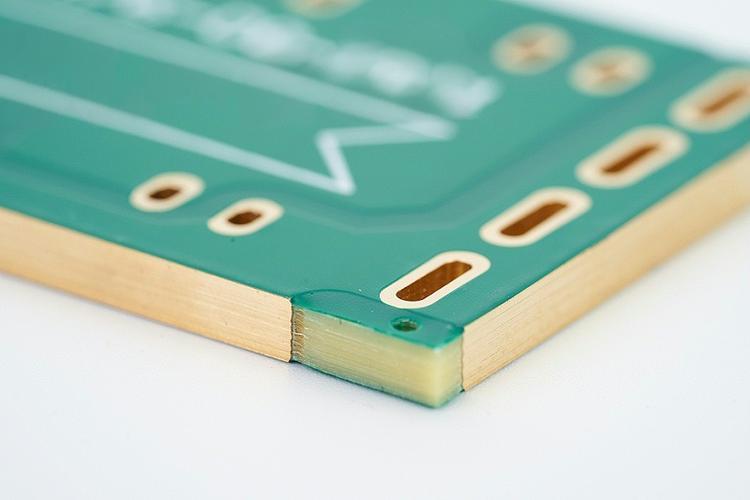
Copper PCB board is a type of circuit board where a thin layer of copper is bonded to an insulating base, usually made from fiberglass, resin, or other non-conductive materials.
What makes copper special is its exceptional electrical conductivity, which ensures fast, stable signal transmission and efficient power delivery. Whether it’s a single sided copper PCB board or a double sided copper clad laminate PCB circuit board, the copper layer is essential for performance, reliability, and heat control.
Available in different thicknesses and configurations, copper clad PCB boards can be tailored to meet the demands of everything from smartphones to medical devices.
Why is copper used in PCBs?
Copper is used in PCBs for one big reason—conductivity. It’s one of the best conductors of electricity. That means signals can move through the board fast, with low resistance. This ensures stable, efficient, and reliable performance in any circuit.
Another reason? Copper is durable. It handles high currents without overheating. It resists corrosion. And it can be etched into very fine lines for dense circuit layouts. Plus, copper is cost-effective. It offers high performance without sky-high prices.
In short, copper keeps signals fast, power stable, and costs low. That’s why it’s the standard across the electronics industry.
How thick is 2 oz of copper on a PCB?
This refers to how much copper is spread over a square foot of board.
2 oz copper thickness equals about 70 microns, or 0.07mm. That may sound thin, but it’s double the thickness of the standard 1 oz copper, which is 35 microns. And that extra thickness brings major benefits:
- Higher current-carrying capacity
- Better heat dissipation
- Stronger, more reliable circuits
Designers choose 2 oz copper when a circuit needs to handle more power or operate in tough environments. It adds strength without a huge increase in cost or size.
What type of copper is used in PCB?
The copper used in PCBs is not just any copper. It’s specifically engineered for electronics manufacturing. The two most common types are:
- Electrolytic Tough Pitch (ETP) Copper: This is the standard. It’s over 99% pure and offers great conductivity and flexibility.
- Rolled Annealed (RA) Copper: This type is used in flexible PCBs. It’s softer, more bendable, and less likely to crack under repeated movement.
For rigid boards, like your TV remote or thermostat, ETP is ideal. For flexible applications, like foldable phones or wearable devices, RA copper shines.
How to choose PCB copper thickness?
Picking the right copper PCB board thickness depends on your needs. Here are some guiding points:
- Current load: More current needs thicker copper. If your board handles power, go for 2 oz or more.
- Heat management: Thicker copper spreads heat better, reducing hotspots.
- Space constraints: If your design is tight, thinner copper can help save room.
- Cost and weight: More copper = more weight and higher cost.
The most common thickness is 1 oz, but 0.5 oz and 2 oz are also widely used. High-power boards may go up to 3 oz or more.
What is a copper clad PCB board?
Copper clad PCB board is a base material, Usually FR4 (fiberglass), CEM-1, or phenolic resin, that’s laminated with a thin layer of copper on one or both sides.
Types of copper clad boards include:
- Single sided copper clad board: copper on one side
- Double sided copper clad board: copper on both sides
- Multilayer boards: multiple layers of copper and insulation stacked together
These boards form the foundation of electronics. Without copper cladding, there’s no signal path, no connectivity, and no functionality.
Types of Copper Clad Boards
There are several variations, each tailored for different needs:
- Single sided copper PCB board: Great for simple, low-cost circuits. Common in calculators or basic toys.
- Double sided copper PCB board: Used in more complex electronics, offering better routing and signal flow.
- Copper clad laminate: This is the raw material, often sold in panels, ready to be etched. Also known as blank copper PCB board.
- Double sided copper clad laminate PCB circuit board: Offers flexibility in circuit design. Common in LED lighting and power supplies.
- Copper strip PCB board: Used for high-current circuits. Thick copper strips are embedded to carry heavy loads.
- Copper clad plate laminate PCB board: Known for high strength, used in industrial environments.
The choice depends on application, current needs, size, and cost.
What is a copper clad board used for?
Copper clad boards are used in every corner of the electronics world.
- Consumer electronics
- Industrial controls
- LED lighting
- Automotive dashboards
- Medical devices
- Communication systems
Their job? To carry signals, distribute power, and provide mechanical support. They’re also vital for EMI shielding, grounding, and signal integrity.
How to remove copper from PCB board?
There are moments in prototyping or repair when removing copper is necessary. Here are some common methods:
- Chemical etching: Ferric chloride or ammonium persulfate can dissolve copper. Be cautious, it’s toxic and requires proper ventilation.
- Mechanical removal: Sandpaper or a rotary tool can physically grind off copper.
- Laser removal: High-end labs use this for ultra-precise control.
Each method has pros and cons. For hobbyists, mechanical methods are safer. For professionals, chemical etching allows for mass removal with precision.
Copper plated PCB board vs copper coated: What’s the difference?
Copper plated PCB boards and copper coated PCB boards may sound similar, but they serve different purposes.
Copper plated PCB board means copper has been electroplated onto certain areas—like holes or edges. This helps with conductivity, especially in via holes and multi-layer connections.
Copper coated PCB board refers to a board where a base material is uniformly covered with copper foil. This is typically done during the lamination stage to form the initial circuit layer.
In short:
- Plated = targeted copper application, used for conductivity enhancement
- Coated = general copper layer across a surface, used to form the main circuit
Conclusion:
Copper PCB boards play a critical role in modern electronics, offering excellent conductivity, thermal performance, and reliability. Whether it’s a single sided copper clad board, double sided copper PCB board, or a blank copper PCB board, each type supports different circuit needs.
If you’re looking for high-quality copper clad PCB boards, reliable support, or expert advice, we’re here to help.
Need help choosing the right copper PCB board? Reach out today at sales@bestpcbs.com
Tags: copper clad pcb board, copper pcb board, copper plated pcb board, double sided copper pcb board, pcb board copper thickness