- 4. Coverlay (Protective Film):
This is the flexible counterpart of a solder mask in rigid PCBs. It shields the copper traces from oxidation, moisture, and mechanical stress.
- 5. Stiffeners:
To provide mechanical support or to facilitate component soldering, stiffeners (made from FR4, stainless steel, or polyimide) are added to specific regions of the FPC.
- 6. Surface Finish:
Finishes like ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative), or Immersion Tin ensure good solderability and long shelf life.
Each of these materials contributes to the flexibility, durability, and performance of the FPCB flexible printed circuit board.
Advantages of FPC Flexible Circuit Board
FPC has a lot of benefits due to its characteristics;
- Lightweight and Space-Saving: FPCs remove the need for bulky connectors and wires.
- Improved Reliability: Since FPCs reduce the number of solder joints and connectors, they lower the risk of mechanical failure.
- Enhanced Signal Transmission: The continuous copper structure of an FPC ensures stable electrical performance with minimal interference and signal loss.
- Flexible Mechanical Properties: They can bend and fold repeatedly without cracking, which is crucial in dynamic applications like foldable screens or wearable sensors.
- Simplified Assembly: Because the circuit can be pre-formed to match product shapes, installation becomes faster and cleaner.
- Excellent Heat Dissipation: PI-based FPCs can handle high operating temperatures, ensuring stability even under heavy thermal loads.
In short, the FPC revolution is not only about flexibility ā itās about smarter, lighter, and more efficient electronic design.
How Flexible PCBs are Manufactured?
- Single-layer flexible PCB manufacturing process
Cutting – drilling – sticking dry film – alignment – exposure – development – etching – stripping – surface treatment – sticking covering film – pressing – curing – surface treatment – nickel gold deposition – character printing – shearing – electrical measurement – punching – final inspection – packaging – shipment
- Double-layer flexible PCB manufacturing process
Cutting – drilling – PTH – electroplating – pretreatment – paste dry film – alignment – exposure – development – graphic electroplating – film removal – pretreatment – paste dry film – alignment exposure – development – etching – film removal – surface treatment – paste covering film – pressing – curing – nickel deposition – character printing – cutting – electrical measurement – punching – final inspection – packaging – shipment
The manufacturing of a flexible printed circuit demands precision and expertise. Even minor deviations can impact flexibility, conductivity, or lifespan. Hereās a simplified look into the process.
- 1. Substrate Preparation:
The process begins with cleaning and preparing the polyimide film to ensure strong adhesion with the copper foil.
- 2. Copper Lamination:
A thin layer of copper foil is laminated onto the base film through heat and pressure. For adhesive-less FPCs, direct lamination is used to enhance mechanical strength.
- 3. Circuit Patterning (Etching):
Using photolithography and chemical etching, circuit traces are formed on the copper layer. The precision here determines the overall electrical performance.
- 4. Drilling and Plating:
Microvias or through-holes are drilled, followed by copper plating to establish electrical connections between layers.
- 5. Coverlay Application:
The protective coverlay film is applied to protect the circuit from environmental damage. Laser or mechanical openings are made where components will be soldered.
- 6. Surface Finishing:
Depending on the requirement, surface finishes such as ENIG, OSP, or Immersion Gold are applied to protect the exposed copper pads.
- 7. Stiffener Attachment and Final Profiling:
Stiffeners are added for mechanical support. Finally, the circuits are laser-cut or die-cut to shape.
Every step is carefully controlled. The process combines chemical, mechanical, and thermal engineering to create a circuit that bends yet performs flawlessly.
What Factors Affect FPC Circuit Board Performance and Lifespan?
The performance of an FPC circuit board depends on material quality, design, and environmental conditions. Several factors play a major role in determining its durability and reliability.
- Bending Radius: Exceeding the minimum bend radius can damage copper traces.
- Material Selection: High-quality polyimide films and rolled annealed copper foils improve flexibility and reduce fatigue.
- Thermal Stress: Excessive heat or repeated temperature cycles can degrade adhesives and coatings.
- Humidity and Corrosion: Moisture can lead to oxidation or delamination.
- Assembly Handling: Over-stressing during installation or rework can cause micro-cracks.
- Design Layout: Sharp corners, uneven trace widths, and improper via placement may concentrate stress.
When designed and manufactured properly, FPCs can last for many years even in demanding environments.
BEST Technology ā Flexible Circuit Production Capability
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we specialize in producing high-quality custom flexible PCBs for diverse industries including automotive, medical, communication, and aerospace.
