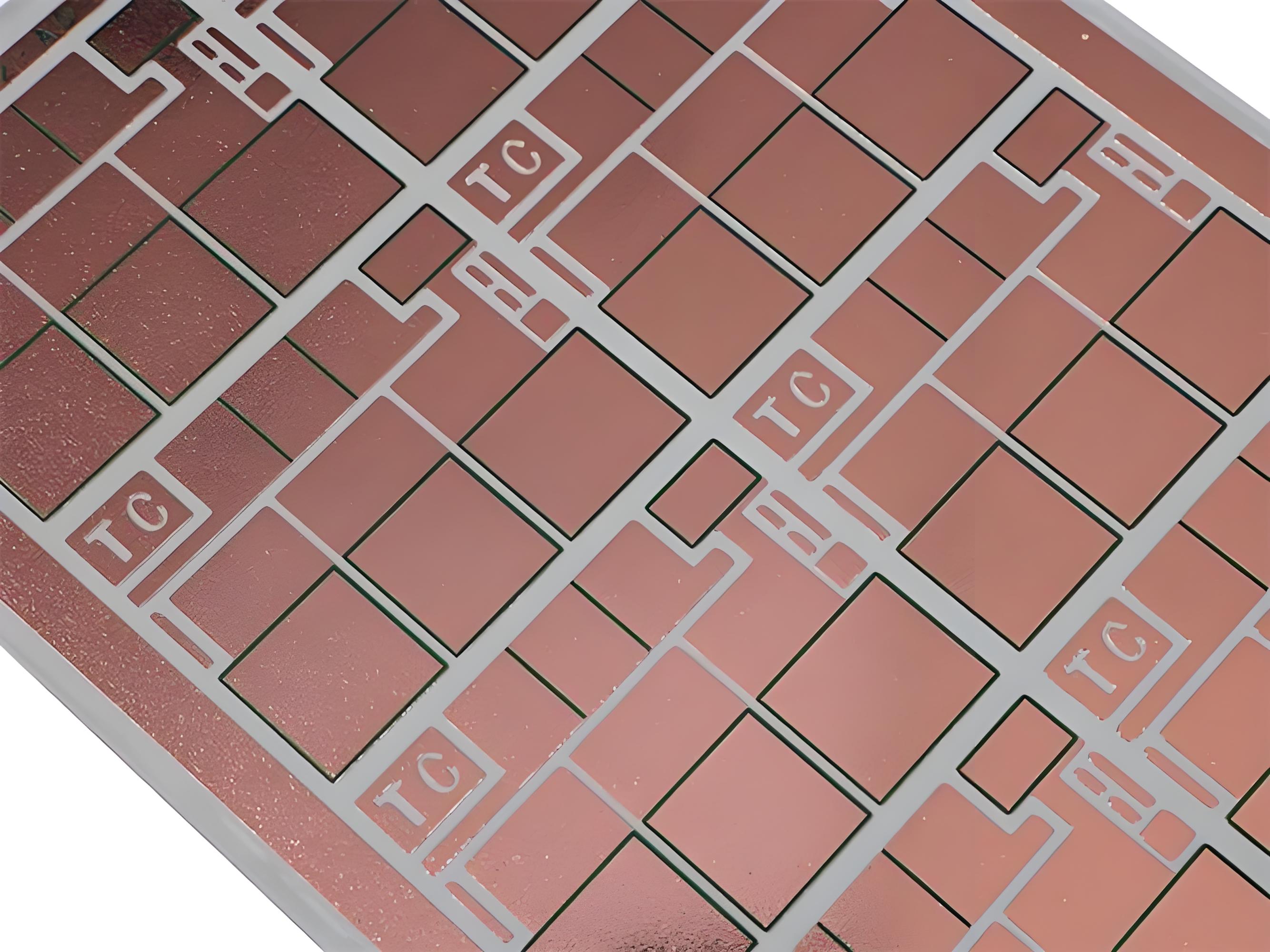
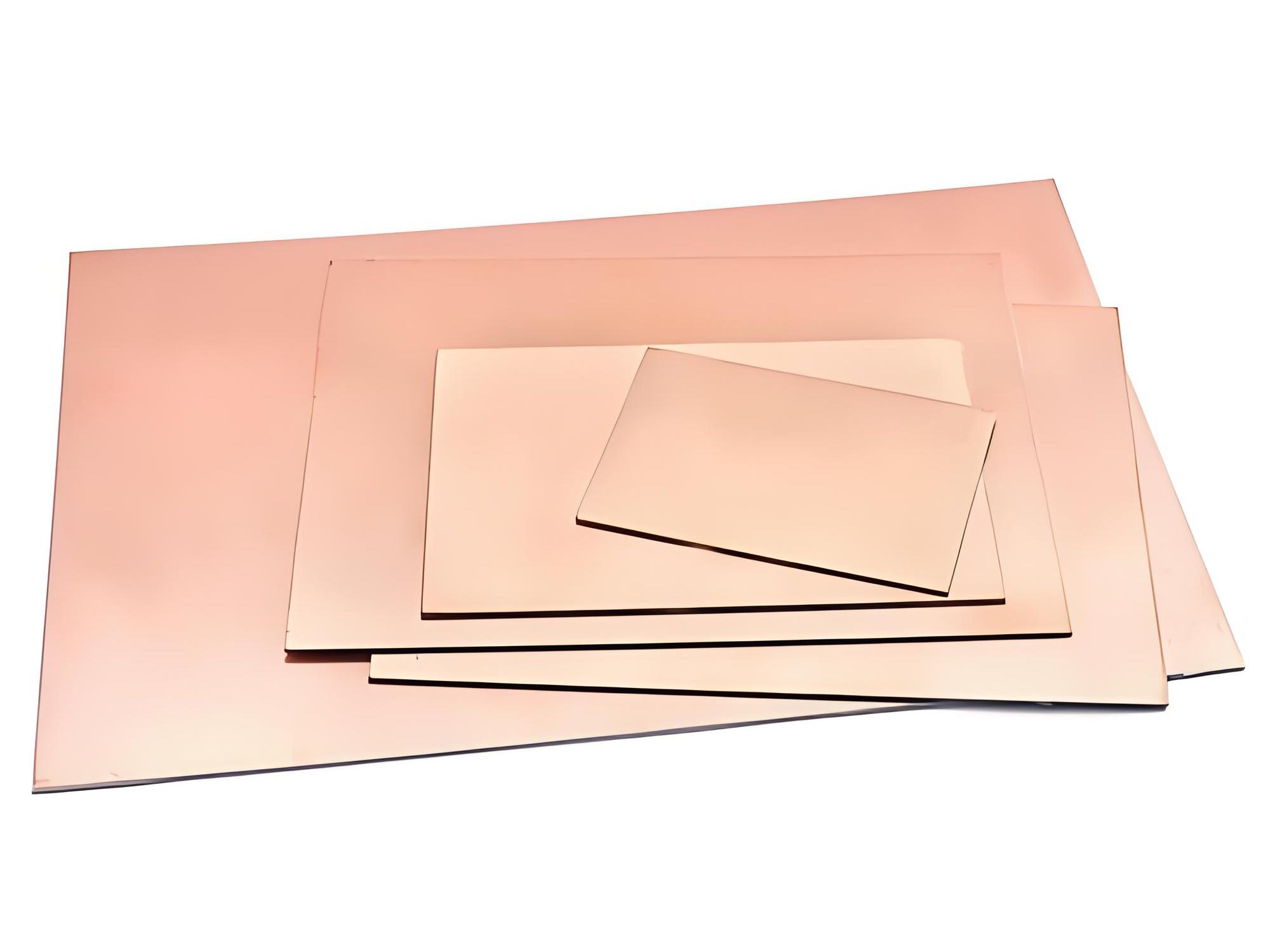
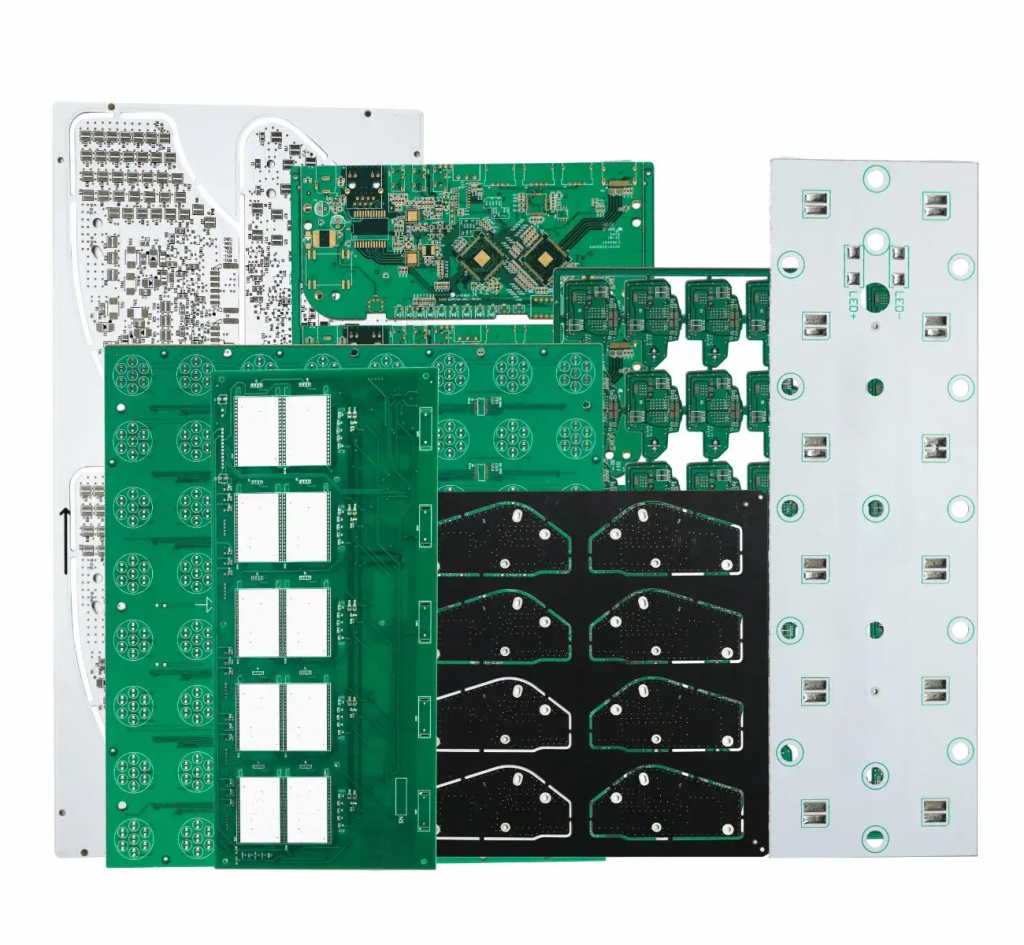
Copper clad PCB are a core material for printed circuit boards (PCBs). Composed of an insulating substrate and copper foil, these materials are heat-pressed to form a composite. They both support components and provide conductive circuits. Depending on the substrate, these materials can be categorized as paper, fiberglass, composite, or metal. They are widely used in consumer electronics, communications, automotive, and industrial control applications.
Are you curious about EBest Circuit (Best Technology)’s copper clad PCBs?
- Does the insulation performance meet circuit insulation requirements?
- Can the material strength withstand the processing and usage environment?
- Is the performance and cost balance balanced?
- Does BEST Technology provide customization and after-sales support?
EBest Circuit (Best Technology)’s copper clad PCB can answer these questions.
