Want to master PCB SMT assembly from basics to advanced solutions? This guide covers everything includes definition, benefits, supplier selection, process optimization, DFM principles, signal integrity fixes, and cost-reliability balance to streamline your electronics manufacturing
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) stands out as your premier SMT PCB assembly and PCBA supplier by delivering unmatched speed and reliability. We specialize in 24-hour rapid turnaround for urgent orders, ensuring your projects stay on schedule without compromise. Our advanced automated SMT production lines guarantee precision and efficiency, while our robust electronic supply chain system eliminates material delays, keeping your production flowing smoothly. With a commitment to rapid response and seamless communication, we help you shorten time-to-market and stay ahead of competitors. Whether it’s prototyping or high-volume production, our expertise in DFM principles ensures flawless execution from design to delivery. Trust EBest Circuit (Best Technology) to handle your most demanding PCB assembly needs with speed, quality, and cost-efficiency. Need a reliable partner for fast, high-quality SMT PCB assembly? Contact us today for a competitive quote and experience the EBest Circuit (Best Technology) advantage: sales@bestpcbs.com.
What Is PCB SMT Assembly?
PCB SMT assembly is the modern method of attaching electronic components directly onto printed circuit boards using automated machinery. During this process, tiny surface-mount devices like resistors and chips are precisely placed and soldered onto designated pads without drilling holes. This streamlined technique allows smaller, faster, and more reliable electronics production than traditional methods. Manufacturers rely on PCB SMT assembly for everyday devices like smartphones and smartwatches, where compact design and high-speed manufacturing matter. Effective PCB SMT assembly ensures components stay securely connected even in demanding conditions like automotive systems or medical equipment.

What Are Benefits of PCB SMT Assembly?
Benefits of PCB SMT Assembly:
- Faster Production, Quicker Time-to-Market: Automated machines place components in seconds, slashing production time. You’ll launch products faster, beat deadlines, and save on labor costs.
- Smaller Gadgets, Bigger Possibilities: Tiny surface-mount parts free up space. Ideal for compact devices like smartwatches or medical sensors—no bulk, no compromises.
- Lower Costs at High Volumes: Fewer errors and less material waste mean cheaper per-unit costs. Scale up without blowing your budget.
- Tougher Products, Fewer Returns: Components soldered directly to the board resist shocks and heat. Your devices last longer, reducing customer complaints.
- Adapt Fast to Market Changes: Tweaking designs? SMT lines adjust quickly. Test ideas, fix flaws, and pivot without lengthy delays.
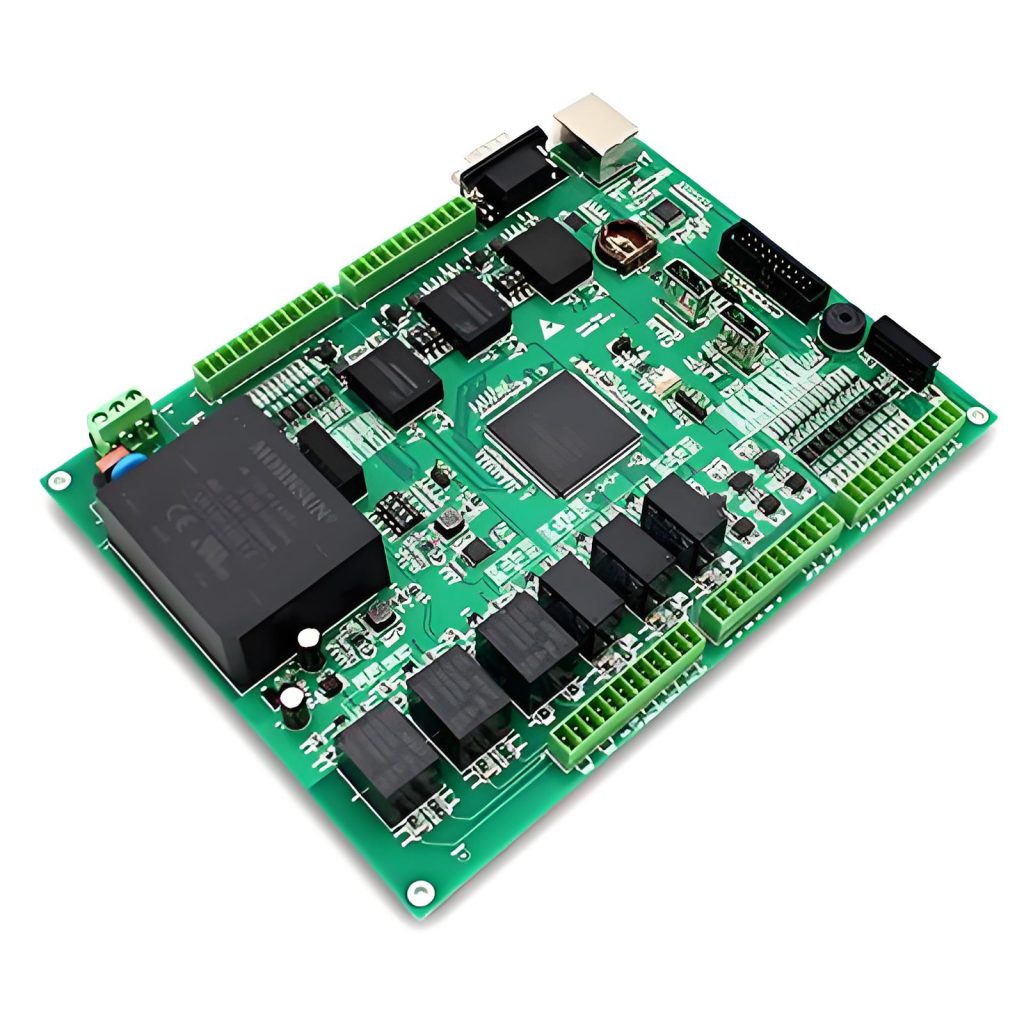

What Is the Purpose of PCB SMT Assembly?
