PCB standard thicknesses play a huge role in how strong and reliable your final product will be. If you’re designing a PCB, picking the right thickness can affect performance, durability, and even cost. Whether you are choosing between 2-layer or 6-layer boards, understanding copper thickness, or dealing with tolerances, this guide is here to help you.
EBest Circuit (Best Technology) provides a one-stop PCB manufacture and assembly service, including NPI Support, DFM analysis, PCB design, quick PCB Prototyping, turn-key PCB assembly, and prompt post-sales. We have SMT factories in Vietnam and China respectively, which could support prototype PCB assembly, small-quantity PCB assembly, mid-volume SMT assembly, high-volume BGA assembly, etc. Every batch undergoes reliability tests like âfirst article inspectionâ, â3D solder paste inspectionâ, âAOIâ, âX-ray inspectionâ, âvisual inspectionâ, âflying probe testingâ, âManufacturing Defect Analysis (MDA)â, âin-circuit testing (ICT)â, and âfunctional testingâ. If any questions about standard PCB thickness in inches, or you have any PCB inquiries, just feel free to let us know at sales@bestpcbs.com.

What Are the Standard PCB Thicknesses?
When designing a PCB, the first thing you might ask is: “What thickness should I choose?” Luckily, the industry offers several standard options. Hereâs a quick view of typical sizes:
- 0.8mm (31 mils)
- 1.0mm (39 mils)
- 1.2mm (47 mils)
- 1.6mm (63 mils) â the most common
- 2.0mm (79 mils)
- 2.4mm (94 mils)
- 3.2mm (126 mils)
Among these, 1.6mm is widely recognized in most applications. It balances strength, flexibility, and cost very well. The standard PCB thickness chart also covers sizes in both inches and millimeters. While 1.6mm suits many consumer electronics, heavier-duty applications like automotive or industrial boards may demand thicker PCBs. Moreover, PCB standard thickness mm is easier to reference internationally, while in the USA, people often refer to PCB standard thickness in inches. Choosing thickness depends on factors like:
- Current carrying capacity
- Mechanical strength
- Space in your enclosure
Here’s a Standard PCB Thickness Chart that is commonly used in the industry:
| PCB Type | Standard Thickness (mm) | Standard Thickness (inches) | Notes |
| Single-Layer PCB | 1.57 mm | 0.062 in | Most common for simple designs |
| 2-Layer PCB | 1.57 mm | 0.062 in | Standard; other options available |
| 4-Layer PCB | 1.6 mm | 0.063 in | Common for compact circuits |
| 6-Layer PCB | 1.6 mm | 0.063 in | Balanced between size and performance |
| 8-Layer PCB | 2.0 mm | 0.079 in | For complex, high-speed designs |
| 10-Layer PCB | 2.0 mm | 0.079 in | High-density boards |
| Custom Thickness PCB | 0.2 mm â 3.2 mm | 0.008 in â 0.126 in | Based on specific project needs |
What Is the Standard PCB Copper Thickness?
Now, letâs talk about copper. Copper is what makes the magic happen â carrying electrical signals across your board. The standard PCB copper thickness usually comes in three levels:
- 0.5 oz/ft² (about 17μm)
- 1.0 oz/ft² (about 35μm)
- 2.0 oz/ft² (about 70μm)
The “oz” refers to ounces of copper spread over one square foot.
Typically, 1 oz copper thickness is the go-to for most designs. It offers a solid balance between performance and cost. Thicker copper â like 2 oz or even more â is needed if your PCB must handle higher currents. In some cases, for heavy power PCBs, up to 6 oz/ft² copper can be used. However, thicker copper adds both to the board thickness and the price. Using a PCB thickness calculator helps when balancing copper thickness with overall board size and performance.
| Copper Weight | Thickness (microns) | Thickness (mil) |
|---|---|---|
| 0.5 oz/ft² | ~17 μm | ~0.67 mil |
| 1.0 oz/ft² | ~35 μm | ~1.37 mil |
| 2.0 oz/ft² | ~70 μm | ~2.74 mil |
| 3.0 oz/ft² | ~105 μm | ~4.1 mil |
What Is the Standard Thickness of a 2-Layer PCB?
If you’re dealing with a simple project, a 2-layer PCB is a popular choice. The standard PCB thickness 2-layer is typically 1.6mm. However, thinner options like 1.0mm or thicker ones like 2.0mm are also common based on project needs. Hereâs why you might pick different thicknesses:
- Thinner PCBs (like 1.0mm) are good for lightweight, compact devices.
- Thicker PCBs (like 2.0mm) offer more strength and are better for rugged use.
Also, when considering copper, many 2-layer boards use 1 oz copper thickness. It gives good electrical performance without driving up the costs.
At the same time, PCB standard sizes usually match common board sizes like 100x100mm, but custom options are widely available too.
