If you have ever opened an electronic device and looked at the green board inside, you may have wondered what all those tiny parts actually do. From smartphones and medical equipment to industrial controllers and home appliances, every electronic product relies on a circuit board to function properly.
Understanding what’s on a circuit board helps you better grasp how electronics work, why certain designs are more reliable than others, and how problems are diagnosed when something fails.
What is a Circuit Board?
Before examining the mounted parts, it is important to recognize that the board itself is an engineered component.
A PCB typically consists of an insulating substrate, most commonly FR-4 glass-reinforced epoxy, laminated with copper layers. These copper layers are patterned into traces that route signals and power between components. Additional features such as solder mask, silkscreen, and surface finish complete the structure.
Key PCB elements include:
- Copper traces for signal and power routing
- Pads and vias to connect components and layers
- Vias that connect different copper layers, especially for multilayer PCBs
- Solder mask to prevent short circuits and protect copper
- Silkscreen for reference designators, polarity marks, and assembly guidance
The PCB defines how components are electrically connected and how heat and mechanical stress are managed.
What’s on a Circuit Board and Why It Matters in Electronics?
So, what’s on a circuit board? From an engineered perspective, a printed circuit board with electronics parts like LEDs, fuses, connectors, resistors, capacitors, ICs are considered as PCBA (PCB assembly product), while a PCB without any soldered components called bare PCB. And between them, PCB is one of a part of PCBA.
There are two kinds of components used on a circuit board, passive components and active components. Passive components do not amplify signals or require control logic, but they shape voltage, current, timing, and stability. While active components control current flow and perform computation, amplification, or switching.
The components are not placed randomly on a PCBA. Each one plays a specific role in controlling power, processing signals, storing data, or enabling communication with other systems.
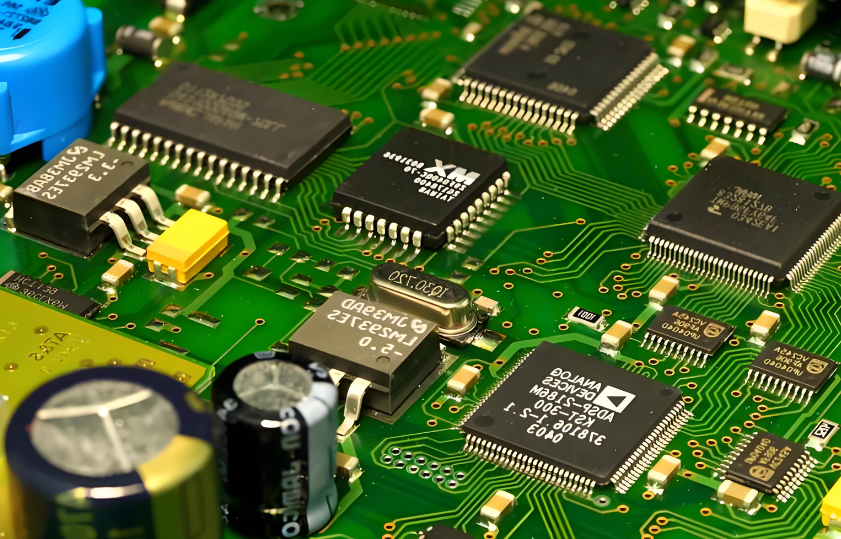
What’s on a Circuit Board?
Passive Components on a Circuit Board
Passive components form the electrical foundation of a circuit. Their main function is to shape and condition electrical energy by controlling current flow, stabilizing voltage, defining timing characteristics, filtering noise, and providing basic protection.
The most common passive components on a circuit board include resistors, capacitors, inductors, transformers and so on. These components are typically small, highly reliable, and present in large quantities on most PCBs.
| Component | Reference Designator | Primary Function | Typical PCB Forms | Common Schematic Symbol |
| Resistor | R | Limits current, divides voltage, sets bias | SMD, axial THT | |
| Capacitor (non-polarized) | C | Charge storage, decoupling, noise filtering | Ceramic SMD | |
| Capacitor (polarized) | C | Bulk energy storage, smoothing | Electrolytic, tantalum | |
| Inductor | L | Current filtering, energy storage | Power inductor, ferrite | |
| Transformer | T | Voltage conversion, isolation | Power, signal transformer | |
| Fuse | F | Over-current protection | SMD fuse, cartridge | |
| Thermistor (NTC / PTC) | RT / TH | Temperature sensing, inrush limiting | Disc, bead | |
| Varistor (MOV) | RV | Surge voltage suppression | Disc MOV |
Active Components on a Circuit Board
Active components control current flow and can amplify, switch, regulate, or process signals. They require power to operate. The most common active components on a circuit board including ICs, diodes, transistors, amplifiers… ICs are the most complex parts on a circuit board. They include microcontrollers, processors, memory devices, analog front ends, and power management ICs. Their package types—such as QFN, QFP, or BGA—directly influence PCB layout density and assembly complexity.
