PCB barcode‚Äč is a machine-readable identifier permanently marked on a bare circuit board. This guide delves into everything from the fundamentals of PCB barcode labels‚Äč to advanced system integration for full traceability.
Without a structured PCB barcode system, manufacturers face hidden risks that directly impact quality, efficiency, and cost.
- No Traceability: Failed boards cannot be reliably linked to PCB lots, materials, or processes.
- Human Errors: Manual serial number entry causes data inaccuracies and quality record gaps.
- MES Disconnection: Board IDs exist but are not tied to MES or production data.
- Slow Identification: Manual checks delay assembly, testing, and inspection steps.
- Higher Recall Costs: Lack of lot-level data forces wide, expensive recalls.
How a Professional PCB Manufacturer Solves These Challenges?
- End-to-End Tracking: Permanent barcode laser marking links each board to its full history.
- Error-Free Data Capture: Machine-readable codes eliminate manual input mistakes.
- MES-Ready Barcodes: Formats align with MES and ERP systems for seamless data flow.
- Faster Production: Automated scanning accelerates SMT, testing, and programming.
- Lower Quality Risk: Precise traceability limits recalls and reduces quality-related costs.
A professional PCB manufacturer embeds PCB barcode capabilities directly into fabrication and production workflows to enable reliable, end-to-end traceability. EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is a professional PCB and PCBA manufacturer‚Äč specializing in advanced identification and traceability solutions. We provide a full range of PCB solutions, including FR4 PCBs, flexible and rigid-flex circuits, metal core and ceramic PCBs, along with PCB layout, PCBA and complete box-build services. For traceable, reliable circuit boards, pls feel free to contact us at sales@bestpcbs.com.
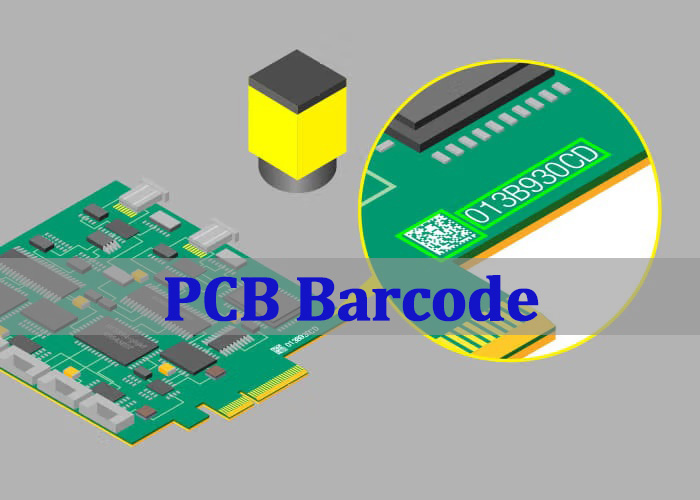
What Is a PCB Barcode?
A PCB barcode‚Äč is a unique, machine-readable data carrier that is directly marked on the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). It serves as the board’s permanent “digital license plate,” enabling automated identification and data collection throughout its lifecycle‚ÄĒfrom fabrication and component assembly (PCBA) to field service.
Core Functions of a PCB Barcode:
- Unique Identification:‚Äč Distinguishes one board from millions of others.
- Data Carrier:‚Äč Stores essential information in a compact format.
- Automation Enabler:‚Äč Allows machines like a barcode scanner PCB‚Äč reader to instantly identify the board.
- Traceability Anchor:‚Äč Links the physical board to its digital record in databases.
In essence, it is the foundational element for Advanced PCB Barcode Integration for Traceable PCB and PCBA, turning a passive component into a smart, trackable asset.
What Information Is Stored in a PCB Barcode?
The barcode itself typically contains a unique identifier, like a serial number. This key is then used to access a comprehensive digital record stored in a database (e.g., MES, ERP). The linked data can include:
| Data Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Manufacturing Data‚Äč | Lot number, fabricator ID, fabrication date, panel ID. |
| Design & Part Data‚Äč | Part number, revision, Gerber version, OEM data. |
| Material Data‚Äč | Laminate batch, solder mask type, copper foil lot. |
| Process Data‚Äč | Test results, inspection history, certifications (UL, ISO). |
| Supply Chain Data‚Äč | Supplier info, PO number, delivery batch. |
In summary, the barcode on PCB‚Äč is a compact key that unlocks a vast, detailed history of the board, which is crucial for quality control and traceability.
What Is the Difference: PCB Barcode vs Serial Number vs QR Code
This comparison highlights how common identifiers on PCB boards differ in purpose, data capacity, and traceability value.