Our production capabilities cover everything from single-layer FPCs to multi-layer and rigid-flex combinations. With precision photolithography, laser drilling, and automated inspection, we ensure every circuit meets global standards.
| Parameter (mm) | Polyimide (PI) | PET | |
| Laminate Thickness | 0.025 / 0.050/ 0.125/ 0.175 | 0.025 / 0.050/ 0.075 | |
| Copper Foil | 0.012,0.018,0.035,0.070 | 0.035,0.070 | |
| Min Pattern width/Space | 0.075(3 mil) | 0.075(3 mil) | |
| Min. Drilled Hole Size | Non-Plated Thru | 0.25+/-0.05mm | |
| Plated Thru | 0.1mm+/-0.075mm | ||
| Outlines Dimension | +/- 0.05mm | +/- 0.05mm | |
| Peeling Strength(180Ā°Direction) | >1.2kgf / cm | >1.2kgf / cm | |
| Solder Hent Resistance | 280ā / 10secs | 280ā / 10secs | |
| Surface Treatment | Ni/Au | 2ļ½5Ī¼m | 2ļ½5Ī¼m |
| Au(Electro/Immersion) | 0.03 ~0.1Ī¼m | 0.03 ~0.1Ī¼m | |
| Sn/Pb (Lead Free) | 3~ 20Ī¼m | 3~ 20Ī¼m | |
| Sn-Cu Plating (Lead Free) | 3~ 5Ī¼m | 3~ 5Ī¼m | |
| Tin Plating (Pure Sn) | 5 ~ 8Ī¼m | 5 ~ 8Ī¼m | |
| Bending flexibility | Meet to IPC Criterion | ||
| Chemical Resistance | Meet to IPC Criterion | ||
How Do Flex Circuits Work?
An FPC circuit works just like any other printed circuit board ā it connects electronic components and transfers electrical signals.
When an FPC bends or folds, the copper traces deform within their elastic limit, maintaining conductivity without breaking.
For example, in a smartphone hinge or wearable device, FPCs move constantly while maintaining stable performance. They act as flexible connectors, replacing multiple wires and reducing assembly complexity.
The efficiency of an FPCB flexible printed circuit board depends on the thickness of the copper, the bend radius, and the quality of the substrate.
What is the Difference Between PCB and FPC?
Both carry electrical signals through copper traces. But their construction and applications are quite different.
- Rigid PCB: Made of fiberglass (FR4) with solid layers that donāt bend. Common in desktops, routers, and industrial machinery.
- Flexible PCB (FPC): Made of polyimide film and thin copper foils. It bends and folds easily, ideal for compact or movable electronics.
| Feature | Rigid PCB | Flexible PCB (FPC) |
| Base Material | FR4 fiberglass | Polyimide / PET |
| Flexibility | Rigid | Bendable |
| Weight | Heavier | Lighter |
| Application | Fixed electronics | Wearables, mobiles, medical |
| Cost | Moderate | Slightly higher (for complex designs) |
However, many modern devices now use rigid-flex circuits, combining both worlds.
What is the Difference Between FPC and FFC?
The terms FPC and FFC often confuse people, but they refer to different things.
- FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit): An actual circuit board with patterned copper traces and insulation layers. It can have multiple layers, vias, and complex circuit routing.
- FFC (Flexible Flat Cable): A simple flat cable made of parallel conductive strips laminated between plastic films. Itās used mainly for straightforward signal transmission between boards.
| Aspect | FPC | FFC |
| Structure | Etched copper circuit | Parallel metal lines |
| Layers | Single to multilayer | Usually single |
| Customization | Highly customizable | Standard configuration |
| Application | Cameras, wearables, automotive | Printers, displays, drives |
In short, FPCs are more advanced and versatile than FFCs. When you need a custom, high-performance connection, custom flexible PCBs are the superior choice.
What is FPC Used For?
The applications of FPC circuit boards span across nearly every electronic sector. Their adaptability and compactness make them indispensable.
- Consumer Electronics
- Medical Devices
- Automotive Systems
- Aerospace and Defense
- Industrial Equipment
- Wearable Technology
With growing demand for compact and high-density electronics, the role of FPC flexible circuit boards will only continue to expand.
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we pride ourselves on being a trusted custom flexible PCB manufacturer in China, offering cutting-edge FPC PCB and rigid-flex circuit board solutions. With advanced production systems, certified quality, and expert engineering support, we help global customers achieve excellence in every design.
For inquiries or quotations, contact sales@bestpcbs.com