| Component | Reference Designator | Primary Function | Typical PCB Forms | Common Schematic Symbol |
| Diode | D | One-way current flow, protection | SMD, axial | |
| Zener Diode | ZD | Voltage regulation, over-voltage clamp | SMD | |
| BJT Transistor (NPN/PNP) | Q | Amplification, switching | SOT-23, TO-92 | |
| MOSFET (N / P channel) | Q | Power switching, control | SOT-23, TO-220 | |
| Operational Amplifier | U / IC | Signal amplification, filtering | SOIC, TSSOP | |
| Integrated Circuit (IC) | U / IC | Logic, processing, control | QFN, QFP, BGA | |
| Voltage Regulator | U | Stable voltage output | SOT-223, QFN | |
| Optocoupler | U / OK | Signal isolation | SOP, DIP |
What Do Resistors Do on a Circuit Board?
Resistors are among the most common components on a circuit board. Their primary role is to control the flow of electrical current. By limiting current, resistors protect sensitive components and help set correct operating conditions within a circuit.
On most boards, resistors are used to:
- Reduce voltage levels
- Control current flowing into LEDs or IC pins
- Create timing and biasing networks
Resistors come in many values and sizes, especially in surface-mount designs. Although they are simple parts, incorrect resistor selection can cause overheating, unstable signals, or component damage.
What Is the Role of Capacitors on a Circuit Board?
Capacitors store and release electrical energy. On a circuit board, they are essential for maintaining stable voltage levels and reducing unwanted electrical noise.
Capacitors are commonly used for:
- Smoothing power supply fluctuations
- Filtering high-frequency noise
- Providing short bursts of energy when current demand suddenly increases
You will often find capacitors placed very close to integrated circuits. This placement helps stabilize power delivery and prevents voltage dips that could cause malfunction or data errors.
What Are Inductors and Coils Used for on a PCB?
Inductors store energy in a magnetic field and resist changes in current. On a circuit board, they are mainly used in power management and signal filtering applications.
Typical uses include:
- DC-DC converters and voltage regulators
- EMI suppression in power and signal lines
- Filtering noise in radio-frequency circuits
Inductors are especially important in designs where power efficiency and electromagnetic compatibility are critical, such as industrial controllers and communication equipment.
What Are Integrated Circuits (ICs) on a Circuit Board?
Integrated circuits, often called ICs or chips, are the most complex components on a circuit board. An IC can contain thousands or even millions of transistors inside a single package.
ICs perform functions such as:
- Processing data and executing software
- Managing power distribution
- Storing memory
- Handling communication protocols
The type of IC used determines much of the board’s functionality. Microcontrollers control system logic, memory chips store data, and power ICs regulate voltage and current. Because ICs are sensitive to heat and electrical stress, their placement and soldering quality are critical.

What Are Diodes, LEDs, and Transistors on a Circuit Board?
Diodes allow current to flow in only one direction. They are commonly used for protection, rectification, and voltage regulation. LEDs are a special type of diode that emits light and is often used for status indication.
Transistors act as electronic switches or amplifiers. They control large currents using small input signals and are fundamental to digital and analog circuits.
Together, these components enable:
- Signal switching and amplification
- Protection against reverse polarity
- Visual feedback through indicator lights
Although small, these parts often determine how safely and efficiently a circuit operates.
What Is the Bare Circuit Board Made Of?
The circuit board itself is made from layered materials designed to provide mechanical strength and electrical insulation. The most common base material is FR-4, a fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate.
A typical circuit board includes:
- Copper layers for electrical connections
- A solder mask to protect copper traces
- Silkscreen markings for component identification
Material selection affects heat resistance, signal integrity, and long-term reliability. High-performance applications may require specialized materials to handle higher temperatures or faster signal speeds.