Quick Comparison of PCB Identification Methods
| Feature | PCB Serial Number | Linear (1D) Barcode | QR Code / PCB 2D Barcode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Format | Human-readable text | Parallel lines (1D) | Square matrix (2D) |
| Data Capacity | Low | Low‚ÄďModerate | High |
| Read Method | Visual / manual | Scanner | Scanner / vision |
| Space Required | Moderate | Long, linear | Compact |
| Durability | Human-dependent | Sensitive to damage | High error correction |
| Traceability Use | Reference only | ID automation | Full traceability |
To conclude, a PCB serial number is intended for human reference, a linear PCB barcode automates reading that identifier, while a PCB QR code or PCB 2D barcode supports high-density data storage and is the preferred choice for modern PCB and PCBA traceability systems.
What Is the Difference: PCB 2D Barcode vs Linear Barcode on PCB Boards
Choosing the right mark impacts your traceability system’s effectiveness.
- Linear Barcode (e.g., Code 128, Codabar):
- Structure:‚Äč Encodes data in the varying widths of parallel lines and spaces.
- Data:‚Äč Can only store a string of numbers/letters (an ID).
- Scanning:‚Äč Requires precise alignment with a laser scanner.
- Space:‚Äč Needs a relatively long, rectangular space.
- Durability:‚Äč A single damaged line can render it unreadable.
- A Codabar barcode example‚Äč is sometimes used in legacy library or logistics systems.
- 2D Barcode (e.g., Data Matrix, QR Code):
- Structure:‚Äč Encodes data in a grid of black/white squares or dots.
- Data:‚Äč Can store hundreds of characters, including text, numbers, and URLs.
- Scanning:‚Äč Can be read from any angle (omnidirectional) by an imager scanner.
- Space:‚Äč Stores vast information in a very small area (as small as 2×2 mm).
- Durability:‚Äč Built-in error correction allows it to be read even if partially damaged.
In brief, for modern PCB barcode laser marking, 2D barcodes‚Äč are overwhelmingly preferred due to their superior data capacity, small size, and reading reliability.
How Do I Identify a PCB Board?
Identifying a PCB board‚Äč involves locating and interpreting its permanent identifiers.
- Visual Inspection:‚Äč Look for a string of text (serial/part number) or a barcode on PCB.
- Locate Markings:‚Äč These are often found in a corner, near the edge, or in an unused area of the solder mask.
- Use a Scanner:‚Äč Employ a handheld barcode scanner‚Äč or fixed barcode scanner PCB‚Äč reader to automatically decode the information.
- Consult Documentation:‚Äč Cross-reference the found number with assembly drawings, bills of materials (BOM), or manufacturer data.
What Is the PCB Identification Number?
The PCB identification number is the structured code used to uniquely identify a PCB design or an individual board throughout manufacturing, assembly, and quality control. In professional PCB and PCBA production, it forms the backbone of traceability and compliance.
In practice, the PCB identification number is implemented in two complementary forms:
Part Number
The part number defines the PCB design itself, including layout, material set, layer stack-up, and revision level (for example, BRD-100A-REV2). All boards produced to the same design share this identifier, making it the reference point for engineering control and document management.
Serial Number (UID)
The serial number is a unique identifier assigned to each individual PCB or PCBA (for example, SN-2049000157). This UID is the foundation of unit-level traceability and is typically encoded into the PCB barcode‚ÄĒeither via barcode labels or permanent laser marking‚ÄĒso every board can be tracked independently.
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), PCB identification numbers are not treated as static markings, but as active data keys within a fully integrated manufacturing and quality system.
- MES-Driven Traceability
Each PCB serial number is digitally bound to our MES, linking fabrication data, process parameters, inspection records, and PCBA assembly history into a single traceable record. - Compliance with ISO13485 and IATF16949
Our identification and barcode practices are designed to meet the traceability requirements of medical and automotive standards, supporting audit-ready documentation, lot control, and recall containment. - Seamless PCB to PCBA Data Continuity
The same PCB identification number follows the board from bare PCB fabrication through SMT, testing, and final assembly, eliminating data breaks between processes. - Laser Marking and Barcode Integration
We apply durable PCB barcode laser marking solutions that ensure long-term readability through reflow, cleaning, and handling, while remaining fully compatible with automated inspection and MES scanning.
In essence, when a quality issue occurs, a properly implemented PCB identification number allows engineers to trace a failure back to a specific board, batch, material set, and process step, instead of isolating entire lots. This level of precision reduces investigation time, limits recall scope, and protects both product reliability and brand reputation.
Where Can I Get My PCB Number?
Your PCB number‚Äč is assigned and applied by your PCB manufacturer.
