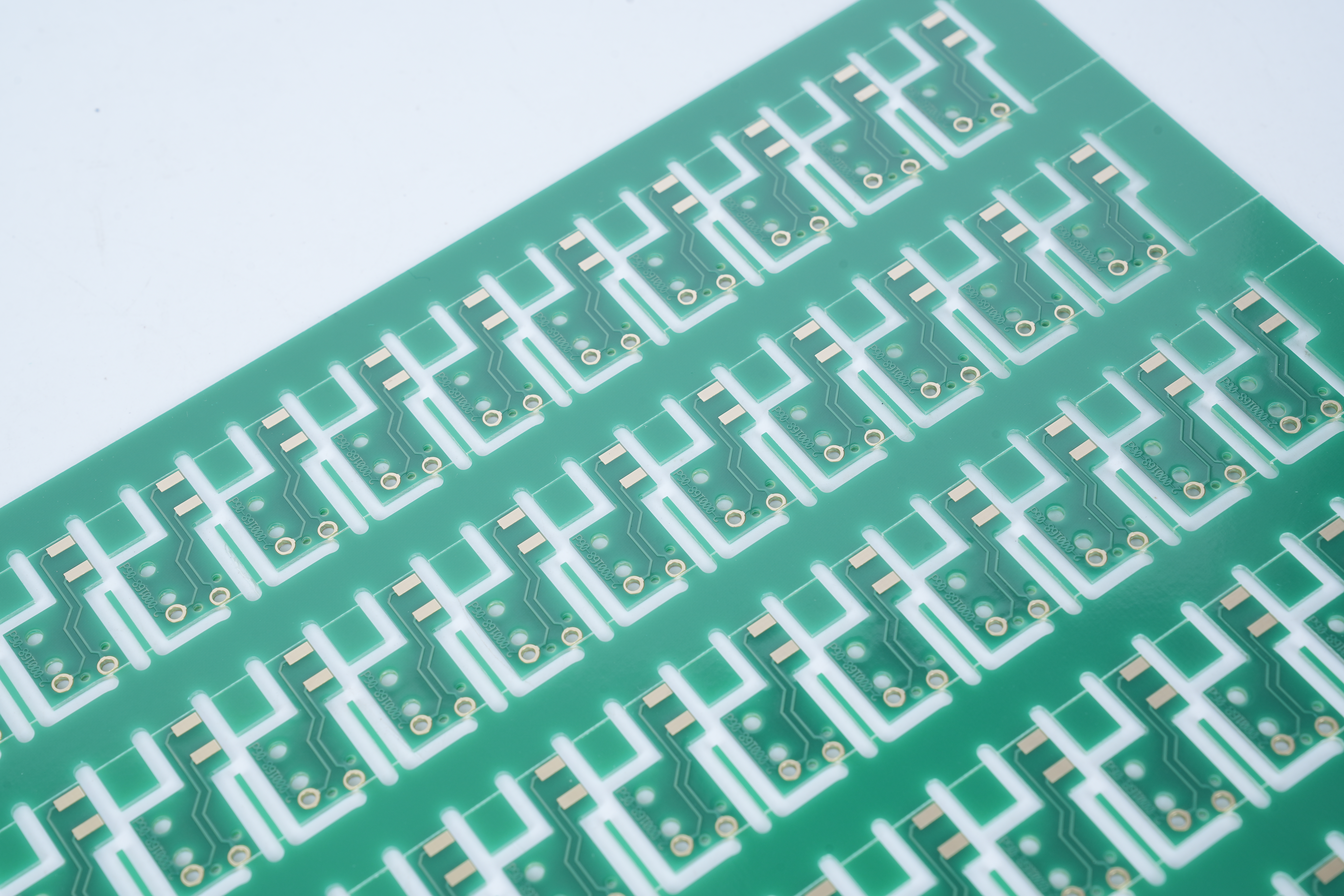
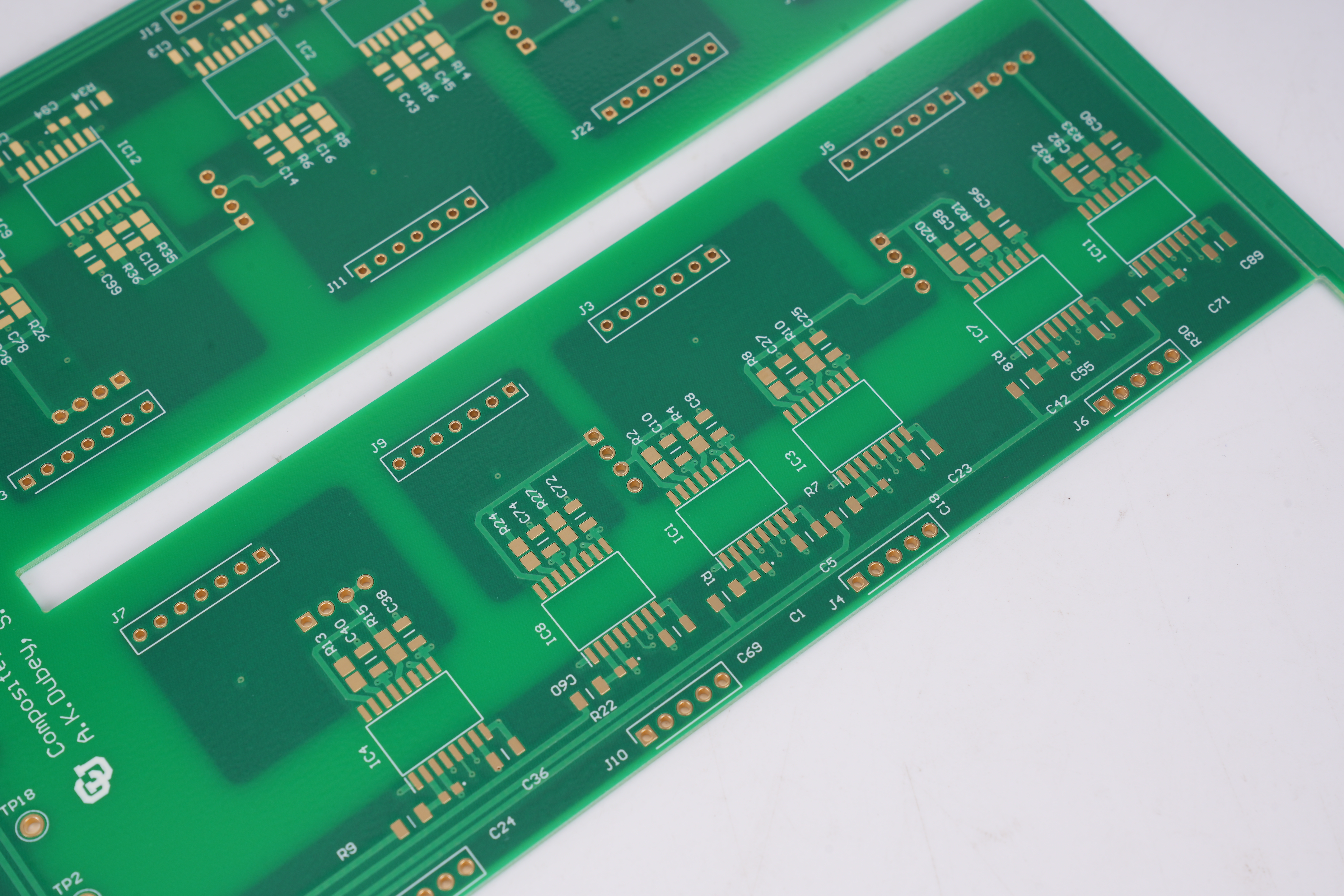
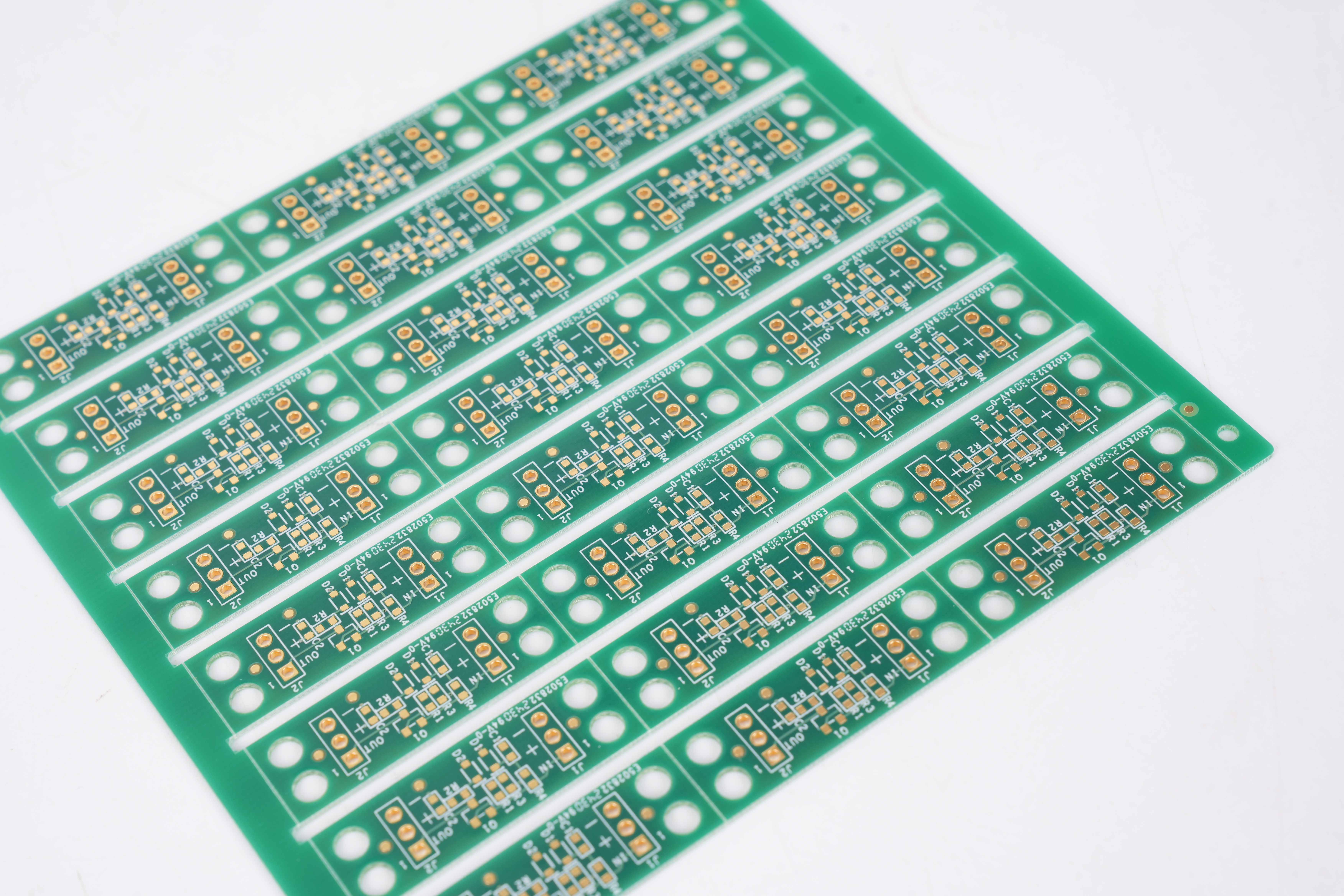
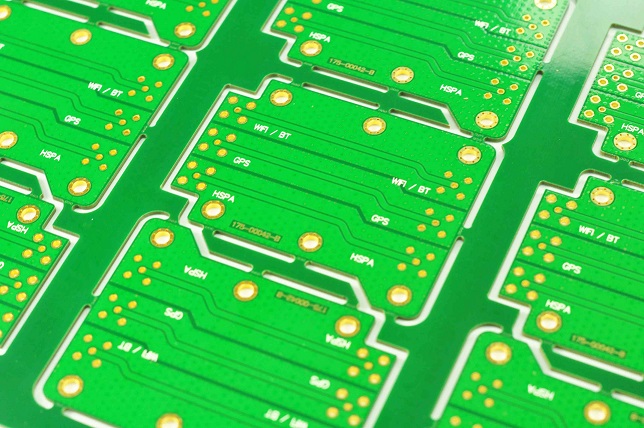
Blank PCB and parts form the base structure of nearly every electronic product. A blank PCB is a printed circuit board without mounted components. It carries copper traces, pads, and vias that guide electrical signals, but it has no chips, connectors, or resistors installed yet. This empty structure becomes the starting point for prototypes, new layouts, and full production builds.
BEST Technology meets these expectations with years of manufacturing experience and a strong focus on quality and service. The company provides dependable blank PCB boards built with strict inspection, solid materials, and fast support. If you have any needs or plan to start a project, feel free to contact: sales@bestpcbs.com
What Is a Blank PCB?
