Copper base PCBs have become increasingly popular in high-power and thermally demanding applications. But many customers still ask: “Is it really suitable for my project?” If you’re in LED lighting, power electronics, automotive, or any field requiring excellent heat dissipation, this article is for you. We’ll walk you through what copper base PCBs are, their key advantages, and how to determine whether they’re the right fit for your product.
What Is a Copper Base PCB?
A Copper Base PCB is a type of metal core printed circuit board (MCPCB) that uses copper as the base material instead of the more common aluminum or FR4. This type of board is specifically designed to handle high heat, high power, and mechanical stress. The copper base acts as a heat sink, pulling heat away from components and distributing it more evenly. Compared with FR4 PCB, copper PCBs offer superior heat conductivity, mechanical strength, and current-carrying capacity.
Typical Structure of a Copper Base PCB
The structure of a copper base PCB is generally composed of three main layers, each playing a critical role in the board’s performance:
- Copper Circuit Layer (Top Layer):
This layer contains the etched copper traces that form the electrical pathways. In copper base PCBs, this layer is often thicker than in standard PCBs—ranging from 1 oz to 20 oz or more—to handle higher current loads and improve heat distribution. These traces can be plated or coated depending on the application or customers requirements (e.g., ENIG, HASL, OSP).
- Thermal Dielectric Layer (Middle Layer):
This is the insulating layer between the circuit and the metal base. It’s designed to have high thermal conductivity and excellent electrical insulation. Its main function is to transfer heat from the components to the copper base below while keeping the circuits electrically isolated. The thermal conductivity of this layer often ranges from 1 W/m·K to over 10 W/m·K, depending on material choice.
- Copper Base Layer (Bottom Layer):
Unlike typical MCPCBs that use aluminum, this layer is made of solid copper—usually ranging from 1 mm to 3.5 mm thick or more. This acts as a heat sink, pulling heat away from the circuit layer and rapidly dispersing it. Copper’s thermal conductivity is about 400 W/m·K, significantly higher than aluminum (~200 W/m·K).
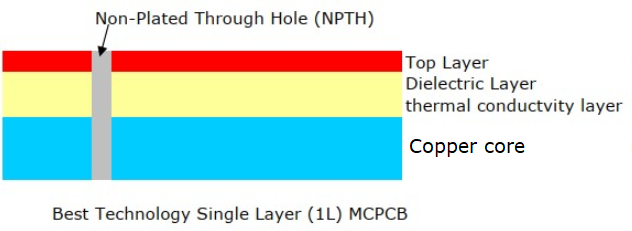
This design structure enables heat to be quickly conducted from the components to the copper baseplate, and then transferred through the heat sink or the casing, thereby enhancing the overall thermal management capability of the system.
What Are the Core Advantages of Copper Base PCBs?
Clients often wonder: “Why should I pay more for a copper base board?” Here’s why it might be worth it:
- Exceptional thermal conductivity – Copper is far more effective at dissipating heat than aluminum or FR4, very suitable for high-wattage components.
- High current tolerance – With thicker copper layers, these PCBs handle larger currents with minimal resistance.
- Excellent mechanical durability – Copper PCBs are stronger and can withstand physical stress, vibration, and temperature cycling.
- Improved electromagnetic shielding – Their dense base helps suppress EMI, a critical benefit in high-frequency applications.
These benefits result in longer product life, more consistent performance, and fewer field failures, especially in mission-critical applications.
Which Industries Benefit Most from Copper Base PCBs?
- LED Lighting – High-power LEDs like COB, UV LED, floodlights, and grow lights require efficient thermal management.
- Power Electronics – Power supplies, inverters, and converters benefit from copper’s high current-carrying capacity.
- Automotive – EV batteries, headlights, and control systems need durability and consistent heat dissipation.
- Telecom & RF Devices – Copper PCBs handle high frequencies with reduced signal loss and better EMI shielding.
- Medical Equipment – High reliability is key for precision instruments that cannot afford overheating.
If your product involves heat, high power, or harsh environments, copper base PCBs are often the most dependable choice.