- Part Number:‚Äč You (the designer/OEM) provide this based on your internal numbering system.
- Serial Number (UID):‚Äč This can be:
- Sequentially Assigned by the Manufacturer:‚Äč The PCB barcode scanner PCB board manufacturer‚Äč generates and marks it.
- Defined by Customer:‚Äč You provide a list of UIDs for the manufacturer to apply.
- Rule-Based Generation:‚Äč Created algorithmically from lot, date, and panel data.
- Ensure your China barcode scanner PCB board suppliers‚Äč or any manufacturer clearly communicates their numbering protocol.
PCB Barcode Laser Marking vs Label PCB Printing Methods
Choosing the right PCB barcode application method directly affects durability, traceability, and long-term reliability.
| Feature | Laser Marking | Label Printing |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Direct marking | Adhesive label |
| Process | Etched on surface | Printed & attached |
| Durability | Permanent | Limited |
| Heat/Chemical Resistance | High | Low‚ÄďModerate |
| Mark Size & Detail | Very high | Moderate |
| Cost Structure | Low per unit | Ongoing materials |
| Typical Use | Production PCBs | Prototypes |
In fact, PCB barcode laser marking creates permanent, high-precision identifiers that survive soldering, cleaning, and long-term use, making it the preferred method for traceable PCB and PCBA manufacturing.
Label PCB printing remains suitable for prototypes, low-stress applications, or cases where direct marking is not feasible.
How PCB Barcodes Are Scanned and Managed in MES Systems?
This is where Advanced PCB Barcode Integration‚Äč delivers value. The process creates a closed-loop data system.
- Marking:‚Äč A unique 2D barcode PCB‚Äč is laser-marked during fabrication.
- SMT & Assembly:‚Äč At each station (paste, pick-place, reflow), a barcode scanner‚Äč reads the board. The MES logs which components from which reels were placed on this specific boardat this specific time.
- Testing & Programming:‚Äč The board ID automatically pulls up the correct test profile or firmware program. Results (pass/fail, values) are saved back to the board’s record.
- Data Hub (MES):‚Äč The MES acts as the central brain, storing the complete history linked to the barcode key.
- Traceability & Analytics:‚Äč For any field return, scanning the barcode reveals its full genealogy and process history, enabling instant root cause analysis.
Why PCB Barcode Matters for Traceability and Quality Control?
Implementing a PCB barcode‚Äč system is a strategic investment, not just a procedural step.
- Full-Unit Traceability:‚Äč Isolate failures to a specific batch, shift, or component reel.
- Process Control:‚Äč Monitor yield in real-time and identify bottleneck stations.
- Automated Data Capture:‚Äč Eliminate manual logs, ensuring data integrity and freeing operator time.
- Compliance & Reporting:‚Äč Easily generate audit trails for industry standards (IATF 16949, ISO 13485).
- Reduced Costs & Waste:‚Äč Target recalls precisely, minimizing scrap and protecting brand reputation.
Overall, PCB barcode‚Äč is the cornerstone of modern electronics traceability, transforming passive boards into intelligent, data-rich assets. This guide has explored its technology, application, and critical role in Advanced PCB Barcode Integration for Traceable PCB and PCBA.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) understands that quality and traceability are indispensable in the medical, industrial control, and IoT industries. To ensure this, our PCB production lines utilize a comprehensive MES system, guaranteeing full traceability for every single PCB and PCBA we manufacture. Our facility holds ISO 13485 and AS9100D certifications, underscoring our commitment to these demanding sectors. We have collaborated with engineers in the medical device and aerospace fields for nearly two decades, with production records for some projects preserved for up to 10 or even 15 years. If you have an upcoming PCB or PCBA project, please send your Gerber files, BOM, and board requirements to sales@bestpcbs.com‚Äč for a quote and a complimentary DFM analysis.
FAQs
What Are PCB Barcode Labels?
PCB barcode labels‚Äč are adhesive tags printed with a barcode (often a PCB QR code‚Äč or 2D symbol) and the human-readable number. They are affixed to the board as an alternative to direct laser marking. While useful for prototypes or certain applications, they are less durable than direct marks for full traceability through PCBA‚Äč processes.
What Is a PCB Number?
A PCB number‚Äč broadly refers to any identifying code on a circuit board. Most critically, it is the Unique Identifier (UID)‚Äč or serial number that is unique to each single board. This number, often encoded in a barcode on PCB, is the primary key for accessing the board’s digital history in a traceability system, answering the fundamental question, “What is a printed circuit board (pcb)’s specific history?“
Tags: Label PCB, PCB 2D Barcode, PCB Barcode, PCB Barcode Laser Marking