Blank PCB is a printed circuit board with no components added. It carries copper traces, pads, and plated holes, but nothing else. It is the base where resistors, chips, and connectors will sit later.
Blank PCBs come in many forms. Single-layer. Double-layer. Even multi-layer. Some people call them blank PCB boards, blank PCBs, or just blank PCB for short. The names change, but the meaning stays the same. These boards offer a strong, stable, and clean foundation for a design to grow.
Because they carry no parts, blank PCBs stay flexible for many uses. They stand ready for prototyping, testing, training, and evaluation.
What Makes Blank PCBs Different From Assembled Boards?
Blank PCBs focus on structure. Assembled boards focus on full function. This simple difference changes their purpose.
Blank PCBs have no active or passive parts. They hold circuits but no energy flows through them yet. You can work on them, test ideas on them, and adjust layouts if needed.
Assembled boards, on the other hand, already include all components. They can power devices. They can run programs. They can be installed inside a product.
Because of this difference, blank PCBs cost less. They are lighter. They are more adaptable. Engineers use them when they want full control over a design. Assembled boards are used only when all details are finalized.
What Are the Uses of a Blank PCB Board?
Blank PCBs are used in numerous fields. Their flexibility allows them to play a role at countless stages of product development.
- They help during early concept work. Designers love blank PCB boards when they start shaping a new circuit layout. They give space to experiment, fix, and refine.
- They support prototype builds. Teams place components on blank PCBs to test behavior. If something needs improvement, they change the board.
- They fit training and education. Blank PCBs give students hands-on experience. They help beginners learn routing, soldering, and assembly.
- They assist small-run production. Blank PCBs are perfect for low-volume builds.
- They help repair tasks. When a specific small board needs replacement, they populate a blank one.
- They support DIY and hobby projects. Makers and innovators use blank PCBs for personal inventions.
- The beauty of blank PCBs comes from their open nature. They can shift roles based on your ideas and goals.
Why Choose Blank PCB Boards for Prototypes?
Prototypes must stay flexible. That is why blank PCB boards win here. You control layout, pads, holes, and shapes.
- You reduce risk. If something is not right, you adjust it. A blank board lets you fix a design without a full redesign of the entire product.
- You save cost. Prototype components can be added or removed easily. Blank boards give freedom without high waste.
- You move faster. Blank PCB boards are available in many sizes. You can quickly test and update the design without delays.
- You keep creativity alive. You can test different parts. You can change trace width. You can add new ideas.
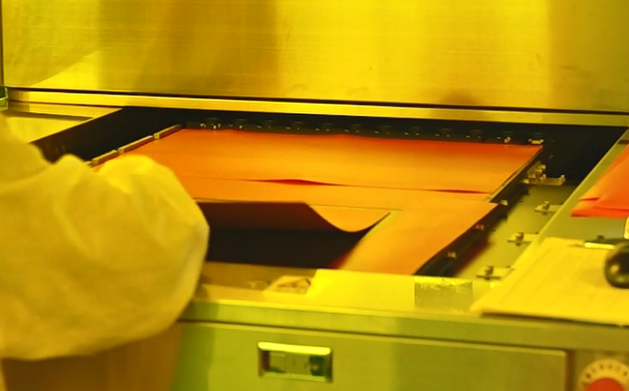
How Are Blank PCB Boards Manufactured?
The manufacturing of blank PCBs looks simple on the outside, but inside it requires strict control.
- 1. Design preparation
The process begins with a PCB layout file. Engineers check trace spacing, hole size, and copper thickness.
- 2. Material cut
Large sheets of laminate get cut into board size. The laminate often includes fiberglass and copper layers.
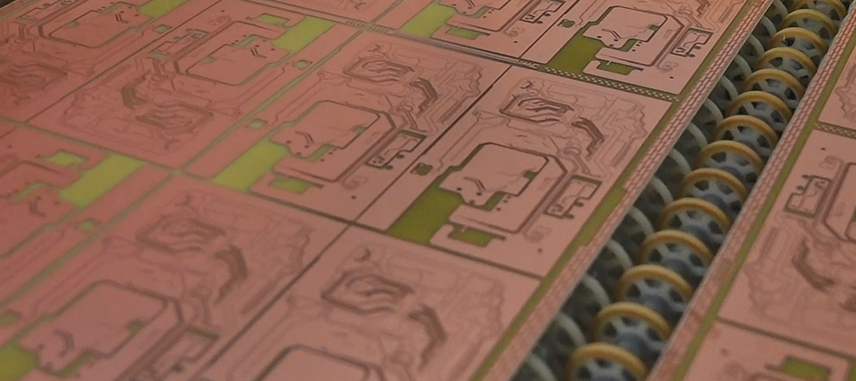
- 3. Image transfer
The circuit pattern transfers onto the copper surface. Light-sensitive film helps protect the needed areas.