- Compatible. Supports standard sizes and customized specifications (thickness, shape), adapting to different PCB design requirements, and enabling fast response for small batches.
- Performance. The base material is highly resistant to bending and impact, and can withstand cutting, drilling, and other processing processes, preventing cracking or deformation after long-term use.
- Achieve. Performance meets industry standards, with over 100 board options for cost optimization, balancing reliability and affordability.
- Provide. Supports customization of materials, specifications, and processes. After-sales service includes rapid response and warranty services, and expedited orders ship within 24 hours.
What is copper clad in PCB?
Copper clad PCB refers to a board where a thin layer of copper foil is bonded to one or both sides of a substrate, usually fiberglass or other insulating material. This copper layer forms the conductive surface where circuit patterns are later etched.
Without this copper cladding, a PCB would just be an insulator with no ability to carry signals. By laminating copper onto the substrate, the board gains electrical conductivity and becomes the foundation for electronic circuits.
The copper clad board is then processed through techniques like imaging, etching, and drilling to create pathways that allow electricity to flow between components.
In short, a copper clad PCB board is the starting point for almost every PCB. It bridges the gap between insulating materials and conductive pathways.
How thick is PCB copper clad?
Copper thickness is one of the most critical specifications in any copper clad PCB sheet. It directly affects current-carrying capacity, heat dissipation, and durability.
The thickness of copper in PCBs is usually measured in ounces per square foot (oz/ft²). Hereâs what it typically looks like:
- 0.5 oz/ft² copper â about 18 microns thick
- 1 oz/ft² copper â about 35 microns thick
- 2 oz/ft² copper â about 70 microns thick
- 3 oz/ft² and above â heavy copper, often used for power electronics
Standard consumer electronics often use 1 oz copper. High-power applications may need 2 oz or more to handle higher currents without overheating.