- Makes Devices Smaller and Lighter – PCB SMT assembly mounts parts directly onto the board’s surface, eliminating bulky wires and holes. This lets designers create slimmer gadgets like fitness trackers and drones without sacrificing performance.
- Boosts Production Efficiency – Automated machines in PCB SMT assembly place hundreds of tiny components in minutes, cutting labor costs and assembly time. For businesses, this means faster product launches and lower manufacturing expenses.
- Improves Reliability – Soldering entire component bases creates stronger bonds than traditional methods. Whether it’s a medical device or a gaming console, PCB SMT assembly ensures stable connections that last through daily wear and tear.
- Supports High-Tech Features – Modern electronics need densely packed circuits for advanced functions like 5G or AI. PCB SMT assembly handles ultra-small chips and high-speed signals, enabling cutting-edge tech in everyday products.
How to Choose A Reliable SMT PCB Assembly Supplier?
Below are tips about how to choose a reliable SMT PCB assembly supplier:
- Prioritize Certifications: Select suppliers with ISO 9001 or IPC-A-610 certifications. These standards ensure their SMT PCB assembly processes meet global quality benchmarks, directly reducing defects in your final products.
- Inspect Equipment Capabilities: Ask about the age and accuracy of their SMT machines. Modern lines handle tiny components (e.g., 0201 chips) and complex packages (BGA) with precision, ensuring your designs are built correctly.
- Demand Rigorous Testing: Reliable suppliers use AOI, X-ray, and functional tests at every stage. This catches solder bridges or misalignments early, saving rework costs and preventing customer complaints.
- Confirm Turnaround Flexibility: Choose partners who adjust schedules for urgent orders and deliver prototypes fast. Clear lead-time guarantees ensure your projects stay on track, even during peak seasons.
- Require Transparent Communication: Work with suppliers who share DFM feedback and respond within 24 hours. Proactive updates prevent costly errors and keep your team aligned.
- Validate References: Request case studies from clients in your industry. Experience with automotive or medical standards ensures compliance with sector-specific rules like traceability.
- Negotiate Clear Contracts: Ensure contracts cover defect liability, IP protection, and pricing breakdowns. Avoid vague terms—get itemized quotes for NRE fees, components, and assembly to prevent surprises.
How to Optimize the Process of SMT PCB Assembly?
- Streamline Equipment Setup: Regularly maintain and calibrate SMT PCB assembly machines to prevent errors. Use quick-change tooling to reduce downtime between jobs. Well-tuned equipment ensures faster transitions and fewer production stops.
- Master Material Flow: Organize components and stencils near the line to minimize delays. Partner with reliable suppliers to avoid shortages. Smooth material handling keeps SMT PCB assembly running without interruptions.
- Fine-Tune Solder Pasting: Test solder paste deposits frequently to avoid bridges or insufficient joints. Adjust stencil thickness and printer settings based on environmental conditions like humidity. Consistent pasting lays the groundwork for flawless PCB SMT assembly.
- Upgrade Inspection Tech: Invest in 3D AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) and X-ray systems to catch defects early. Real-time feedback loops help operators fix issues instantly, saving hours of rework later.
- Train Teams Skillfully: Run regular workshops on handling tiny components, programming machines, and interpreting inspection data. Skilled workers troubleshoot faster, keeping SMT PCB assembly lines efficient.