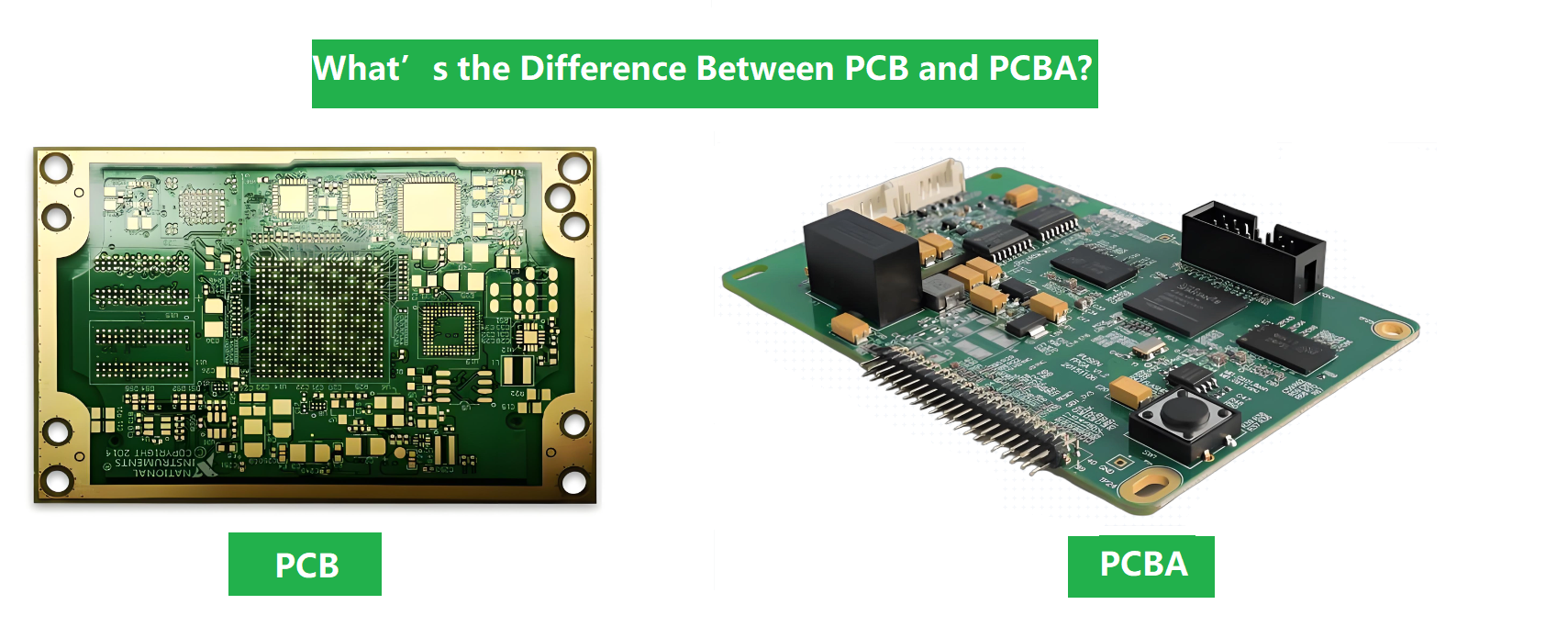
What’s the Difference Between PCB and PCBA?
A PCB refers to the bare board without components installed. PCBA describes a board after all components have been mounted and soldered.
This distinction is important because:
- A PCB is only a foundation
- A PCBA is a functional electronic assembly
Many people use these terms interchangeably, but in manufacturing and sourcing, the difference affects cost, lead time, and quality control requirements.
How Do All Circuit Board Components Work Together as a System?
A circuit board functions as a coordinated system rather than a collection of isolated parts. Power enters the board through connectors, flows through regulators and filters, and reaches active components in a controlled manner. Signals move along copper traces, passing through resistors, capacitors, and ICs to perform specific tasks.
Good circuit board design ensures:
- Stable power distribution
- Clean signal paths
- Effective heat dissipation
Poor design choices can lead to noise, overheating, or intermittent failures, even when high-quality components are used.
FAQs
1. What components are found on most circuit boards?
Most circuit boards include resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits, diodes, connectors, and the board substrate itself. The exact mix depends on the application.
2. Can you identify circuit board components by looking at them?
Many components can be visually identified by shape and markings, but precise identification often requires a schematic or part number reference.
3. What is the most important component on a circuit board?
There is no single most important component. The board functions as a system, and each part contributes to overall performance and reliability.
4. Are all circuit boards made of the same materials?
No. While FR-4 is common, specialized boards use materials designed for high temperatures, high frequencies, or harsh environments.
5. Why do some circuit boards have very few components?
Highly integrated ICs can replace many discrete parts, allowing compact designs with fewer visible components.
6. What’s the difference between through-hole and surface-mount components?
Through-hole components use leads inserted into holes, while surface-mount components are soldered directly onto the board surface. Surface-mount designs allow higher component density and automated assembly.


