BNC PCB refers to the integration of BNC (Bayonet Neill‚ÄďConcelman) connectors directly onto printed circuit boards, providing a robust interface for RF (radio frequency) signals in applications ranging from test equipment to communication devices. This article explores the types, selection criteria, layout practices, and performance considerations for implementing BNC connectors on PCBs, with a focus on achieving reliable high-frequency connectivity.
Are you struggling with signal loss, impedance mismatches, or mechanical instability in your RF designs? Many engineers face recurring challenges when integrating coaxial interfaces like BNC connectors onto PCBs. Common frustrations include:
- Poor impedance continuity leading to signal reflections and degraded performance.
- Mechanical strain causing connector loosening or PCB pad damage.
- Inadequate grounding strategies that increase electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Difficulty selecting the right connector type (vertical, right-angle, or edge-mount) for spatial and electrical needs.
- Time-consuming prototyping cycles due to footprint or layout errors.
These issues can be systematically addressed with thoughtful design and manufacturing support. Here’s how a specialized PCB provider can help:
- Impedance-controlled routing ensures minimal signal distortion from connector to trace.
- Robust anchoring features (like through-hole pins or metal brackets) enhance mechanical stability.
- Optimized ground plane design and via fencing reduce EMI and crosstalk.
- Expert guidance on connector selection based on frequency, space, and mounting orientation.
- Rapid prototyping services with validated footprints to accelerate development.
At BEST Technology, we specialize in high-frequency PCB solutions, including precision-engineered BNC interconnects. Our team supports your design with impedance-matching expertise, durable board materials, and fast turnaround for prototypes and production. A warm welcome to contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com to discuss your project requirements.
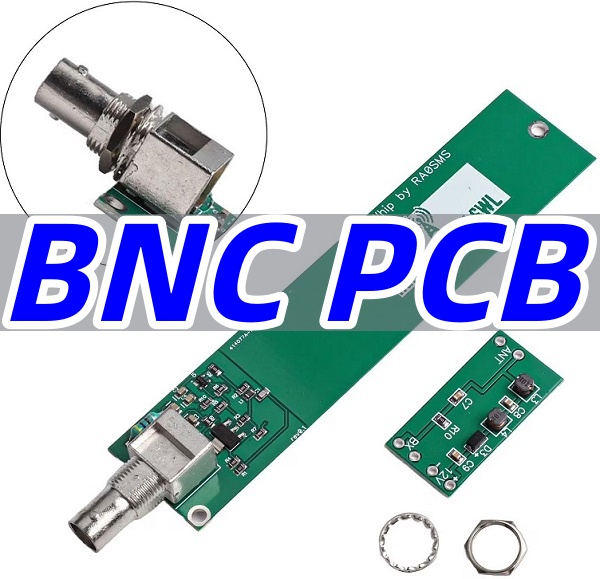
What is a BNC PCB?‚Äč
A BNC PCB incorporates a BNC connector‚ÄĒtypically a BNC PCB connector‚ÄĒdirectly mounted to the board, serving as a coaxial interface for RF signals. These connectors use a bayonet coupling mechanism for quick, secure connections and are designed to maintain a 50-ohm or 75-ohm characteristic impedance.
- Signal Support:
The BNC PCB connector preserves signal integrity by providing a shielded path from the cable to the PCB traces.
Its coaxial structure minimizes EMI, while the board layout ensures impedance continuity between the connector’s center conductor and the microstrip or stripline transmission line. - Applications:
Commonly used in video equipment, RF test instruments, and data communication systems where frequent connection cycles and RF performance are critical.
In summary, a BNC PCB enables efficient RF signal transition between external cables and internal circuitry, with careful attention to impedance matching and shielding.
‚ÄčWhat Types of BNC Connector PCB Mount Options Are Most Common in RF Boards?
Engineers can choose from several mounting styles, each suited to different mechanical and spatial constraints.
- Vertical Mount (BNC PCB mount):
The connector stands perpendicular to the board, ideal for applications where space is limited in the horizontal plane. - Right-Angle Mount (BNC connector PCB mount right angle):
The connector body parallels the board, saving vertical height‚ÄĒuseful for compact modules or stacked assemblies. - Edge Mount (BNC edge mount PCB):
Installed on the board’s edge, often used when the connector must align with an enclosure panel. - Surface-Mount or Through-Hole:
Through-hole versions offer stronger mechanical retention, while surface-mount types suit automated assembly.
The BNC connector PCB mount style is selected based on layout density, cable orientation, and shielding requirements.