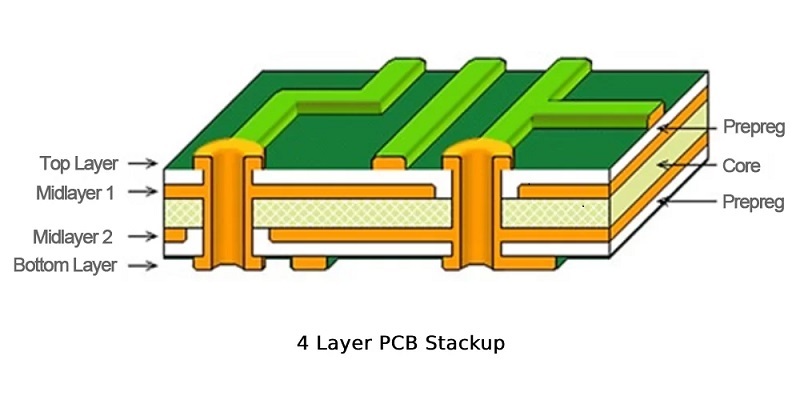
How Thick Is Standard 4 Layer PCB?
Moving into multi-layer territory, a 4-layer PCB opens up a lot of possibilities. The standard PCB thickness 4-layer often sticks close to 1.6mm. But depending on design needs, it can vary between 1.0mm and 2.4mm. Building a 4-layer PCB typically looks like this:
- Signal layer
- Ground layer
- Power layer
- Signal layer
The dielectric material between the layers, plus the standard prepreg thicknesses, affects the overall size. Choosing a thicker 4-layer board helps when more mechanical strength is needed. It also manages better thermal dissipation, which can be vital in complex circuits. When browsing through the standard PCB thickness chart, you’ll see that many companies offer flexible options for multi-layer designs.
How Thick Is a 6 Layer PCB?
If your design needs even more complexity, a 6-layer PCB could be the answer. The standard PCB thickness 6 layer generally ranges between 1.6mm and 2.4mm. However, advanced designs can go thinner or thicker. Inside a 6-layer PCB, the typical stack-up includes:
- Top signal layer
- Ground plane
- Inner signal layer
- Power plane
- Ground plane
- Bottom signal layer
6 layer PCB thickness matters a lot when working with high-speed signals. Having extra ground and power planes helps reduce noise and boosts signal integrity.
Additionally, if you use heavier copper, the final thickness can slightly increase. So always check specifications carefully.
For space-constrained applications, you might select a thinner 6-layer PCB. But when strength and performance matter more, a thicker design is better.
What Is the Standard Thickness Tolerance for PCB?
Even the best manufacturing process canât guarantee perfect thickness every time. Thatâs where PCB thickness tolerance comes in. Typically, tolerance ranges around ±10% of the nominal thickness. That means a 1.6mm PCB could measure anywhere from about 1.44mm to 1.76mm. Factors affecting tolerance include:
- Copper thickness variation
- Prepreg material thickness
- Lamination pressure
Also, standard PCB thickness tolerance might change depending on how many layers your board has. More layers often bring tighter control needs. Manufacturers usually list their tolerance ranges clearly. Always check before finalizing your design, especially for precision devices. If you want extra control over thickness, some suppliers offer tighter tolerances â but it may cost a bit more.

What Is the Standard Thickness of Prepreg in PCB?
Prepreg plays a big role between PCB layers. It bonds the layers and affects electrical and mechanical properties. The standard prepreg thicknesses usually fall into these categories:
- 106 prepreg: around â2 milsï¼0.05mmï¼
- 1080 prepreg: around 2.5 milsï¼0.064mmï¼
- 2116 prepreg: around â4.5 milsï¼0.114mmï¼
- 7628 prepreg: around 6.5 mils (0.165mm)
The more prepreg you have between layers, the thicker your final board will be. Besides thickness, prepreg also impacts dielectric strength and signal performance. This is why choosing the right prepreg type is key, especially for high-speed circuits. In most standard boards, manufacturers use combinations of prepregs and cores to reach the target thickness.
| Prepreg Type | Thickness (μm) | Thickness (mm) |
|---|---|---|
| 106 | ~50 μm | ~0.05 mm |
| 1080 | ~75 μm | ~0.075 mm |
| 2116 | ~110 μm | ~0.11 mm |
| 7628 | ~180 μm | ~0.18 mm |
As you can see, understanding PCB standard thicknesses is critical to building a successful board. It influences electrical performance, mechanical strength, thermal behavior, and even how easy your PCB is to assemble. Choosing the right thickness depends on Number of layers, Copper weight, Device application, Space limitations, and Mechanical needs. If youâre unsure, the safest starting point is usually a 1.6mm board with 1 oz copper. However, your projectâs needs might call for thicker or thinner options.
At EBest Circuit (Best Technology), we specialize in helping customers pick the perfect PCB thickness for their projects. Our team works closely with you, offering flexible options for 2-layer, 4-layer, 6-layer, or even more complex PCBs. We follow strict quality control systems, with certifications like ISO9001, ISO13485 for medical, IATF16949 for automotive, and AS9100D for aerospace industries. With top-notch engineering, and traceability through our MES system, EBest Circuit (Best Technology) is your trusted PCB partner. Contact EBest Circuit (Best Technology) at sales@bestpcbs.com to get the exact PCB thickness you need for your next PCB project!
Tags: PCB Standard Thicknesses, Standard PCB Thickness Chart