- 4. Etching
Chemical etching removes exposed copper and forms the final traces.
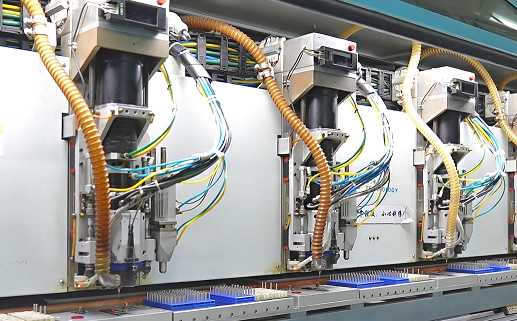
- 5. Drilling
CNC drills create holes for future component mounting.
- 6. Plating
Copper plating coats the hole walls to create strong electrical paths.
- 7. Solder mask coating
A green, black, white, blue, or red coating protects the copper. It prevents oxidation and solder bridging.
- 8. Silkscreen printing
Labels and markings get printed for easy recognition.
- 9. Surface finish
Finishes like HASL, ENIG, OSP, or immersion silver protect pads and support soldering.
- 10. Testing and inspection
Each blank PCB passes electrical checks. This ensures there are no shorts or opens.
The entire flow requires precision. Even small errors can break the final circuit. That is why reliable suppliers take manufacturing very seriously.
What Materials Are Common in a Blank PCB?
Blank PCB and parts rely on stable materials. Each type supports a specific group of applications.
- FR4: The most common material. It provides strength, durability, and cost balance. Many blank PCB boards use FR4 because it fits most electronic projects.
- Aluminum substrate: Used for LED applications and high-power circuits. Aluminum offers better heat control.
- Flexible polyimide: For flex circuits. These boards can bend and twist without damage.
- Rogers materials: Used for high-frequency systems. These boards deliver better signal control.
- CEM materials: A mix of resin and fiberglass. They fit basic designs at lower cost.
The right material affects performance, durability, and heat handling.
What Factors Affect Blank PCB Quality?
Blank PCBs may look simple, but their quality depends on many points.
- Copper thickness: Thicker copper supports higher current. Thin copper suits low-power circuits.
- Trace width and spacing: Accurate spacing prevents signal loss and heat buildup.
- Drill accuracy: Precise holes ensure clean component mounting.
- Layer alignment: Multi-layer boards need perfect alignment to avoid breaks.
- Material purity: High-quality laminates reduce warping and improve lifespan.
- Surface finish: A strong finish helps soldering and protects copper.
- Solder mask quality: A stable solder mask prevents peeling and cracking.
When these factors stay under control, blank PCB boards become more reliable. They also last longer and support better performance.
Where to Find a Reliable Blank PCB Board Supplier?
Finding a trustworthy supplier of blank PCB boards is very important. A strong supplier gives you confidence. They offer quality, speed, and clear communication.
Look for suppliers with:
- Stable process control: A supplier with strong production systems avoids defects and delays.
- Long-term experience: Years in the industry translate into better handling of special needs.
- Clear certifications: ISO9001, RoHS, and UL show strong quality management.
- Material transparency: Suppliers should always share material sources.
- Fast feedback and support: A good supplier stays reachable. They answer questions quickly.
- Flexible order size: Small prototype orders and large production runs should both be possible.
- Strong inspection process: Reliable suppliers test every board, even the blank ones.
BEST Technology Co., Ltd. meets these standards with confidence. The company has been working in the PCB field since 2006 and has earned strong trust from global customers.
Our blank PCB boards go through strict process control, complete inspections, and advanced production steps. We use stable materials, follow ISO9001:2015, and support both small prototype runs and high-volume orders. Our team responds quickly, offers honest technical guidance, and keeps communication smooth from start to finish.
Conclusion:
Blank PCBs may look simple. They create a clean, stable path for components. They help teams test, explore, and refine every detail.
For further help or cooperation, feel free to reach us at sales@bestpcbs.com