How Do You Choose the Right BNC Female PCB Mount Connector for Your Design?‚Äč
Selecting the appropriate BNC female PCB mount connector involves evaluating electrical, mechanical, and environmental factors.
- Impedance: Ensure the connector matches the system impedance (e.g., 50 ohms for most RF applications).
- Frequency Range: Standard BNC connectors perform up to 4 GHz; verify the model’s rated frequency.
- Mounting Style: Choose vertical, right-angle (BNC female right angle solder PCB mount connector), or edge-mount based on space and cable routing.
- Termination Type: Soldering (through-hole or surface-mount) vs. crimping; through-hole provides better strain relief.
- Material and Plating: Brass with gold or nickel plating ensures corrosion resistance and stable conductivity. A well-chosen BNC female PCB connector minimizes VSWR (voltage standing wave ratio) and withstands mating cycles.
What Layout Rules Matter Most When Creating a Reliable BNC Connector PCB Footprint?‚Äč
The BNC connector PCB footprint must maintain impedance integrity and mechanical stability. Key rules include:
- Impedance Matching: Design the pad pattern and adjacent ground structures to match the connector’s characteristic impedance (e.g., 50 ohms).
- Grounding: Place grounding vias near the connector’s shield pins to create a low-inductance path to the ground plane.
- Pad Size and Shape: Follow the manufacturer’s datasheet to avoid tombstoning or solder voids.
- Keep-Out Zones: Avoid placing components or traces under the connector body to prevent short circuits.
- Strain Relief: Include metal anchors or epoxy trenches for high-vibration environments. A precise BNC PCB footprint is critical for signal fidelity and long-term reliability.
When Should Engineers Use a BNC Right Angle PCB Mount Instead of a Vertical One?‚Äč
A BNC right angle PCB mount is preferred when:
- Vertical Space is Limited:
Such as in slimline instruments or stacked PCBs. - Cable Routing Constraints:
The cable must exit parallel to the board to avoid sharp bends. - Panel-Mount Alignment:
The connector interfaces with a side-panel port. In contrast, a vertical BNC PCB mount is better when cables connect from above, as in rack-mounted equipment.
The right-angle version (90 degree BNC PCB mount) reduces mechanical leverage on the PCB, lowering the risk of pad lifting.
How Does an Ultra-Tiny BNC Jack PCB Help in Compact RF Modules?‚Äč
An ultra-tiny bnc jack pcb(e.g., sub-miniature versions) saves space without sacrificing performance. Benefits include:
- High Density: Enables more connectors per board area in portable devices.
- Lightweight Design: Critical for aerospace or handheld instruments.
- Preserved Performance: Maintains impedance control and shielding despite smaller dimensions. These jacks are ideal for high-density RF systems like multi-channel data acquisition boards.
What Routing Practices Improve Performance When Working With a 90 Degree BNC PCB Mount?‚Äč
For a 90 degree BNC PCB mount, follow these routing guidelines:
- Impedance Continuity: Use controlled-impedance traces from the connector pin to the IC, avoiding abrupt width changes.
- Minimal Stub Length: Keep the transition from the connector pad to the main trace as short as possible.
- Ground Plane Integrity: Ensure an unbroken ground plane beneath the trace; add grounding vias near the connector.
- Avoid Sharp Bends: Use curved or 45-degree trace bends to reduce reflections. Proper routing ensures that the BNC right angle PCB maintains low VSWR and insertion loss.
