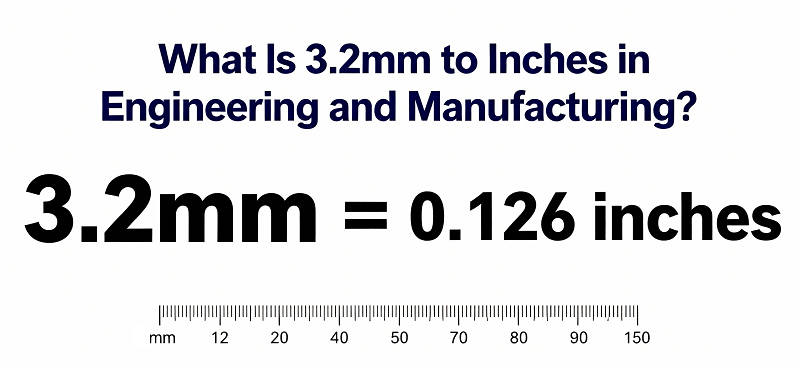
3.2mm to inches equals 0.12598 inches, commonly rounded to 0.126 inches.
lthough 3.2mm is often associated with 1/8 inch, it is slightly larger than 1/8″ (which equals 3.175mm). For general PCB fabrication, hardware selection, and sheet material, treating 3.2mm as â 1/8 inch is acceptable. For tight-tolerance or mating components, always use the exact value: 0.12598 inches.
This conversion is frequently referenced in PCB thickness control, mechanical part matching, and cross-standard manufacturing, especially when metric-designed components are produced or assembled in imperial-based environments.
Engineering Method for Converting 3.2mm to Inches
All engineering-grade conversions rely on a fixed constant.
1 inch = 25.4 millimeters (exact, not approximate)
To convert millimeters to inches:
3.2 ÷ 25.4 = 0.12598 inches
In CAD systems, CAM outputs, and inspection reports, engineers usually keep four to five decimal places to prevent cumulative dimensional deviation. Rounding is applied only at the documentation or purchasing stage.
Why 3.2mm Is Widely Used in PCB and Mechanical Manufacturing?
3.2mm is considered a hybrid-standard thickness. It bridges metric design logic with imperial production habits.
In PCB manufacturing, 3.2mm is commonly selected for:
- Power distribution boards
- Backplanes and structural PCBs
- Boards used as mounting or support elements
- Industrial controller PCBs requiring stiffness
In mechanical manufacturing, 3.2mm sheet thickness is frequently used for:
- Aluminum and steel brackets
- Equipment enclosures
- Protective covers and panels
This thickness offers good rigidity while remaining compatible with standard drilling, routing, and bending processes.
3.2mm to Inches Chart ((Fractional & Decimal)
The table below shows 3.2mm to inches alongside nearby metric sizes, including fractional inch equivalents commonly used in hardware, PCB thickness, and metal stock selection.
| Millimeters (mm) | Fractional Inches | Decimal Inches |
| 2.0 mm | 5/64″ | 0.0787″ |
| 2.4 mm | 3/32″ | 0.0937″ |
| 3.2 mm | â 1/8″ | 0.12598″ (â 0.126″) |
| 3.5 mm | 9/64″ | 0.1378″ |
| 4.0 mm | 5/32″ | 0.1575″ |
| 4.8 mm | 3/16″ | 0.1890″ |
| 6.4 mm | 1/4″ | 0.2520″ |
Engineering note:
1/8 inch equals 3.175mm, not 3.2mm. The 0.025mm difference may matter in precision machining, PCB slot sizing, or press-fit applications.
Why 3.2mm Is Commonly Treated as 1/8 Inch?
In practice, 3.2mm is widely treated as a nominal 1/8-inch equivalent because:
- The dimensional difference is very small
- Standard drill bits and tooling align closely
- PCB thickness tolerances usually exceed ±0.025mm
- Hardware and sheet stock are often sold by nominal size
This is why datasheets, BOMs, and supplier listings frequently group 3.2mm and 1/8 inch together.
3.2mm to cm in Technical Documentation
3.2mm equals 0.32 cm.
This conversion is exact and does not involve rounding. It is often used in:
- Engineering specifications
- International standards
- Educational and training materials
Centimeter notation is common in documentation intended for non-manufacturing audiences.
3.2mm to Feet in Industrial Context
3.2mm equals 0.0105 feet.
While feet are rarely used for small dimensions, this conversion may appear in:
- Mixed-unit architectural layouts
- Legacy documentation
- Facility-level mechanical references
For fabrication work, inches or millimeters remain preferred.
Is 3.2mm the Same as 1/8 Inch in PCB and Mechanical Design?
No. 1/8 inch equals 3.175mm, not 3.2mm.
The difference is 0.025mm, which may seem negligible but can impact:
- PCB edge connector fit
- Slot and cutout tolerances
- Press-fit components
- Stack-up alignment in assemblies
In high-reliability PCB designs, this difference must be evaluated rather than assumed acceptable.