So, when choosing a PCB copper clad board, thickness depends on your circuitâs power requirements and performance needs.
What are the materials of copper clad laminate (CCL)?
The copper clad laminate (CCL) is not just copper. Itâs a composite material made of multiple layers. Each one has a specific role.
Here are the primary materials used:
1. Copper Foil
- Conductive layer
- Provides the pathways for current flow
- Usually treated to improve adhesion
2. Resin System
- Often epoxy or modified epoxy
- Acts as a binder
- Provides mechanical strength
3. Reinforcement Material
- Fiberglass cloth is the most common
- Ensures dimensional stability
- Improves heat resistance
4. Additives
- Flame retardants
- Fillers for mechanical stability
- Special compounds for high-frequency applications
The combination of these elements gives the copper clad laminate PCB its strong insulation, mechanical toughness, and long-term reliability.
What is a PCB with copper clad on only one side called?
PCB with copper laminated on only one side is known as a single-sided copper clad board. Itâs the simplest form of PCB copper clad laminate.
These are widely used in low-cost and less complex electronic devices. For example:
- Calculators
- Power supplies
- LED lighting modules
- Consumer gadgets
On the other hand, a double sided copper clad PCB board has copper foil on both sides. This allows more complex designs and higher component density.
Therefore, depending on the complexity of the circuit, a single-sided or double-sided option can be chosen.
What are the types of copper clad laminate (CCL)?
Copper clad laminates are available in different types to suit varied applications. Here are the main categories:
Based on Substrate
- Paper-based (phenolic resin) â Affordable, good for household appliances
- Glass fabric (epoxy resin) â More durable, widely used in general electronics
- Composite CCL â A mix of paper and fiberglass
Based on Copper Foil
- Electrolytic copper foil â Smooth surface, ideal for precision circuits
- Rolled annealed copper foil â Excellent ductility, used in flexible PCBs
Based on Application
- General-purpose CCL â Cost-effective and widely used
- High-frequency CCL â Designed for RF and microwave devices
- High-speed CCL â Used in data communication systems
- Thermal conductive CCL â Great for LED and power devices
Each type of copper clad laminate PCB material is designed to handle unique performance demands.
Why use a copper clad PCB board?
Copper clad PCBs bring several advantages that make them a preferred choice:
- Excellent Conductivity: Copper provides stable and reliable current flow.
- Thermal Management: Thicker copper spreads heat efficiently, preventing damage.
- Mechanical Strength: Fiberglass reinforcement adds stability.
- Design Flexibility: Available in single, double, or multilayer forms.
- Cost Efficiency: Paper-based and FR4 laminates reduce manufacturing costs.
These advantages have led to the widespread use of copper clad PCBs in consumer electronics, automotive systems, and medical devices.
What is copper clad used for?
Copper clad boards serve as the base for many electronic products. Some key applications include:
1. Consumer Electronics
- Smartphones, tablets, laptops
- Wearable devices
2. Automotive Electronics
- Control modules
- Safety systems
- Infotainment units
3. LED Lighting
- High thermal conductivity versions
- Used in LED lighting aluminum substrates
4. Industrial Control Systems
- Robust designs for high current
- Suitable for harsh environments
5. Medical Devices
- Compact and reliable circuits
- Long-term performance stability
In short, copper clad PCBs are used anywhere reliable electronic connections are required.
How to choose a copper clad board for PCB?
Choosing the right copper clad laminate PCB requires balancing performance, cost, and application needs. Hereâs how you can decide:
1. Power Requirements
- High current? Choose thicker copper.
- Low power? Standard 1 oz copper is enough.
2. Frequency Performance
- For RF or high-speed circuits, select low-loss laminates.
- For simple circuits, FR4 is cost-effective.
3. Thermal Demands
- LEDs and power devices benefit from thermal conductive laminates.
4. Design Complexity
- Single-sided for simple devices.
- Double-sided or multilayer for complex designs.
5. Budget Considerations
- Paper-based laminates are cheaper.
- Glass-fiber laminates offer longer life.
By considering these factors, you can select the best copper clad board PCB for your project.
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we specialize in PCB copper clad laminates that meet international standards and deliver long-term reliability. If you are seeking a trustworthy supplier for your copper clad PCB boards, our team is here to help. Contact us today at sales@bestpcbs.com