How Can You Tell If a Copper Base PCB Is Right for Your Project?
Before committing, ask yourself the following:
1. Does your design generate significant heat?
2. Is there limited space, but high power density?
3. Are you struggling with product reliability or failures due to overheating?
4. Is your end-product used in mission-critical or high-reliability environments?
If you answered “yes” to two or more of these, a copper base PCB could greatly improve your performance and reliability.
What Are the Limitations or Considerations of Copper Base PCBs?
While copper base PCBs offer outstanding thermal and electrical performance, they are not suitable for every project. Understanding their limitations and key design considerations is essential to avoid overdesign, unnecessary costs, or compatibility issues in your application.
1. Higher Material and Production Cost
Copper is significantly more expensive than aluminum or fiberglass (FR4). This cost factor affects both raw material pricing and manufacturing expenses. Additionally, the thicker copper layers and heavier base not only cost more to source, but they also require more energy and effort to process, increasing the total cost of production.
2. Heavier Board Weight
Copper has a high density (8.96 g/cm³ compared to aluminum’s 2.70 g/cm³), which means copper base PCBs are substantially heavier. This can present challenges in:
- Weight-sensitive products such as drones or handheld devices
- Shipping and logistics costs, especially for large quantities
- Mechanical handling in assembly lines
Tip: If you’re designing a compact or mobile device, consider whether the weight trade-off justifies the thermal benefit.
3. More Challenging to Fabricate and Process
Due to the hardness and thickness of the copper base, special tooling, slower machining speeds, and experienced operators are required. Fabricators must use tougher drill bits, precise CNC machines, and advanced lamination processes to ensure:
- Clean drill holes
- Accurate etching and layering
- Strong adhesion between layers
Poor processing can result in delamination, cracks, or electrical leakage—especially at the dielectric interface.
4. Limited Flexibility in Complex Layer Stack-Ups
While single-layer copper PCBs are common, multi-layer copper base PCBs are difficult and expensive to produce. This is because:
- Each additional layer increases complexity in lamination
- Heat must still flow effectively through the stack
- Alignment and insulation tolerance become more critical
Not all manufacturers offer multi-layer copper PCBs due to the strict processing requirements and lower production yields.
5. Thermal Expansion and Stress Considerations
Copper has a relatively low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), which is good for dimensional stability. However, when paired with dielectric materials or mounted in assemblies with mismatched CTEs, thermal stress can build up during repeated heating and cooling cycles.
This can lead to:
- Micro-cracking
- Solder joint fatigue
- Mechanical warping of the board
If you need help evaluating whether copper base PCBs are the right choice for your next project, EBest Circuit (Best Technology)’s engineering team is here to offer thermal simulation, design review, and cost-performance optimization—so you only pay for what you truly need.
Why Choose EBest Circuit (Best Technology) for Your Copper Base PCBs?
When it comes to copper base PCBs, expertise matters. At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we provide end-to-end solutions — from thermal simulation and material selection to rapid prototyping and mass production.
Why choose us?
✅ One-on-one engineering support
✅ In-house thermal and mechanical design assistance
✅ Certified quality (ISO9001, ISO13485, IATF16949, AS9100D)
✅ MES system for full traceability
✅ On-time delivery and competitive pricing
Let us help you build reliable, high-performance PCBs tailored to your application needs.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Is copper base PCB better than aluminum base for heat dissipation?
Yes, copper offers superior thermal conductivity compared to aluminum and handles higher thermal loads.
Q2: What thicknesses are available for copper base PCBs?
Copper thickness typically ranges from 1oz to 20oz or more depending on your current/thermal needs.
Q3: Can copper base PCBs support multi-layer structures?
Yes, although complex and costly, multi-layer copper base PCBs are feasible with the right process control.
Q4: How can I improve thermal performance in my copper PCB design?
Use thermal vias, select high-conductivity dielectric layers, and optimize component placement.
Q5: Why is copper base PCB more expensive?
Copper material, heavier base layers, and specialized manufacturing processes contribute to the higher cost.
Tags: copper base pcb, copper core pcb