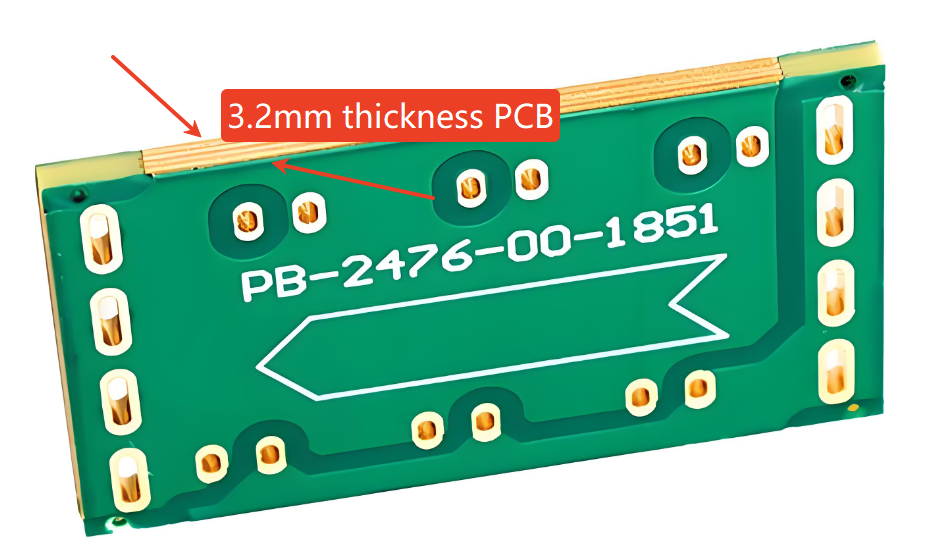
Practical PCB Applications of 3.2mm Thickness
In PCB fabrication, 3.2mm thickness is often chosen when mechanical strength is more important than weight reduction.
Typical PCB use cases include:
- High-current power boards
- Backplanes in industrial systems
- PCBs acting as mechanical supports
- Boards exposed to vibration or shock
Thicker boards reduce flexing, which helps protect solder joints and large components.
Manufacturing Implications of 3.2mm Thickness
From a production perspective, 3.2mm thickness affects multiple processes:
- Drilling requires adjusted feed rates
- Routing needs deeper cut passes
- Plating thickness becomes more critical
- Panel warpage control becomes more important
Manufacturers often adjust tooling and process parameters specifically for boards or parts at this thickness.

Metric vs Imperial Units in Global PCB Manufacturing
Most PCB designs originate in metric units. However, many:
- Assembly fixtures
- Test equipment
- Mechanical interfaces
still follow imperial standards.
This creates frequent conversion scenarios where 3.2mm to inches must be clearly defined to avoid misinterpretation between design, fabrication, and assembly teams.
Common Engineering Errors When Converting 3.2mm to Inches
Errors often occur when:
- Designers assume 3.2mm equals 1/8 inch
- Finished thickness is confused with core thickness
- Copper weight and surface finish are ignored
- Units are converted without tolerance context
These mistakes can lead to fit issues, assembly delays, or rejected parts.
FAQs About 3.2mm to Inches
1. How many inches is 3.2mm?
3.2mm equals 0.12598 inches, which is commonly rounded to 0.126 inches for practical use. This value is widely accepted in engineering, PCB manufacturing, and hardware selection.
2. Is 3.2mm the same as 1/8 inch?
No. 3.2mm is slightly larger than 1/8 inch.
1/8 inch equals 3.175mm, while 3.2mm equals 0.12598 inches. The difference is small but can matter in precision applications.
3. Why is 3.2mm often called 1/8 inch?
3.2mm is often treated as 1/8 inch because the dimensional difference is minimal and usually falls within standard manufacturing tolerances. Many suppliers group these sizes together for convenience.
4. Is 3.2mm a standard PCB thickness?
Yes. 3.2mm is a common PCB thickness, especially for power boards, backplanes, and mechanically reinforced PCBs. It provides higher rigidity compared to thinner boards.
5. Can 3.2mm replace 1/8 inch material?
In most cases, yes.
For sheet metal, PCB panels, and brackets, 3.2mm can replace 1/8 inch. Always verify tolerance requirements for mating or press-fit parts.
6. What is the formula to convert 3.2mm to inches?
The formula is:
Inches = millimeters ÷ 25.4
3.2 ÷ 25.4 = 0.12598 inches
7. Does PCB copper thickness affect the final 3.2mm board thickness?
Yes. The finished PCB thickness includes laminate, copper layers, and surface finish. Copper weight and plating can slightly increase the final thickness beyond the nominal 3.2mm.
Tags: 3.2mm to cm, 3.2mm to Feet, 3.2mm to Inches, 3.2mm to Inches Chart