- Redesign Layouts for Efficiency: Arrange machines in a logical sequence to reduce board movement. Group similar jobs to minimize setup changes. A smart layout trims wasted steps and accelerates throughput.
- Analyze Data Relentlessly: Track metrics like first-pass yield, cycle time, and equipment OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness). Use MES (Manufacturing Execution System) software to spot bottlenecks and prioritize improvements.
- Embrace Lean Principles: Eliminate non-value-added steps, like excess paperwork or redundant approvals. Apply 5S (Sort, Set, Shine, Standardize, Sustain) to keep workspaces tidy and organized. Lean practices make SMT PCB assembly leaner too.
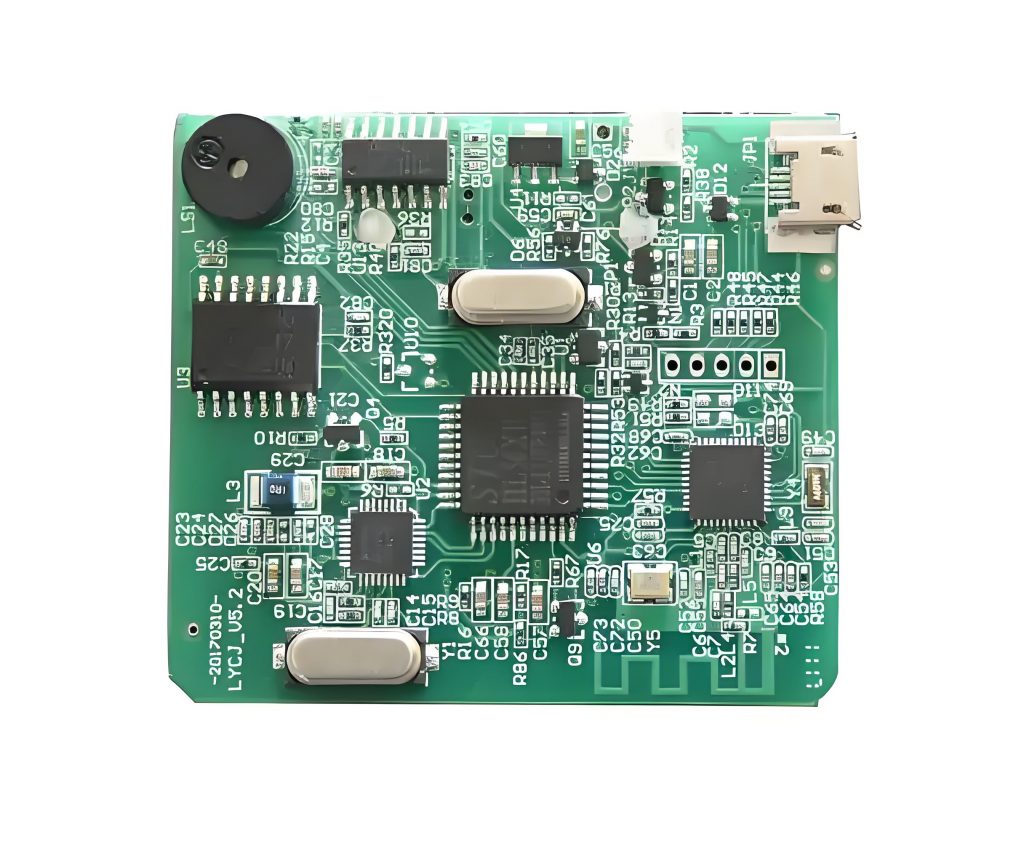

How to Avoid SMT PCB Assembly Problems Through DFM Principles?
- Choose Standard Component Sizes: Select widely used packages like 0402 resistors or QFN chips. Non-standard or overly tiny parts complicate SMT PCB assembly, increasing placement errors and rework costs.
- Optimize Component Spacing: Leave at least 0.2mm between pads and 0.5mm between tall components. Ample spacing prevents solder bridges during SMT PCB assembly and simplifies inspection.
- Design Clear Solder Masks: Define solder paste areas precisely to avoid excess or insufficient solder. Well-defined masks reduce defects like tombstoning (components standing upright) in SMT PCB assembly.
- Add Fiducial Markers: Place three fiducials on the board to guide machines during alignment. This ensures accurate component placement, especially for fine-pitch parts.
- Label Polarity and Orientation: Use bold silkscreen labels for diodes, ICs, and polarized capacitors. Clear markings help operators place parts correctly, avoiding costly assembly mistakes.