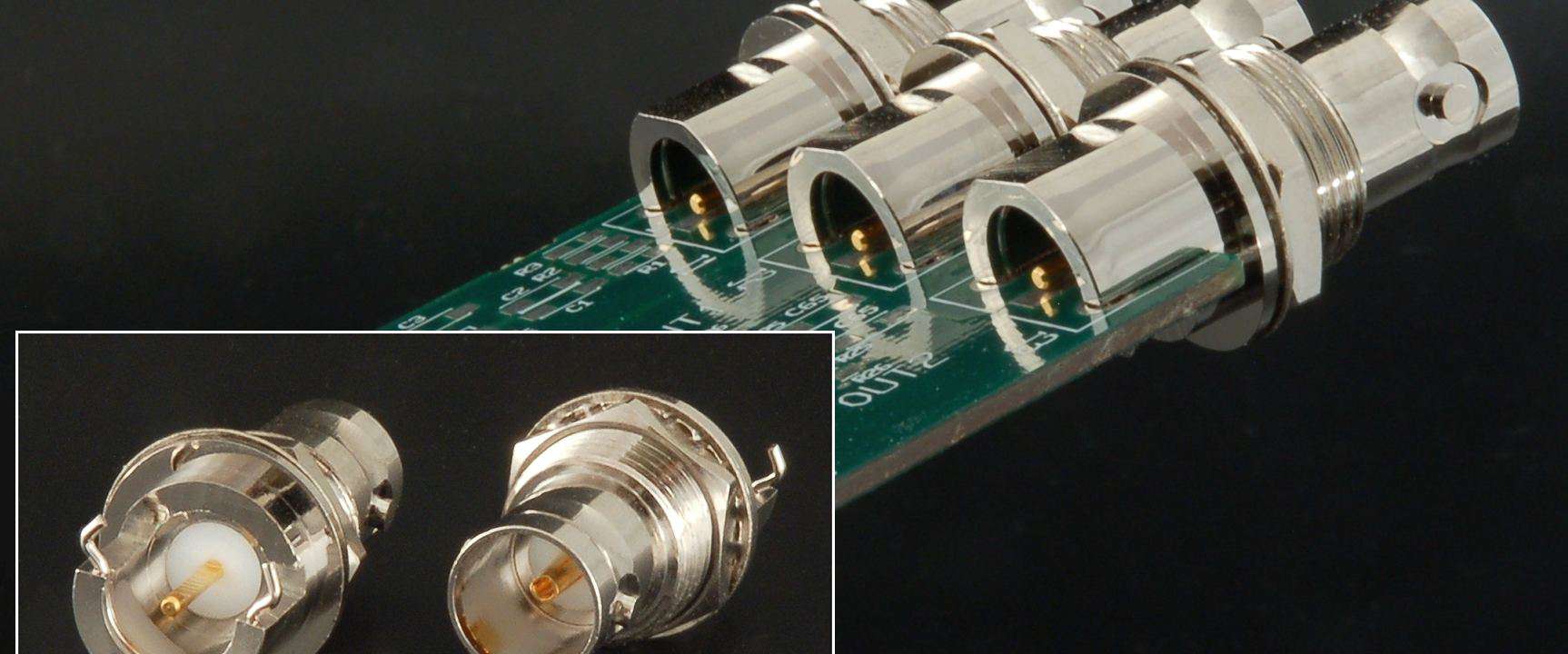

Why Do RF Teams Rely on EBest Circuit (Best Technology) for BNC Prototype PCB Production?‚Äč
RF teams choose EBest Circuit (Best Technology) for BNC prototype PCB manufacturing due to:
- Impedance Expertise: We control dielectric thickness and trace geometry to achieve precise impedance matching.
- High-Frequency Materials: Expertise with Rogers, Taconic, or FR-4 hybrids for optimal RF performance.
- Rapid Prototyping: Quick-turn services with validated designs to accelerate testing.
- Quality Assurance: Rigorous testing for VSWR, insertion loss, and mechanical stability. Our capability to produce reliable BNC prototype PCB assemblies reduces iteration cycles and ensures performance compliance.
In a nutshell, BNC PCB solutions enable precise RF connectivity by integrating robust coaxial interfaces directly onto circuit boards. This guide has detailed connector selection, layout techniques, and routing practices to ensure signal integrity in high-frequency designs. At BEST Technology, we combine engineering support with advanced manufacturing to deliver reliable BNC PCBs for prototyping and production. Pls feel free to reach out to us at sales@bestpcbs.com for your next RF PCB project.
FAQs about BNC PCB‚Äč
Is BNC better than SMA?‚Äč
- BNC offers quick bayonet coupling for frequent connections but is typically rated to 4 GHz. SMA uses a threaded interface for higher frequencies (up to 18 GHz) and better EMI shielding. Choose BNC for ease of use in lower-frequency applications.
Is BNC better than Ethernet?‚Äč
- BNC is designed for RF signals (e.g., video, radio), while Ethernet (RJ45) carries digital data. They serve different purposes; BNC provides superior impedance control for analog RF.
Is BNC the same as RF?‚Äč
- BNC is a type of RF connector. “RF” is a broad term for radio frequency signals, while BNC refers to a specific connector family commonly used for RF interconnects.
How to crimp a BNC?‚Äč
- Strip the coaxial cable to expose the center conductor and shield. Insert the center conductor into the connector pin and crimp. Slide the shield braid over the body, and crimp the outer sleeve. Use a BNC crimping tool for consistent results.
Tags: BNC connector PCB, bnc connector pcb footprint, bnc connector pcb mount, BNC PCB, bnc prototype pcb