- Avoid High-Density Layouts: Spread large connectors or heat-sensitive parts away from dense component clusters. This prevents heat damage during soldering and simplifies repairs.
- Use Through-Hole for Heavy Components: Secure connectors or heatsinks with through-hole pins. SMT-only designs risk parts falling off during vibration or thermal cycling.
- Test Early with Prototypes: Build a small batch first to identify issues like component lifting or solder voids. Early testing saves money compared to mass production failures.
- Collaborate with Assemblers Early: Share Gerber files and 3D models with your SMT PCB assembly partner before finalizing designs. Their feedback can catch issues like incompatible part footprints.
How to Solve Signal Integrity Issues of SMT PCB Assembly?
- Use Low-Parasitic Components: Select SMT parts like 0201 capacitors or low-ESL inductors to minimize inductance and capacitance. Smaller packages reduce signal distortion during SMT PCB assembly.
- Control Trace Impedance: Design PCB traces for 50Ω or 75Ω impedance (matching your driver/receiver specs). Use controlled-dielectric materials and consistent widths to prevent signal reflections.
- Shrink Signal Loops: Route high-speed traces (e.g., HDMI, USB 3.0) near their return paths (ground planes). Smaller loops cut electromagnetic interference (EMI) and crosstalk.
- Separate Noisy and Sensitive Traces: Keep analog/digital sections and power traces away from high-speed lines. Add guard traces or grounded copper to shield vulnerable signals from EMI.
- Route Differential Pairs Correctly: Match trace lengths and keep differential pairs (e.g., PCIe, Ethernet) tightly coupled. This rejects noise and balances signals for reliable SMT PCB assembly.
- Avoid Sharp Trace Bends: Use 45° angles or arcs instead of 90° bends. Sharp angles create impedance changes that degrade signal quality.
- Limit Vias on High-Speed Traces: Fewer vias mean less signal reflection. Use blind/buried vias or backdrilling to reduce stub lengths above 5GHz.
- Strengthen Power Delivery: Place decoupling capacitors (0.1µF to 10µF) near power pins and use thick copper planes. Stable power prevents voltage drops that corrupt signals.
- Simulate Early: Run SI/PI tools (e.g., HyperLynx) to spot issues like ringing. Fix problems before SMT PCB assembly to avoid costly rework.
- Validate with Oscilloscopes: Test post-assembly boards with oscilloscopes and TDR. Catch impedance mismatches or crosstalk early—before mass production.
How to Balance Cost and Long Reliability of SMT PCB Assembly?
- Use Durable, Affordable Materials: Select FR-4 laminates with 1oz copper for most projects. Reserve high-TG or halogen-free boards for extreme environments. This cuts material costs without risking SMT PCB assembly failures.
- Simplify Designs with Common Parts: Stick to 0603 resistors, SOIC chips, and other standard components. Avoid custom or tiny packages to minimize assembly errors in SMT PCB assembly.
- Apply DFM Rules Upfront: Adjust pad sizes, spacing, and component placement to match your assembler’s equipment. Proactive DFM tweaks prevent costly rework during SMT PCB assembly.
- Automate High-Volume Runs: Use pick-and-place machines and stencil printers for large batches. Automation lowers labor costs and boosts consistency, even if setup fees rise.
- Test Smartly, Not Exhaustively: Run AOI on high-risk areas like BGA joints instead of inspecting every trace. Targeted testing reduces costs while catching critical defects.
- Buy Components in Bulk: Purchase resistors, capacitors, and LEDs from trusted distributors. For ICs, let your SMT PCB assembly partner leverage their volume discounts.
- Skip Unnecessary Upgrades: Use HASL finishes instead of gold plating unless dealing with harsh chemicals. Cheaper surface finishes work for most consumer products.
- Stress-Test Prototypes: Build 5–10 boards and test them under vibration, heat, and cold. Fixing issues early avoids expensive recalls later.
- Choose Certified Assemblers: Partner with ISO 9001 or IPC-A-610-certified shops. Their proven processes reduce defects, saving money on rework and warranties.
- Design for Part Longevity: Pick components with 5+ years of availability. Avoid niche parts to prevent costly redesigns when suppliers discontinue items.
Conclusion
PCB SMT Assembly drives faster, cheaper, and smarter electronics manufacturing. From streamlining designs with DFM rules to solving signal integrity and reliability challenges, mastering SMT PCB Assembly processes ensures flawless products. Partner with EBest Circuit (Best Technology), your expert SMT PCB Assembly supplier, for rapid prototyping, optimized production, and bulletproof quality. Cut costs, accelerate timelines, and dominate markets with boards built to last. Contact us today and turn your PCB projects into winners.
Tags: PCB SMT Assembly


